Sandbox Reserved 7
| This Sandbox is Reserved from May 10, 2015, through July 31, 2015 for use by the class Protein 3D Structure Visualization & Structural Bioinformatics taught by Eric Martz and Keiichi Namba at Osaka University, Japan. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1 through Sandbox Reserved 10. Syllabus. |
To get started:
More help: Getting Started in Proteopedia, Help:Editing, Main Help Page. |
|
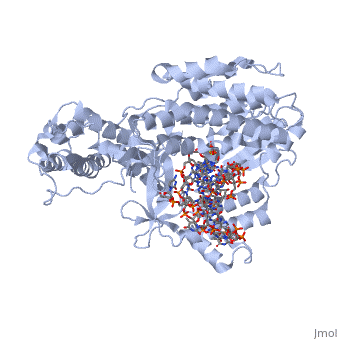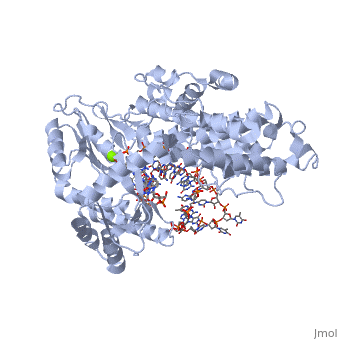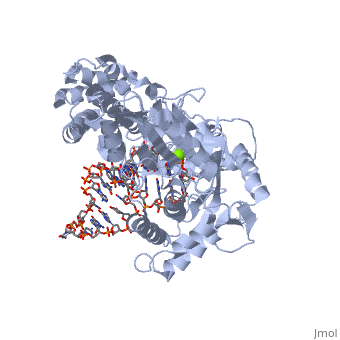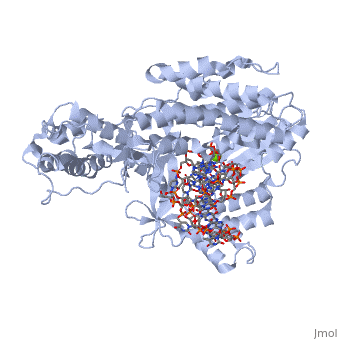
The structure of the catalytic subunit of telomerase bound to its RNA template and telomeric DNAThe structure of the catalytic subunit of telomerase bound to its RNA template and telomeric DNA
Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) is involved in catalyzing the extension of telomeres in eukaryotic DNA. Telomeres are repetitive sequences of nucleotides at the end of eukaryotic DNA which limit the erosion of the genome during DNA replication.
- TERT activity has been found to be activated by magnesium, and the short-term deficiency of magnesium in all chambers of the heart, and smooth muscle in animals has been shown to down-regulate telomerase activity[1]. Here,.
- In this scene, where the DNA/RNA complex sits may be seen. It may be posited that locations of positive charge indicate locations where the nucleic acids contact the protein chain. In this scene, the DNA/RNA complex is shown as an orange string structure for simplicity.
ReferencesReferences
- 1. Nilank C Shah, Gatha J Shah, Zhiqiang Li, Xian-Cheng Jiang, Bella T Altura, and Burton M Altura1. Short-term magnesium deficiency downregulates telomerase, upregulates neutral sphingomyelinase and induces oxidative DNA damage in cardiovascular tissues: relevance to atherogenesis, cardiovascular diseases and aging. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014; 7(3): 497–514. PMCID: PMC3992387.