Major histocompatibility complex
FunctionMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules bind peptides derived from degraded proteins and present these peptides on the surface of the cell. T-cells or natural killer receptors recognize the MHC:peptide complex and trigger an immune response if the presented peptide (“antigen”) is suggestive of a pathogenic or foreign protein. Thus, MHC molecules allow for immune system detection of intracellular activity, making them an essential part of the organism’s immune system.
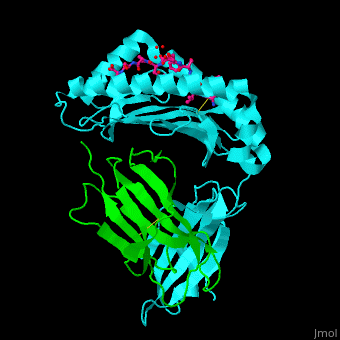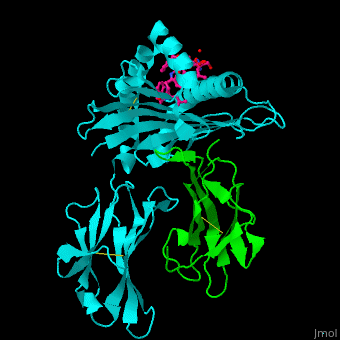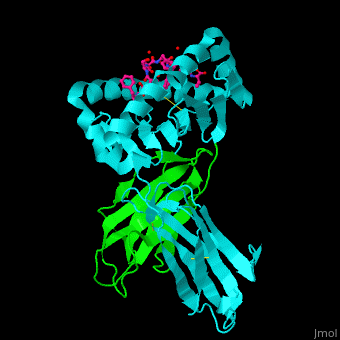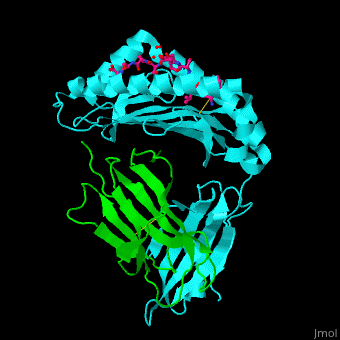
For MHC class II interactions with T-cell receptor and gliadin peptide see SP3.4-TCR-HLA-DQ8-α-1-gliadin complex. Structural highlights. The [3]. Water molecules shown as red spheres. 3D structures of MHC |
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Raghavan M, Del Cid N, Rizvi SM, Peters LR. MHC class I assembly: out and about. Trends Immunol. 2008 Sep;29(9):436-43. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.06.004. PMID:18675588 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2008.06.004
- ↑ Holling TM, Schooten E, van Den Elsen PJ. Function and regulation of MHC class II molecules in T-lymphocytes: of mice and men. Hum Immunol. 2004 Apr;65(4):282-90. PMID:15120183 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2004.01.005
- ↑ Liu J, Chen KY, Ren EC. Structural insights into the binding of hepatitis B virus core peptide to HLA-A2 alleles: Towards designing better vaccines. Eur J Immunol. 2011 Jul;41(7):2097-106. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041370. PMID:21538979 doi:10.1002/eji.201041370