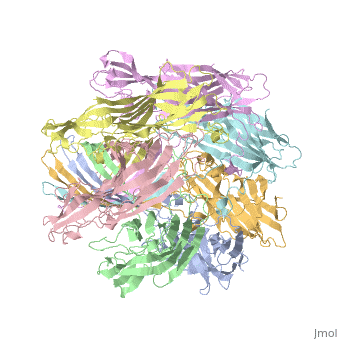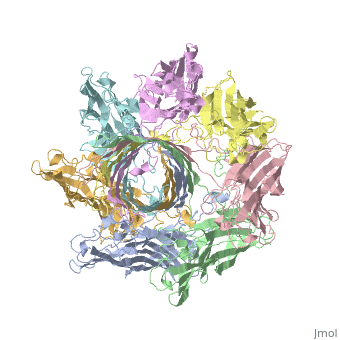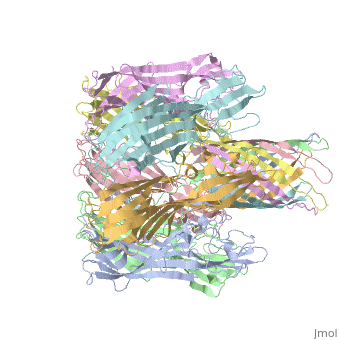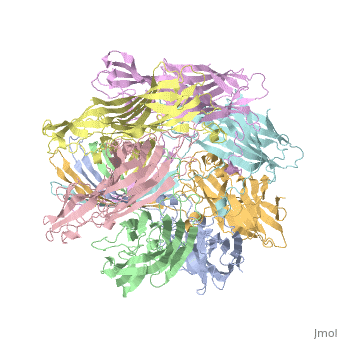Hemolysin: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. ''' | '''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. | ||
*'''delta-hemolysin''' is a 26 main acid peptide from the bacterium ''Staphylococcus'' exhibiting antimicrobial activity against'' Legionerlla'' <ref>PMID:19150639</ref>. | |||
See details for α-hemolysin in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | See details for α-hemolysin in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | ||
Revision as of 13:06, 1 July 2024
FunctionHemolysin (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells[1].
See details for α-hemolysin in Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin. See details of hemolysin E in Molecular Playground/ClyA. For toxins in Proteopdia see Toxins. RelevanceHL acts as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of invasive infections[3]. 3D Printed Physical Model of HemolysinShown below is a 3D printed physical model of Hemolysin. The model is shown in alpha carbon backbone format with each chain colored uniquely. The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling uses 3D printing technology to create physical models of protein and molecular structures, making the invisible molecular world more tangible and comprehensible. To view more protein structure models, visit our Model Gallery. 3D Structures of hemolysin
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Mestre MB, Fader CM, Sola C, Colombo MI. Alpha-hemolysin is required for the activation of the autophagic pathway in Staphylococcus aureus-infected cells. Autophagy. 2010 Jan;6(1):110-25. PMID:20110774
- ↑ Verdon J, Girardin N, Lacombe C, Berjeaud JM, Héchard Y. delta-hemolysin, an update on a membrane-interacting peptide. Peptides. 2009 Apr;30(4):817-23. PMID:19150639 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2008.12.017
- ↑ Nizet V. Streptococcal beta-hemolysins: genetics and role in disease pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2002 Dec;10(12):575-80. PMID:12564994