3wa0: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
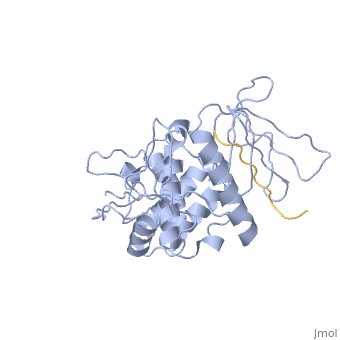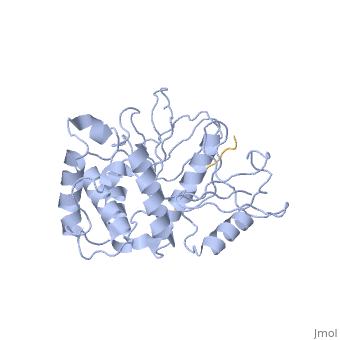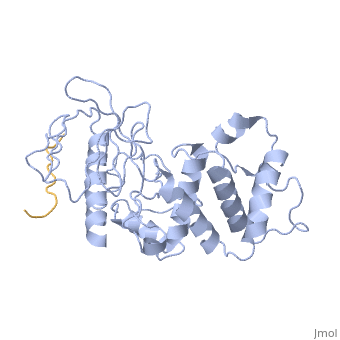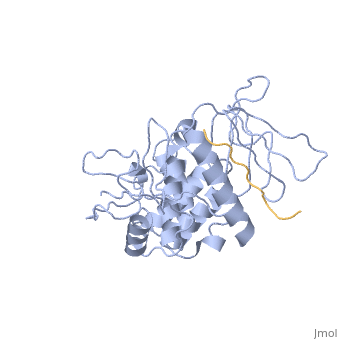
==Crystal structure of merlin complexed with DCAF1/VprBP== | ==Crystal structure of merlin complexed with DCAF1/VprBP== | ||
<StructureSection load='3wa0' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3wa0]]' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3wa0' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3wa0]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.31Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3WA0 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3WA0 FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3wa0]] is a 11 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3WA0 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3WA0 FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3wa0 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3wa0 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3wa0 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3wa0 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3wa0 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3wa0 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.31Å</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3wa0 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3wa0 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3wa0 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3wa0 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3wa0 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3wa0 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/MERL_MOUSE MERL_MOUSE] Probable regulator of the Hippo/SWH (Sav/Wts/Hpo) signaling pathway, a signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Along with WWC1 can synergistically induce the phosphorylation of LATS1 and LATS2 and can probably function in the regulation of the Hippo/SWH (Sav/Wts/Hpo) signaling pathway. May act as a membrane stabilizing protein. May inhibit PI3 kinase by binding to AGAP2 and impairing its stimulating activity. Suppresses cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by inhibiting the CUL4A-RBX1-DDB1-VprBP/DCAF1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex (By similarity). Plays a role in lens development and is required for complete fiber cell terminal differentiation, maintenance of cell polarity and separation of the lens vesicle from the corneal epithelium.<ref>PMID:20181838</ref> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
Merlin, a tumor suppressor encoded by the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene, has been shown to suppress tumorigenesis by inhibiting the Cullin 4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4DCAF 1 in the nucleus. This inhibition is mediated by direct binding of merlin to DDB1-and-Cullin 4-associated Factor 1 (DCAF1), yet the binding mode of merlin to DCAF1 is not well defined. Here, we report structural and biophysical studies of the merlin binding to DCAF1 and its interference with CD44 binding. The crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain bound to the DCAF1 C-terminal acidic tail reveals that the hydrophobic IILXLN motif located at the C-terminal end of DCAF1 binds subdomain C of the FERM domain by forming a beta-strand. The binding site and mode resemble that of merlin binding to the CD44 cytoplasmic tail. Competition binding assay showed that CD44 and DCAF1 compete for binding to the merlin FERM domain in solution. The CD44 cytoplasmic tail is known to be cleaved for nuclear translocation by regulated intra-membrane proteolysis (RIP). Our structure implies that, in the nucleus, the CD44 cytoplasmic tail cleaved by RIP could release DCAF1 from merlin by competing for binding to the merlin FERM domain, which results in the inhibition of merlin-mediated suppression of tumorigenesis. | |||
Structural basis of DDB1-and-Cullin 4-associated Factor 1 (DCAF1) recognition by merlin/NF2 and its implication in tumorigenesis by CD44-mediated inhibition of merlin suppression of DCAF1 function.,Mori T, Gotoh S, Shirakawa M, Hakoshima T Genes Cells. 2014 Jun 9. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12161. PMID:24912773<ref>PMID:24912773</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 3wa0" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 23: | ||
*[[Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures|Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures]] | *[[Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures|Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures]] | ||
*[[VprBP|VprBP]] | *[[VprBP|VprBP]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | |||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | |||
[[Category: Gotoh S]] | [[Category: Gotoh S]] | ||
[[Category: Hakoshima T]] | [[Category: Hakoshima T]] | ||
[[Category: Mori T]] | [[Category: Mori T]] | ||
[[Category: Shirakawa M]] | [[Category: Shirakawa M]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:00, 8 November 2023
Crystal structure of merlin complexed with DCAF1/VprBPCrystal structure of merlin complexed with DCAF1/VprBP
Structural highlights
FunctionMERL_MOUSE Probable regulator of the Hippo/SWH (Sav/Wts/Hpo) signaling pathway, a signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Along with WWC1 can synergistically induce the phosphorylation of LATS1 and LATS2 and can probably function in the regulation of the Hippo/SWH (Sav/Wts/Hpo) signaling pathway. May act as a membrane stabilizing protein. May inhibit PI3 kinase by binding to AGAP2 and impairing its stimulating activity. Suppresses cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by inhibiting the CUL4A-RBX1-DDB1-VprBP/DCAF1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex (By similarity). Plays a role in lens development and is required for complete fiber cell terminal differentiation, maintenance of cell polarity and separation of the lens vesicle from the corneal epithelium.[1] Publication Abstract from PubMedMerlin, a tumor suppressor encoded by the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene, has been shown to suppress tumorigenesis by inhibiting the Cullin 4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4DCAF 1 in the nucleus. This inhibition is mediated by direct binding of merlin to DDB1-and-Cullin 4-associated Factor 1 (DCAF1), yet the binding mode of merlin to DCAF1 is not well defined. Here, we report structural and biophysical studies of the merlin binding to DCAF1 and its interference with CD44 binding. The crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain bound to the DCAF1 C-terminal acidic tail reveals that the hydrophobic IILXLN motif located at the C-terminal end of DCAF1 binds subdomain C of the FERM domain by forming a beta-strand. The binding site and mode resemble that of merlin binding to the CD44 cytoplasmic tail. Competition binding assay showed that CD44 and DCAF1 compete for binding to the merlin FERM domain in solution. The CD44 cytoplasmic tail is known to be cleaved for nuclear translocation by regulated intra-membrane proteolysis (RIP). Our structure implies that, in the nucleus, the CD44 cytoplasmic tail cleaved by RIP could release DCAF1 from merlin by competing for binding to the merlin FERM domain, which results in the inhibition of merlin-mediated suppression of tumorigenesis. Structural basis of DDB1-and-Cullin 4-associated Factor 1 (DCAF1) recognition by merlin/NF2 and its implication in tumorigenesis by CD44-mediated inhibition of merlin suppression of DCAF1 function.,Mori T, Gotoh S, Shirakawa M, Hakoshima T Genes Cells. 2014 Jun 9. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12161. PMID:24912773[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||