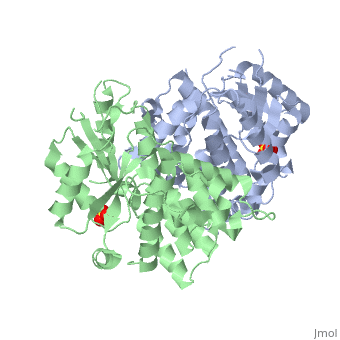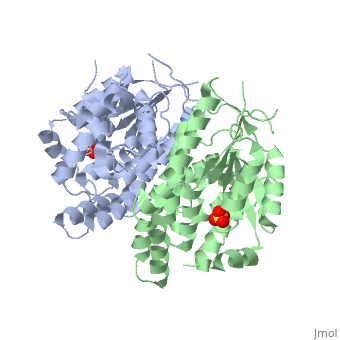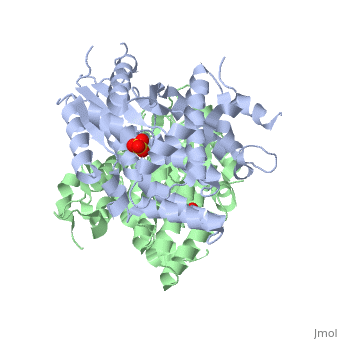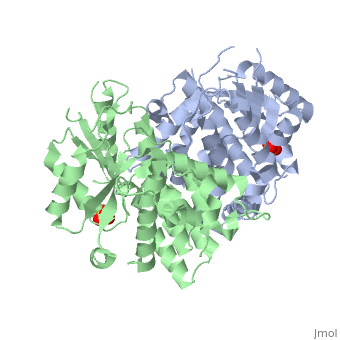
1e2h
| |||||||||
| 1e2h, resolution 1.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Activity: | Thymidine kinase, with EC number 2.7.1.21 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1kim, 1vtk, 2vtk, 3vtk, 1ki2, 1ki4, 1ki5, 1ki6, 1ki7, 1ki8, 1e2i, 1e2j, 1e2k, 1e2l, 1e2m, 1e2n, 1e2p | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
THE NUCLEOSIDE BINDING SITE OF HERPES SIMPLEX TYPE 1 THYMIDINE KINASE ANALYZED BY X-RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY
OverviewOverview
The crystal structures of the full-length Herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase in its unligated form and in a complex with an adenine analogue have been determined at 1.9 A resolution. The unligated enzyme contains four water molecules in the thymidine pocket and reveals a small induced fit on substrate binding. The structure of the ligated enzyme shows for the first time a bound adenine analogue after numerous complexes with thymine and guanine analogues have been reported. The adenine analogue constitutes a new lead compound for enzyme-prodrug gene therapy. In addition, the structure of mutant Q125N modifying the binding site of the natural substrate thymidine in complex with this substrate has been established at 2.5 A resolution. It reveals that neither the binding mode of thymidine nor the polypeptide backbone conformation is altered, except that the two major hydrogen bonds to thymidine are replaced by a single water-mediated hydrogen bond, which improves the relative acceptance of the prodrugs aciclovir and ganciclovir compared with the natural substrate. Accordingly, the mutant structure represents a first step toward improving the virus-directed enzyme-prodrug gene therapy by enzyme engineering.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1E2H is a Single protein structure of sequence from Human herpesvirus 1. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Nucleoside binding site of herpes simplex type 1 thymidine kinase analyzed by X-ray crystallography., Vogt J, Perozzo R, Pautsch A, Prota A, Schelling P, Pilger B, Folkers G, Scapozza L, Schulz GE, Proteins. 2000 Dec 1;41(4):545-53. PMID:11056041 Page seeded by OCA on Fri May 2 14:34:37 2008