Flagellar protein: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
====Lists of Flagellar Structures==== | ====Lists of Flagellar Structures==== | ||
These are automatically-generated lists of [[PDB codes]]. | These are automatically-generated lists of [[PDB codes]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 2 July 2019
Function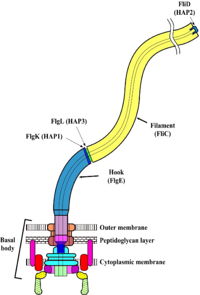
Flagella (singular: flagellum) enable bacteria to swim towards sources of nutrition, and away from sources of toxins. Such directed motility is termed chemotaxis. Rapid swimming helps Bdellovibrio penetrate and parasitize their host bacteria, but flagella are not always essential for virulence[1]. Flagella are important in responses to quorum sensing[2] and biofilm formation[3][4]. Flagella may also be involved in functions other than motility[5]. For further information, please see Flagellum at Wikipedia. The bacterial flagellum is made up of about 25 different proteins. There are only a few copies of some proteins, and tens of thousands of copies of the filament protein, FliC. The flagellum is made up of three major regions, as follows. MotorAt the base of a bacterial flagellum is a reversible motor, also called the basal body. The source of energy driving the motor is an electromotive gradient of, in some bacteria, protons (hydrogen ions, H+) or, in other bacteria, sodium ions (Na+). The gradient has a higher concentration of ions outside the cell, and a lower concentration of ions inside the cell. Ions flow from outside to inside the bacterial cell, passing through the motor and driving its rotation by a mechanism which is poorly understood. For more details see Flagellar biosynthetic protein Filament (Propeller)The flagellar filament is a relatively rigid, helical rod, typically many times the length of the bacterial cell. Many motile bacteria, including Salmonella, have multiple flagella extending from each cell. Rotation of the filaments by the motor is what propels the cell. More... For more details see Flagellar proteins and Flagellar filament of bacteria. Hook (Universal Joint)The filament is attached to the motor with the flagellar hook, which is a molecular universal joint. The hook is flexible, allowing the angle between the filament and the bacterial cell surface to change over a wide range. However, the hook efficiently transmits torque from the motor to the filament, causing it to rotate. For details see Assembly
During assembly of the flagellum, its protein components are transported through hollow cores of the basal body, hook and filament, assembling at the end of the nascent flagellum[6]. The Namba Group has prepared a movie illustrating their understanding of the assembly process as of about 2004. 3D structures of flagellar proteinFlagellar protein 3D structures
|
| |||||||||||||
Lists of Flagellar StructuresLists of Flagellar Structures
These are automatically-generated lists of PDB codes.
- Special:Prefixindex/Category:Flagell includes categories beginning with Flagellar, Flagellin, Flagella, Flagellum.
- Special:Prefixindex/Category:Bacterial flagell
- Category:Chlamydomonas flagella
- Category:The bacterial flagellar motor
- Category:Putative flagellar motor switch protein flin
and there are undoubtedly other flagellum-related Categories ...
See AlsoSee Also
Within Proteopedia:
External Links
- Flagellum at Wikipedia
- Protonic Nanomachine Group, Osaka University
- MOVIES from the Protonic Nanomachine Project, Osaka University
</StructureSection>
References and NotesReferences and Notes
- ↑ Lockman HA, Curtiss R 3rd. Salmonella typhimurium mutants lacking flagella or motility remain virulent in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):137-43. PMID:2152887
- ↑ Daniels R, Vanderleyden J, Michiels J. Quorum sensing and swarming migration in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004 Jun;28(3):261-89. PMID:15449604
- ↑ Yildiz FH, Visick KL. Vibrio biofilms: so much the same yet so different. Trends Microbiol. 2009 Mar;17(3):109-18. Epub 2009 Feb 21. PMID:19231189 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2008.12.004
- ↑ Lemon KP, Higgins DE, Kolter R. Flagellar motility is critical for Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. J Bacteriol. 2007 Jun;189(12):4418-24. Epub 2007 Apr 6. PMID:17416647 doi:10.1128/JB.01967-06
- ↑ Guerry P. Campylobacter flagella: not just for motility. Trends Microbiol. 2007 Oct;15(10):456-61. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:17920274 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2007.09.006
- ↑ Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. Mechanisms of type III protein export for bacterial flagellar assembly. Mol Biosyst. 2008 Nov;4(11):1105-15. Epub 2008 Sep 24. PMID:18931786 doi:10.1039/b808065h