Hydrogen bonds: Difference between revisions
Eric Martz (talk | contribs) →Donor and Acceptor Atoms: polishing |
Eric Martz (talk | contribs) →Donor and Acceptor Atoms: polishing |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Donor and Acceptor Atoms== | ==Donor and Acceptor Atoms== | ||
<table align='right' border='0' width='184' cellpadding='10' bgcolor='#d0d0d0' hspace='8'><tr><td rowspan='2'> </td><td bgcolor='#e8e8e8'> | <table align='right' border='0' width='184' cellpadding='10' bgcolor='#d0d0d0' hspace='8'><tr><td rowspan='2'> </td><td bgcolor='#e8e8e8'> | ||
[[Image:Hbond.gif]]</td></tr><tr><td bgcolor='#e8e8e8'><div style='color: white; background-color: black;'> Elements: {{Template:ColorKey_Element_C}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_H}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_N}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_O}}.</div>A hydrogen bond (dotted white line) between a <font color='#6565b4'><b>nitrogen donor</b></font> and an <font color='red'><b>oxygen acceptor</b></font>. Distances shown are typical for those found in proteins.</td></tr></table> | [[Image:Hbond.gif]]</td></tr><tr><td bgcolor='#e8e8e8'><div style='color: white; background-color: black;'> Elements: {{Template:ColorKey_Element_C}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_H}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_N}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Element_O}}.</div>A hydrogen bond (dotted white line) between a <font color='#6565b4'><b>nitrogen donor</b></font> and an <font color='red'><b>oxygen acceptor</b></font>. Distances shown in Å are typical for those found in proteins.</td></tr></table> | ||
Hydrogen bonds ("hbonds") are non-covalent bonds that occur when a ''donor'' atom donates its covalently bonded hydrogen atom to an electronegative ''acceptor'' atom. Typical donor atoms are the oxygens in -OH (e.g. the sidechains of Ser, Thr, Tyr), HOH, and the nitrogen in -NH3+ (as in the sidechains of Lys, Arg) or -NH- (as in the main chain peptide bond, and the sidechains of Trp, His, Arg, and nucleotide bases). The lone electron pairs on these same donors can serve as hbond acceptor sites. So can those on carbonyl oxygens =O (as in the protein main chain) or nitrogens with three covalent bonds =N- (as in the sidechains of His, Trp, or in nucleotide bases). Lacking hydrogens, these latter cannot serve as donors. | Hydrogen bonds ("hbonds") are non-covalent bonds that occur when a ''donor'' atom donates its covalently bonded hydrogen atom to an electronegative ''acceptor'' atom. Typical donor atoms are the oxygens in -OH (e.g. the sidechains of Ser, Thr, Tyr), HOH, and the nitrogen in -NH3+ (as in the sidechains of Lys, Arg) or -NH- (as in the main chain peptide bond, and the sidechains of Trp, His, Arg, and nucleotide bases). The lone electron pairs on these same donors can serve as hbond acceptor sites. So can those on carbonyl oxygens =O (as in the protein main chain) or nitrogens with three covalent bonds =N- (as in the sidechains of His, Trp, or in nucleotide bases). Lacking hydrogens, these latter cannot serve as donors. | ||
Revision as of 03:06, 19 October 2008
Donor and Acceptor AtomsDonor and Acceptor Atoms
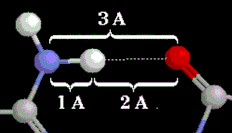 | |
Elements: C, H, N, O. A hydrogen bond (dotted white line) between a nitrogen donor and an oxygen acceptor. Distances shown in Å are typical for those found in proteins. |
Hydrogen bonds ("hbonds") are non-covalent bonds that occur when a donor atom donates its covalently bonded hydrogen atom to an electronegative acceptor atom. Typical donor atoms are the oxygens in -OH (e.g. the sidechains of Ser, Thr, Tyr), HOH, and the nitrogen in -NH3+ (as in the sidechains of Lys, Arg) or -NH- (as in the main chain peptide bond, and the sidechains of Trp, His, Arg, and nucleotide bases). The lone electron pairs on these same donors can serve as hbond acceptor sites. So can those on carbonyl oxygens =O (as in the protein main chain) or nitrogens with three covalent bonds =N- (as in the sidechains of His, Trp, or in nucleotide bases). Lacking hydrogens, these latter cannot serve as donors.
Distances and EnergiesDistances and Energies
The mean donor-acceptor distances in protein secondary structure elements are close to 3.0 Å, as are those between bases in Watson-Crick pairing (Jeffrey[1], pp. 191, 200). Jeffrey[1] (page 12) categorizes hbonds with donor-acceptor distances of 2.2-2.5 Å as "strong, mostly covalent", 2.5-3.2 Å as "moderate, mostly electrostatic", and 3.2-4.0 Å as "weak, electrostatic". Energies are given as 40-14, 15-4, and <4 kcal/mol respectively. Most hbonds in proteins are in the moderate category. Strong hbonds require moieties or conditions that are rare within proteins. The hydrogen atoms in moderate hbonds often do not lie on the straight line connecting the donor to acceptor, so donor-acceptor distance slightly underestimates the length of the hbond (Jeffrey[1], p. 14).
Finding and Visualizing HbondsFinding and Visualizing Hbonds
Few, if any, free molecular visualization programs show hbonds as rods or sticks between atoms. This is because determining the positions of hbonds with high confidence requires expert and detailed examination of the donor-acceptor chemistry and geometry. Instead, some molecular visualization programs display potential donor-acceptor pairs, deeming them "putatively" hbonded. Protein Explorer and FirstGlance in Jmol have Contacts dialogs that show putatively hbonded donors and acceptors based simply on the chemical elements and interatomic distances.
Since many PDB files lack hydrogen atoms, the presence of an energetically significant hydrogen bond can be inferred when a probable donor and acceptor are within 3.5 Å of each other.
FirstGlance in Jmol has a Contacts dialog, where you can select any moiety by clicking on it. (The moiety can be a chain, a segment of a chain, a single residue or ligand, or a single atom.) All the likely non-covalent bonds to the designated target moiety are then shown automatically. The putatively non-covalently bonded atoms can be hidden or shown in any combination of seven subsets: hydrogen bonds not involving water, hydrogen bonds involving water, water bridges, hydrophobic interactions, salt bridges, cation-pi orbital interactions, metal and miscellaneous interactions. This display defines "likely hydrogen bonded bonded" oxygens and nitrogens (shown as balls) as those within 3.5 Å of other oxygens or nitrogens.
An interactive example in Jmol is needed here.
Content AttributionContent Attribution
The text initially provided on this page was adapted by Eric Martz from the hydrogen bonds entry that he wrote several years earlier for the glossary in ProteinExplorer.Org.