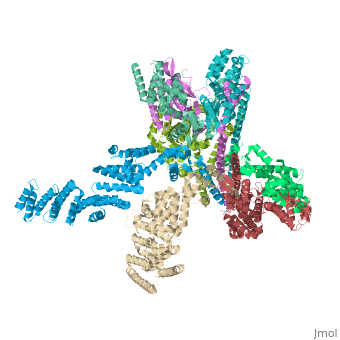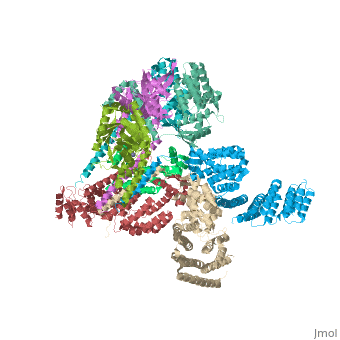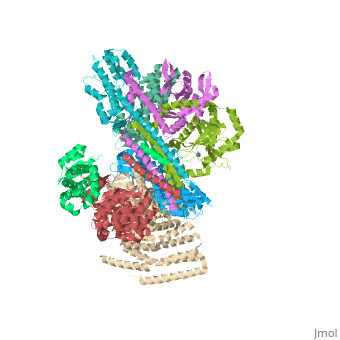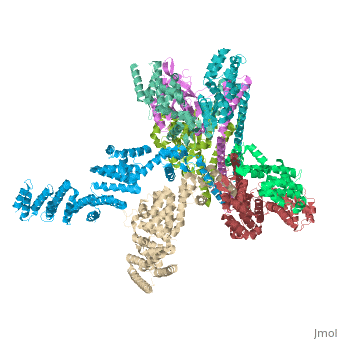4d10: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Crystal structure of the COP9 signalosome== | ==Crystal structure of the COP9 signalosome== | ||
<StructureSection load='4d10' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4d10]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.80Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4d10' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4d10]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.80Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4d10]] is a 16 chain structure. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4D10 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4D10 FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4d10]] is a 16 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4D10 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4D10 FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4d0p|4d0p]], [[4d18|4d18]]</td></tr> | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4d0p|4d0p]], [[4d18|4d18]]</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4d10 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4d10 OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4d10 PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4d10 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4d10 PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4d10 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4d10 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4d10 OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4d10 PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4d10 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4d10 PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4d10 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN6_HUMAN CSN6_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Has some glucocorticoid receptor-responsive activity. Stabilizes RFWD2/COP1 through reducing RFWD2 auto-ubiquitination and decelerating RFWD2 turnover rate, hence regulates the ubiquitination of RFWD2 targets.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:21625211</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN3_HUMAN CSN3_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN7A_HUMAN CSN7A_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, JUN, I-kappa-B-alpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN2_HUMAN CSN2_HUMAN]] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Involved in early stage of neuronal differentiation via its interaction with NIF3L1.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN8_HUMAN CSN8_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN1_HUMAN CSN1_HUMAN]] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Suppresses G-protein- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated signal transduction.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN4_HUMAN CSN4_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. Also involved in the deneddylation of non-cullin subunits such as STON2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1, IRF8/ICSBP and SNAPIN, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:21102408</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN5_HUMAN CSN5_HUMAN]] Probable protease subunit of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of the SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. In the complex, it probably acts as the catalytic center that mediates the cleavage of Nedd8 from cullins. It however has no metalloprotease activity by itself and requires the other subunits of the CSN complex. Interacts directly with a large number of proteins that are regulated by the CSN complex, confirming a key role in the complex. Promotes the proteasomal degradation of BRSK2.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:19214193</ref> <ref>PMID:22609399</ref> | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN6_HUMAN CSN6_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Has some glucocorticoid receptor-responsive activity. Stabilizes RFWD2/COP1 through reducing RFWD2 auto-ubiquitination and decelerating RFWD2 turnover rate, hence regulates the ubiquitination of RFWD2 targets.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:21625211</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN3_HUMAN CSN3_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN7A_HUMAN CSN7A_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, JUN, I-kappa-B-alpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN2_HUMAN CSN2_HUMAN]] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Involved in early stage of neuronal differentiation via its interaction with NIF3L1.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN8_HUMAN CSN8_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN1_HUMAN CSN1_HUMAN]] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Suppresses G-protein- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated signal transduction.