1cza
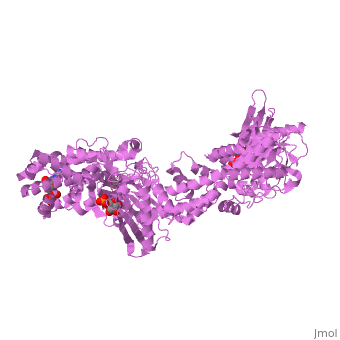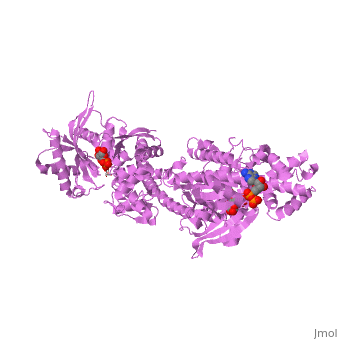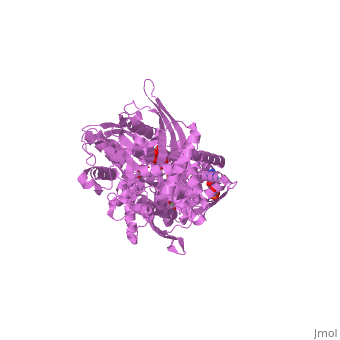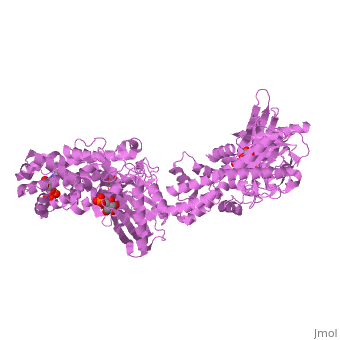
MUTANT MONOMER OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH GLUCOSE, GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE, AND ADPMUTANT MONOMER OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH GLUCOSE, GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE, AND ADP
Structural highlights
Disease[HXK1_HUMAN] Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:235700]. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedHexokinase I, the pacemaker of glycolysis in brain tissue, is composed of two structurally similar halves connected by an alpha-helix. The enzyme dimerizes at elevated protein concentrations in solution and in crystal structures; however, almost all published data reflect the properties of a hexokinase I monomer in solution. Crystal structures of mutant forms of recombinant human hexokinase I, presented here, reveal the enzyme monomer for the first time. The mutant hexokinases bind both glucose 6-phosphate and glucose with high affinity to their N and C-terminal halves, and ADP, also with high affinity, to a site near the N terminus of the polypeptide chain. Exposure of the monomer crystals to ADP in the complete absence of glucose 6-phosphate reveals a second binding site for adenine nucleotides at the putative active site (C-half), with conformational changes extending 15 A to the contact interface between the N and C-halves. The structures reveal distinct conformational states for the C-half and a rigid-body rotation of the N-half, as possible elements of a structure-based mechanism for allosteric regulation of catalysis. Crystal structures of mutant monomeric hexokinase I reveal multiple ADP binding sites and conformational changes relevant to allosteric regulation.,Aleshin AE, Kirby C, Liu X, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Fromm HJ, Honzatko RB J Mol Biol. 2000 Mar 3;296(4):1001-15. PMID:10686099[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||