Akt/PKB signaling pathway: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
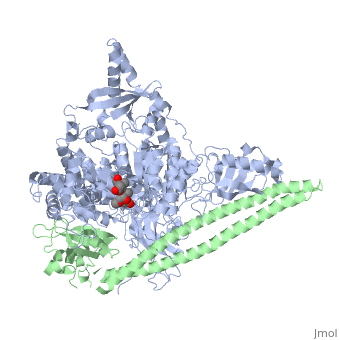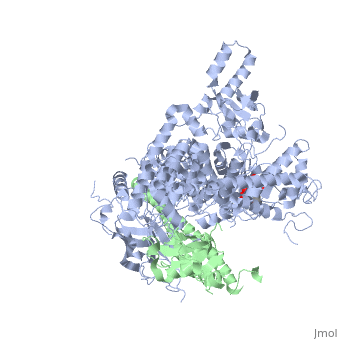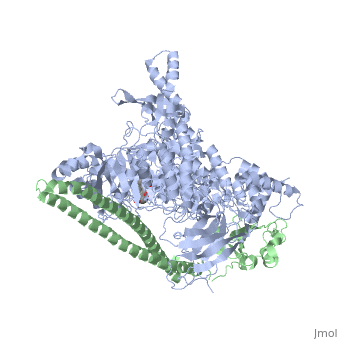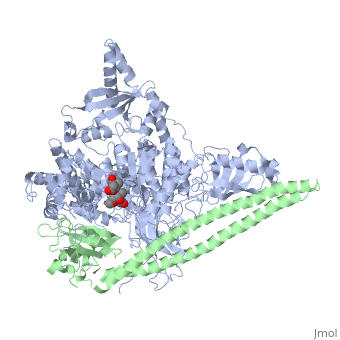
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K ([[phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase]]) and Akt (protein kinase B). See also [[Signal transduction]]. | The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K ([[phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase]]) and Akt (protein kinase B). See also [[Signal transduction]]. | ||
=Activation Akt/PKB via Receptor tyrosine kinases/Ras= | |||
==[[Receptor tyrosine kinases]]== | |||
==Ras activation== | |||
[[GTPase KRas]] | |||
[[Allosteric modulation of H-Ras GTPase]] | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 1 March 2022
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) and Akt (protein kinase B). See also Signal transduction. Activation Akt/PKB via Receptor tyrosine kinases/RasReceptor tyrosine kinasesRas activation |
| ||||||||||