Introduction to protein structure
Levels of Protein StructureLevels of Protein Structure
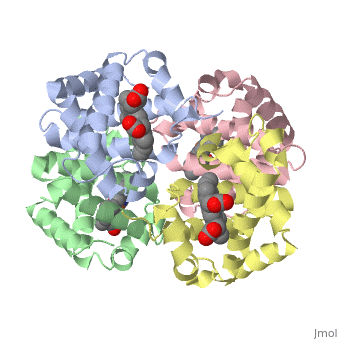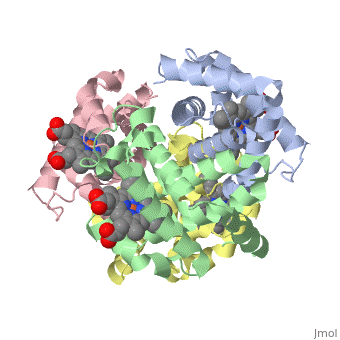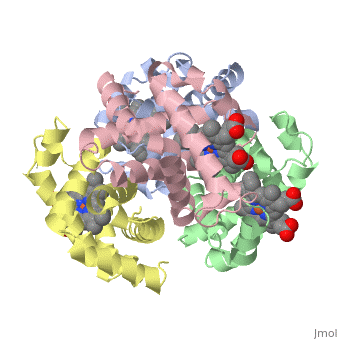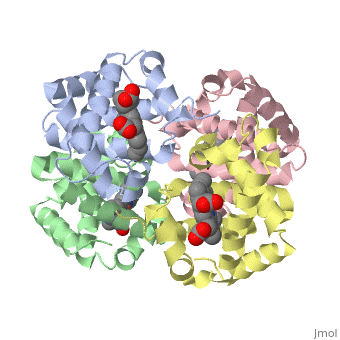
Proteins are condensation polymers of amino acids. The is the amino acid sequence. The is the local structure over short distances. This level of structure is stabilized by along the . These secondary structures pack together to form the overall form of the entire peptide chain, called the . Some proteins, such as the displayed hemoglobin molecule, have more than one polypeptide chain that associate to form the functional unit of the protein; this is called . Questions based upon these scenes: What is the primary sequence shown in the first link? Is the secondary structure shown an alpha helix or beta sheet? The ith C=O of the backbone is hydrogen bonded to which N(-H) (use i +/- # to represent the number)? What atom does this program NOT show? Ways of representing protein structureSecondary Structures |
| ||||||||||