Stimulator of interferon genes: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
**[[4f5e]] – hSTING CTD (mutant) <br /> | **[[4f5e]] – hSTING CTD (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[4jc5]], [[4kc0]] – mSTING CTD - mouse <br /> | **[[4jc5]], [[4kc0]] – mSTING CTD - mouse <br /> | ||
**[[6nt6]] – cSTING – chicken – Cryo EM <br /> | |||
**[[5cfo]], [[5cfr]] – saSTING CTD – sea anemone <br /> | **[[5cfo]], [[5cfr]] – saSTING CTD – sea anemone <br /> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
**[[4emt]] – hSTING residues 155-341 + c-di-GMP <br /> | **[[4emt]] – hSTING residues 155-341 + c-di-GMP <br /> | ||
**[[4f5d]] – hSTING CTD (mutant) + c-di-GMP <br /> | **[[4f5d]] – hSTING CTD (mutant) + c-di-GMP <br /> | ||
**[[4ksy]] – hSTING CTD + cGAMP <br /> | **[[4ksy]] – hSTING CTD + cGAMP <br /> | ||
**[[5bqx]] – hSTING CTD + c-GMP <br /> | **[[5bqx]] – hSTING CTD + c-GMP <br /> | ||
**[[4loh]], [[4loi]] – hSTING CTD + c-di-GMP derivative<br /> | **[[4loh]], [[4loi]] – hSTING CTD + c-di-GMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[4qxo]], [[4qxp]], [[4qxq]], [[4qxr]] – hSTING CTD + chemptherapeutic agent DMXAA<br /> | |||
**[[4kby]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-GMP <br /> | |||
**[[4loj]], [[4lok]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-GMP derivative<br /> | **[[4loj]], [[4lok]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-GMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[4yp1]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-AMP derivative<br /> | **[[4yp1]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-AMP derivative<br /> | ||
**[[4lol]] – mSTING CTD + chemptherapeutic agent DMXAA<br /> | **[[4lol]] – mSTING CTD + chemptherapeutic agent DMXAA<br /> | ||
**[[4kby]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-GMP <br /> | **[[4kby]] – mSTING CTD + c-di-GMP <br /> | ||
**[[6nt7]], [[6nt8]] – cSTING + GMP-AMP – Cryo EM <br /> | |||
**[[6nt9]] – cSTING + TBK1 – Cryo EM <br /> | |||
**[[5cfl]] – saSTING CTD + c-di-GMP <br /> | **[[5cfl]] – saSTING CTD + c-di-GMP <br /> | ||
**[[5cfp]] – saSTING CTD (mutant) + c-di-GMP <br /> | **[[5cfp]] – saSTING CTD (mutant) + c-di-GMP <br /> | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 10 February 2020
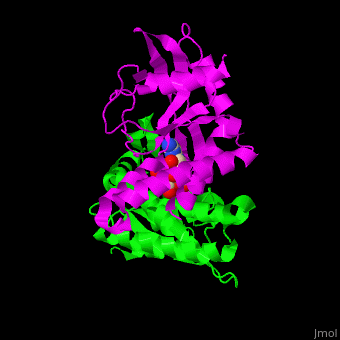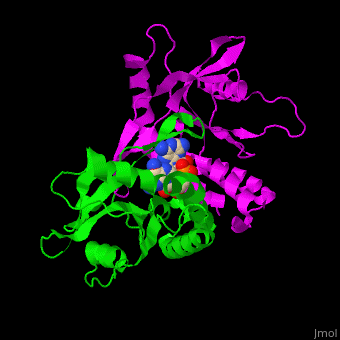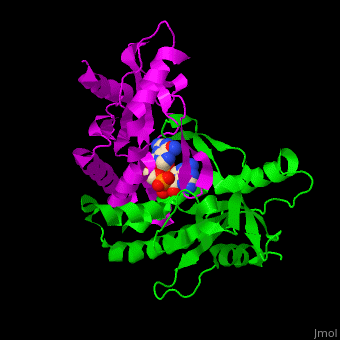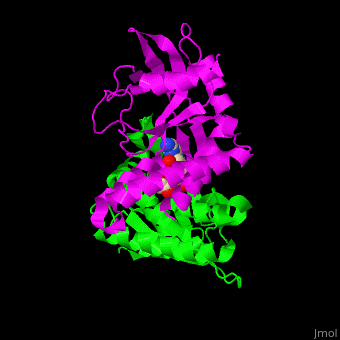
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) induces production of type I interferon when cells are infected by viruses, mycobacteria and intracellular parasites. STING recognizes and binds cyclic-di-GMP produced by bacteria and cyclic-GMP AMP (cGAMP) produced by viruses. The C-terminal domain (CTD) (residues 139-379 in human) of STING binds cyclic-di-GMP. STING is a facilitator of innate immune signaling[1]. Structural highlightsThe [2]. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of STING3D structures of STING
(Updated on 10-February-2020
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Poltorak A, Kurmyshkina O, Volkova T. Stimulator of interferon genes (STING): A "new chapter" in virus-associated cancer research. Lessons from wild-derived mouse models of innate immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Jun;29:83-91. doi:, 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Mar 4. PMID:26980676 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.02.009
- ↑ Gao P, Ascano M, Zillinger T, Wang W, Dai P, Serganov AA, Gaffney BL, Shuman S, Jones RA, Deng L, Hartmann G, Barchet W, Tuschl T, Patel DJ. Structure-Function Analysis of STING Activation by c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] and Targeting by Antiviral DMXAA. Cell. 2013 Aug 15;154(4):748-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Aug, 1. PMID:23910378 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.023