Interferon regulatory factor (IRF) regulate transcription of interferons.
- IRF-1 functions as a transcriptional activator by binding to an interferon-stimulated response element in the gene promoter.
- IRF-3 and IRF-7 are activated by viruses or after binding to Toll-like receptors.
- IRF-4 is lymphoid-specific and functions in the development of immune cells.
3D structures of interferon regulatory factor
Interferon regulatory factor 1
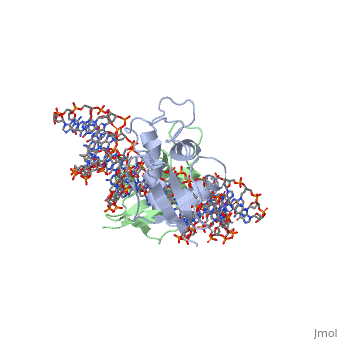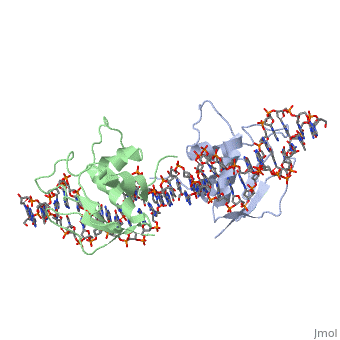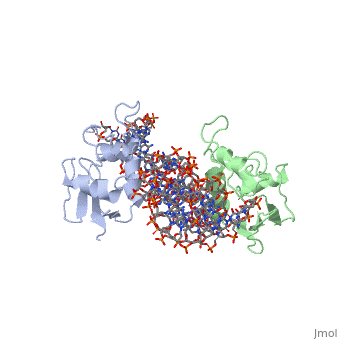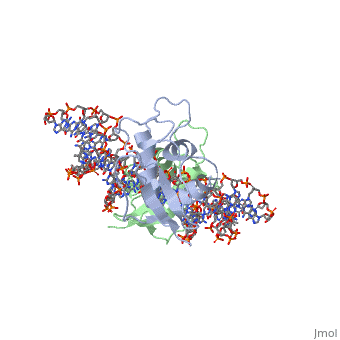
1if1 - mIRF DNA binding domain + DNA – mouse
Interferon regulatory factor 2
1irf, 1irg – mIRF DNA binding domain – NMR
2irf - mIRF DNA binding domain + DNA
Interferon regulatory factor 3
1qwt, 1j2f – mIRF
3a77 – hIRF DNA binding domain
3qu6 - hIRF DNA binding domain (mutant)
1t2k - hIRF DNA binding domain + interferon B enhancer + transcription factor AP-1 + DNA – human
2o6g - hIRF DNA binding domain + interferon B enhancer
2pi0 - hIRF DNA binding domain + interferon B promoter
1zoq – hIRF + CREB-binding protein
2o61 – hIRF3/IRF7/transcription factor + nuclear factor + DNA
Interferon regulatory factor 4
2dll – hIRF IRF domain - NMR
Interferon regulatory factor 5
3dsh – hIRF IRF domain (mutant)
Interferon regulatory factor 7
3qu3 - mIRF DNA binding domain