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN4_HUMAN CSN4_HUMAN]] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. Also involved in the deneddylation of non-cullin subunits such as STON2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1, IRF8/ICSBP and SNAPIN, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:21102408</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CSN5_HUMAN CSN5_HUMAN]] Probable protease subunit of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of the SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. In the complex, it probably acts as the catalytic center that mediates the cleavage of Nedd8 from cullins. It however has no metalloprotease activity by itself and requires the other subunits of the CSN complex. Interacts directly with a large number of proteins that are regulated by the CSN complex, confirming a key role in the complex. Promotes the proteasomal degradation of BRSK2.<ref>PMID:9535219</ref> <ref>PMID:11285227</ref> <ref>PMID:11337588</ref> <ref>PMID:12732143</ref> <ref>PMID:12628923</ref> <ref>PMID:19214193</ref> <ref>PMID:22609399</ref> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Human]] | |||
[[Category: Bunker, R D]] | [[Category: Bunker, R D]] | ||
[[Category: Lingaraju, G M]] | [[Category: Lingaraju, G M]] | ||
[[Category: Thoma, N H]] | [[Category: Thoma, N H]] | ||
[[Category: Signaling protein]] | [[Category: Signaling protein]] | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 6 March 2019
Crystal structure of the COP9 signalosomeCrystal structure of the COP9 signalosome
Structural highlights
Function[CSN6_HUMAN] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Has some glucocorticoid receptor-responsive activity. Stabilizes RFWD2/COP1 through reducing RFWD2 auto-ubiquitination and decelerating RFWD2 turnover rate, hence regulates the ubiquitination of RFWD2 targets.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [CSN3_HUMAN] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.[7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [CSN7A_HUMAN] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, JUN, I-kappa-B-alpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.[12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [CSN2_HUMAN] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Involved in early stage of neuronal differentiation via its interaction with NIF3L1.[17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [CSN8_HUMAN] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.[22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [CSN1_HUMAN] Essential component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8/ICSBP, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. Suppresses G-protein- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated signal transduction.[27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [CSN4_HUMAN] Component of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. Also involved in the deneddylation of non-cullin subunits such as STON2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1, IRF8/ICSBP and SNAPIN, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively.[32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [CSN5_HUMAN] Probable protease subunit of the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN), a complex involved in various cellular and developmental processes. The CSN complex is an essential regulator of the ubiquitin (Ubl) conjugation pathway by mediating the deneddylation of the cullin subunits of the SCF-type E3 ligase complexes, leading to decrease the Ubl ligase activity of SCF-type complexes such as SCF, CSA or DDB2. The complex is also involved in phosphorylation of p53/TP53, c-jun/JUN, IkappaBalpha/NFKBIA, ITPK1 and IRF8, possibly via its association with CK2 and PKD kinases. CSN-dependent phosphorylation of TP53 and JUN promotes and protects degradation by the Ubl system, respectively. In the complex, it probably acts as the catalytic center that mediates the cleavage of Nedd8 from cullins. It however has no metalloprotease activity by itself and requires the other subunits of the CSN complex. Interacts directly with a large number of proteins that are regulated by the CSN complex, confirming a key role in the complex. Promotes the proteasomal degradation of BRSK2.[38] [39] [40] [41] [42] [43] [44] Publication Abstract from PubMedUbiquitination is a crucial cellular signalling process, and is controlled on multiple levels. Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) are regulated by the eight-subunit COP9 signalosome (CSN). CSN inactivates CRLs by removing their covalently attached activator, NEDD8. NEDD8 cleavage by CSN is catalysed by CSN5, a Zn2+-dependent isopeptidase that is inactive in isolation. Here we present the crystal structure of the entire approximately 350-kDa human CSN holoenzyme at 3.8 A resolution, detailing the molecular architecture of the complex. CSN has two organizational centres: a horseshoe-shaped ring created by its six proteasome lid-CSN-initiation factor 3 (PCI) domain proteins, and a large bundle formed by the carboxy-terminal alpha-helices of every subunit. CSN5 and its dimerization partner, CSN6, are intricately embedded at the core of the helical bundle. In the substrate-free holoenzyme, CSN5 is autoinhibited, which precludes access to the active site. We find that neddylated CRL binding to CSN is sensed by CSN4, and communicated to CSN5 with the assistance of CSN6, resulting in activation of the deneddylase. Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome.,Lingaraju GM, Bunker RD, Cavadini S, Hess D, Hassiepen U, Renatus M, Fischer ES, Thoma NH Nature. 2014 Jul 16. doi: 10.1038/nature13566. PMID:25043011[45] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||