2h7f
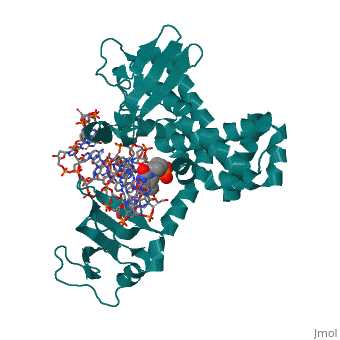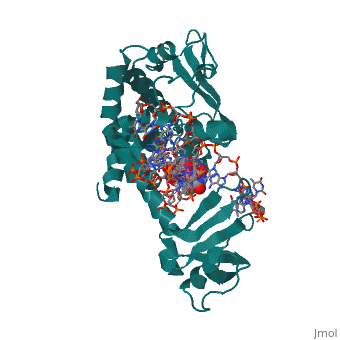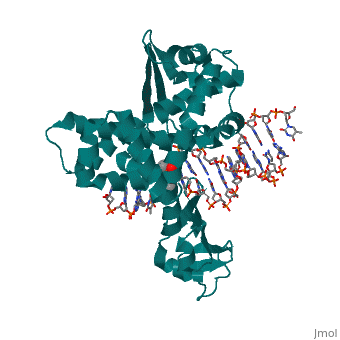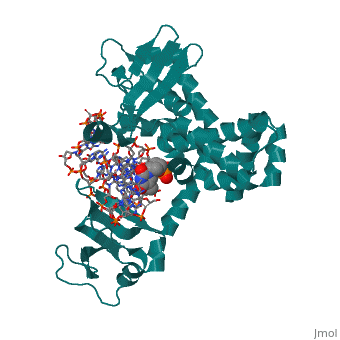
Structure of variola topoisomerase covalently bound to DNAStructure of variola topoisomerase covalently bound to DNA
Structural highlights
Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedAlthough smallpox has been eradicated from the human population, it is presently feared as a possible agent of bioterrorism. The smallpox virus codes for its own topoisomerase enzyme that differs from its cellular counterpart by requiring a specific DNA sequence for activation of catalysis. Here we present crystal structures of the smallpox virus topoisomerase enzyme bound both covalently and noncovalently to a specific DNA sequence. These structures reveal the basis for site-specific DNA recognition, and they explain how catalysis is likely activated by formation of a specific enzyme-DNA interface. Unexpectedly, the poxvirus enzyme uses a major groove binding alpha helix that is not present in the human enzyme to recognize part of the core recognition sequence and activate the enzyme for catalysis. The topoisomerase-DNA complex structures also provide a three-dimensional framework that may facilitate the rational design of therapeutic agents to treat poxvirus infections. Structural basis for specificity in the poxvirus topoisomerase.,Perry K, Hwang Y, Bushman FD, Van Duyne GD Mol Cell. 2006 Aug 4;23(3):343-54. PMID:16885024[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||