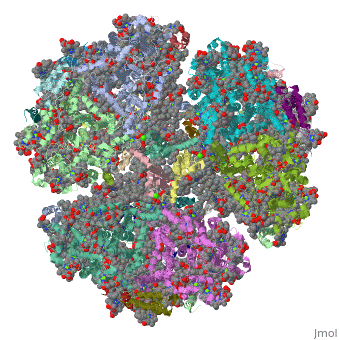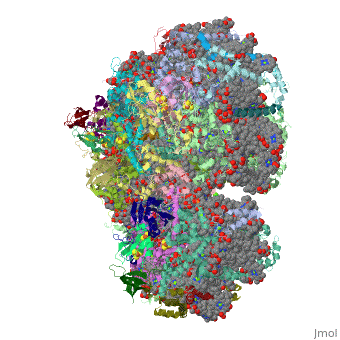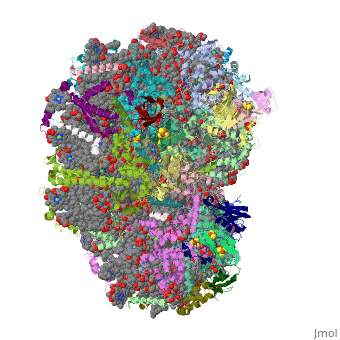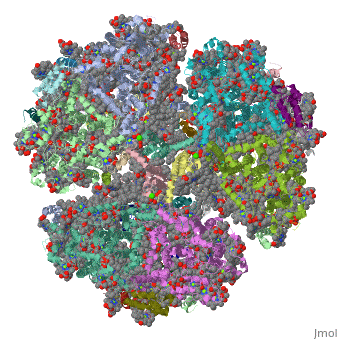
1jb0
Crystal Structure of Photosystem I: a Photosynthetic Reaction Center and Core Antenna System from CyanobacteriaCrystal Structure of Photosystem I: a Photosynthetic Reaction Center and Core Antenna System from Cyanobacteria
Structural highlights
Function[PSAF_SYNEL] Probably participates in efficiency of electron transfer from plastocyanin to P700 (or cytochrome c553 in algae and cyanobacteria). This plastocyanin-docking protein contributes to the specific association of plastocyanin to PSI. [PSAC_SYNEL] Apoprotein for the two 4Fe-4S centers FA and FB of photosystem I (PSI); essential for photochemical activity. FB is the terminal electron acceptor of PSI, donating electrons to ferredoxin. The C-terminus interacts with PsaA/B/D and helps assemble the protein into the PSI complex. Required for binding of PsaD and PsaE to PSI. PSI is a plastocyanin/cytochrome c6-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, converting photonic excitation into a charge separation, which transfers an electron from the donor P700 chlorophyll pair to the spectroscopically characterized acceptors A0, A1, FX, FA and FB in turn.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_01303] [PSAI_SYNEL] May help in the organization of the PsaL subunit (By similarity). [PSAB_SYNEL] PsaA and PsaB bind P700, the primary electron donor of photosystem I (PSI), as well as the electron acceptors A0, A1 and FX. PSI is a plastocyanin/cytochrome c6-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, converting photonic excitation into a charge separation, which transfers an electron from the donor P700 chlorophyll pair to the spectroscopically characterized acceptors A0, A1, FX, FA and FB in turn. Oxidized P700 is reduced on the lumenal side of the thylakoid membrane by plastocyanin or cytochrome c6. [PSAJ_SYNEL] May help in the organization of the PsaE and PsaF subunits. [PSAA_SYNEL] PsaA and PsaB bind P700, the primary electron donor of photosystem I (PSI), as well as the electron acceptors A0, A1 and FX. PSI is a plastocyanin/cytochrome c6-ferredoxin oxidoreductase, converting photonic excitation into a charge separation, which transfers an electron from the donor P700 chlorophyll pair to the spectroscopically characterized acceptors A0, A1, FX, FA and FB in turn. Oxidized P700 is reduced on the lumenal side of the thylakoid membrane by plastocyanin or cytochrome c6. [PSAD_SYNEL] PsaD can form complexes with ferredoxin and ferredoxin-oxidoreductase in photosystem I (PS I) reaction center. [PSAE_SYNEL] Stabilizes the interaction between PsaC and the PSI core, assists the docking of the ferredoxin to PSI and interacts with ferredoxin-NADP oxidoreductase.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_00613] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedLife on Earth depends on photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy from the Sun to chemical energy. In plants, green algae and cyanobacteria, this process is driven by the cooperation of two large protein-cofactor complexes, photosystems I and II, which are located in the thylakoid photosynthetic membranes. The crystal structure of photosystem I from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus described here provides a picture at atomic detail of 12 protein subunits and 127 cofactors comprising 96 chlorophylls, 2 phylloquinones, 3 Fe4S4 clusters, 22 carotenoids, 4 lipids, a putative Ca2+ ion and 201 water molecules. The structural information on the proteins and cofactors and their interactions provides a basis for understanding how the high efficiency of photosystem I in light capturing and electron transfer is achieved. Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 A resolution.,Jordan P, Fromme P, Witt HT, Klukas O, Saenger W, Krauss N Nature. 2001 Jun 21;411(6840):909-17. PMID:11418848[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||