1r9f: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<jmolCheckbox> | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/r9/1r9f_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | <scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/r9/1r9f_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/ | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
</jmolCheckbox> | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1r9f ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1r9f ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
RNA silencing (also known as RNA interference) is a conserved biological response to double-stranded RNA that regulates gene expression, and has evolved in plants as a defence against viruses. The response is mediated by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which guide the sequence-specific degradation of cognate messenger RNAs. As a counter-defence, many viruses encode proteins that specifically inhibit the silencing machinery. The p19 protein from the tombusvirus is such a viral suppressor of RNA silencing and has been shown to bind specifically to siRNA. Here, we report the 1.85-A crystal structure of p19 bound to a 21-nucleotide siRNA, where the 19-base-pair RNA duplex is cradled within the concave face of a continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet, formed across the p19 homodimer interface. Direct and water-mediated intermolecular contacts are restricted to the backbone phosphates and sugar 2'-OH groups, consistent with sequence-independent p19-siRNA recognition. Two alpha-helical 'reading heads' project from opposite ends of the p19 homodimer and position pairs of tryptophans for stacking over the terminal base pairs, thereby measuring and bracketing both ends of the siRNA duplex. Our structure provides an illustration of siRNA sequestering by a viral protein. | |||
Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing.,Ye K, Malinina L, Patel DJ Nature. 2003 Dec 18;426(6968):874-8. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:14661029<ref>PMID:14661029</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1r9f" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 36: | ||
*[[Suppression of RNA Silencing by Viruses|Suppression of RNA Silencing by Viruses]] | *[[Suppression of RNA Silencing by Viruses|Suppression of RNA Silencing by Viruses]] | ||
*[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | *[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:18, 30 October 2024
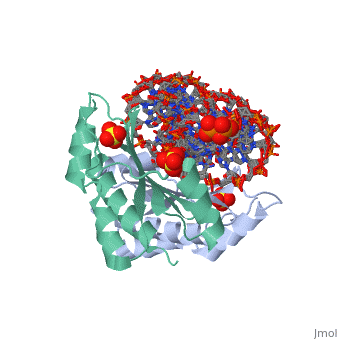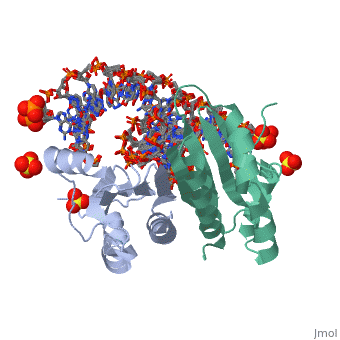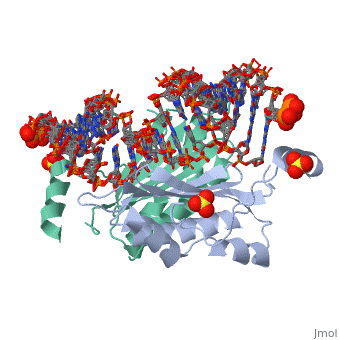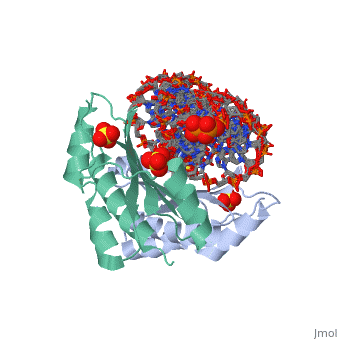
Crystal structure of p19 complexed with 19-bp small interfering RNACrystal structure of p19 complexed with 19-bp small interfering RNA
Structural highlights
FunctionP19_TBSVC Acts as a suppressor of RNA-mediated gene silencing, also known as post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), a mechanism of plant viral defense that limits the accumulation of viral RNAs. Binds to short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) with high affinity. Acts as a molecular caliper to specifically select siRNAs based on the length of the duplex region of the RNA (By similarity). Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedRNA silencing (also known as RNA interference) is a conserved biological response to double-stranded RNA that regulates gene expression, and has evolved in plants as a defence against viruses. The response is mediated by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which guide the sequence-specific degradation of cognate messenger RNAs. As a counter-defence, many viruses encode proteins that specifically inhibit the silencing machinery. The p19 protein from the tombusvirus is such a viral suppressor of RNA silencing and has been shown to bind specifically to siRNA. Here, we report the 1.85-A crystal structure of p19 bound to a 21-nucleotide siRNA, where the 19-base-pair RNA duplex is cradled within the concave face of a continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet, formed across the p19 homodimer interface. Direct and water-mediated intermolecular contacts are restricted to the backbone phosphates and sugar 2'-OH groups, consistent with sequence-independent p19-siRNA recognition. Two alpha-helical 'reading heads' project from opposite ends of the p19 homodimer and position pairs of tryptophans for stacking over the terminal base pairs, thereby measuring and bracketing both ends of the siRNA duplex. Our structure provides an illustration of siRNA sequestering by a viral protein. Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing.,Ye K, Malinina L, Patel DJ Nature. 2003 Dec 18;426(6968):874-8. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:14661029[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See Also
References
|
| ||||||||||||||||||