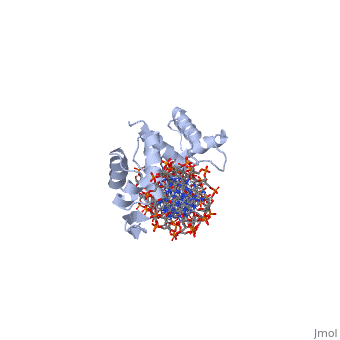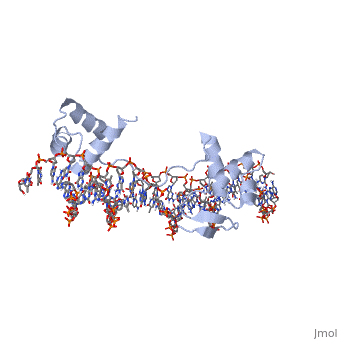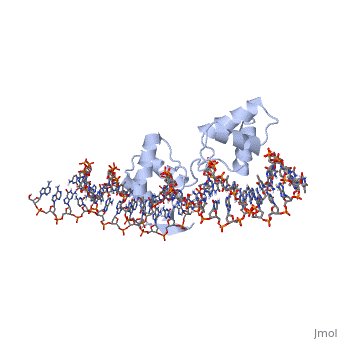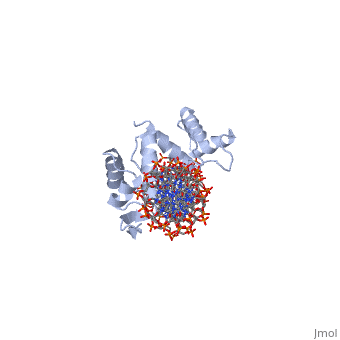
Paired box protein
FunctionPaired box protein (PAX) are transcription factors which contain paired box domain and a paired-type homeodomain (60 amino acid helix-turn-helix). • PAX-6 contain 2 DNA-binding domains. It is a regulatory factor in eye and brain development. Mutations in PAX-6 are associated with aniridia and Peter’s anomaly. • PAX-5 is associated with B-cell differentiation.
DiseaseRelevanceStructural highlights |
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of paired box protein3D Structures of paired box protein
Updated on 02-December-2014