1suk: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==HOMOLOGY MODEL OF THE FACILITATIVE GLUCOSE TRANSPORTER I (GLUT1)== | ==HOMOLOGY MODEL OF THE FACILITATIVE GLUCOSE TRANSPORTER I (GLUT1)== | ||
<StructureSection load='1suk' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1suk]]' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1suk' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1suk]]' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1SUK FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1SUK FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1suk" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | <div class="pdbe-citations 1suk" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | |||
*[[GLUT4|GLUT4]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 24: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Theoretical Model]] | [[Category: Theoretical Model]] | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | |||
[[Category: Fischbarg, J]] | [[Category: Fischbarg, J]] | ||
[[Category: Iserovich, P]] | [[Category: Iserovich, P]] | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 18 December 2019
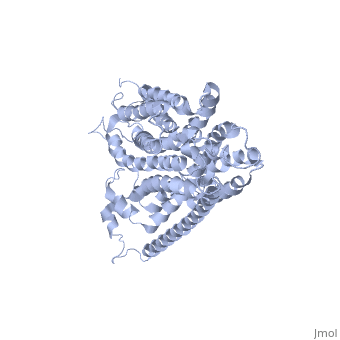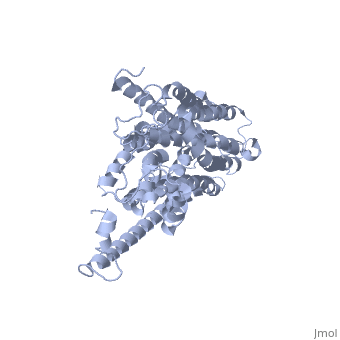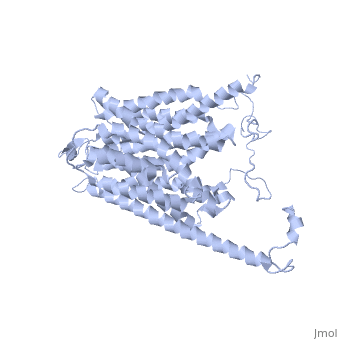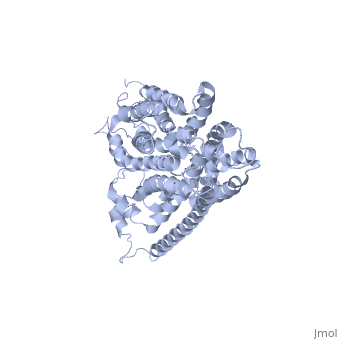
HOMOLOGY MODEL OF THE FACILITATIVE GLUCOSE TRANSPORTER I (GLUT1)HOMOLOGY MODEL OF THE FACILITATIVE GLUCOSE TRANSPORTER I (GLUT1)
Structural highlights
Publication Abstract from PubMedThe glucose transporters (GLUT/SLC2A) are members of the major facilitator superfamily. Here, we generated a three-dimensional model for Glut1 using a two-step strategy: 1), GlpT structure as an initial homology template and 2), evolutionary homology using glucose-6-phosphate translocase as a template. The resulting structure (PDB No. 1SUK) exhibits a water-filled passageway communicating the extracellular and intracellular domains, with a funnel-like exofacial vestibule (infundibulum), followed by a 15 A-long x 8 A-wide channel, and a horn-shaped endofacial vestibule. Most residues which, by mutagenesis, are crucial for transport delimit the channel, and putative sugar recognition motifs (QLS, QLG) border both ends of the channel. On the outside of the structure there are two positively charged cavities (one exofacial, one endofacial) delimited by ATP-binding Walker motifs, and an exofacial large side cavity of yet unknown function. Docking sites were found for the glucose substrate and its inhibitors: glucose, forskolin, and phloretin at the exofacial infundibulum; forskolin, and phloretin at an endofacial site next to the channel opening; and cytochalasin B at a positively charged endofacial pocket 3 A away from the channel. Thus, 1SUK accounts for practically all biochemical and mutagenesis evidence, and provides clues for the transport process. Predicting the three-dimensional structure of the human facilitative glucose transporter glut1 by a novel evolutionary homology strategy: insights on the molecular mechanism of substrate migration, and binding sites for glucose and inhibitory molecules.,Salas-Burgos A, Iserovich P, Zuniga F, Vera JC, Fischbarg J Biophys J. 2004 Nov;87(5):2990-9. Epub 2004 Aug 23. PMID:15326030[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||