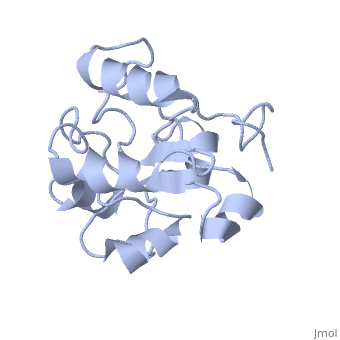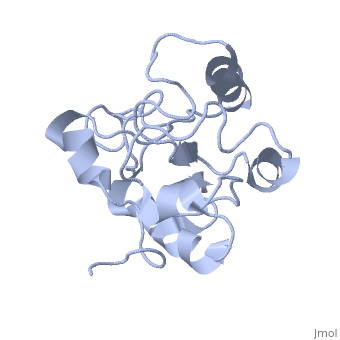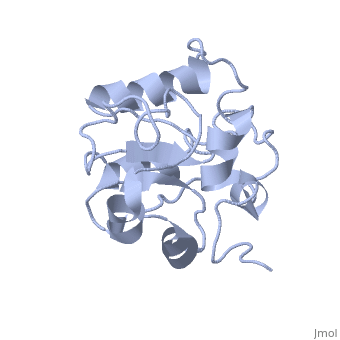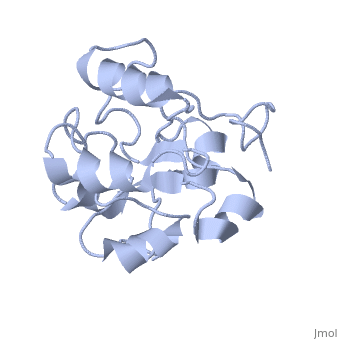1hzm
STRUCTURE OF ERK2 BINDING DOMAIN OF MAPK PHOSPHATASE MKP-3: STRUCTURAL INSIGHTS INTO MKP-3 ACTIVATION BY ERK2
|
OverviewOverview
MAP kinases (MAPKs), which control mitogenic signal transduction in all, eukaryotic organisms, are inactivated by dual specificity MAPK, phosphatases (MKPs). MKP-3, a prototypical MKP, achieves substrate, specificity through its N-terminal domain binding to the MAPK ERK2, resulting in the activation of its C-terminal phosphatase domain. The, solution structure and biochemical analysis of the ERK2 binding (EB), domain of MKP-3 show that regions that are essential for ERK2 binding, partly overlap with its sites that interact with the C-terminal catalytic, domain, and that these interactions are functionally coupled to the active, site residues of MKP-3. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism by which, the EB domain binding to ERK2 is transduced to cause a conformational, change of the C-terminal catalytic domain, resulting in the enzymatic, activation of MKP-3.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1HZM is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Solution structure of ERK2 binding domain of MAPK phosphatase MKP-3: structural insights into MKP-3 activation by ERK2., Farooq A, Chaturvedi G, Mujtaba S, Plotnikova O, Zeng L, Dhalluin C, Ashton R, Zhou MM, Mol Cell. 2001 Feb;7(2):387-99. PMID:11239467
Page seeded by OCA on Fri Feb 15 15:58:54 2008