Core-binding factor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*Core-binding factor β subunit | *Core-binding factor β subunit | ||
**[[1ilf]] – mCBFb<br /> | **[[1ilf]], [[2jhb]] – mCBFb<br /> | ||
**[[4n9f]] – hCBFb + cullin-5 + transcription elongation factor B + virion infectivity factor<br /> | **[[4n9f]] – hCBFb + cullin-5 + transcription elongation factor B + virion infectivity factor<br /> | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 15 April 2018
FunctionCore-binding factor (CBF) is a heterodimeric transcription factor which is composed of . CBF binds to various enhancers and promoters including murine leukemia virus and polyomavirus enhancer. [1] DiseaseMutations in CBF β are implicated in breast cancer. Rearrangements of CBF α and β genes are implicated in acute myeloid leukemia. Structural highlightsCBF α contains a DNA-binding runt domain (residues 50-177).
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of core-binding factor3D Structures of core-binding factor
Updated on 15-April-2018
- Core-binding factor β subunit
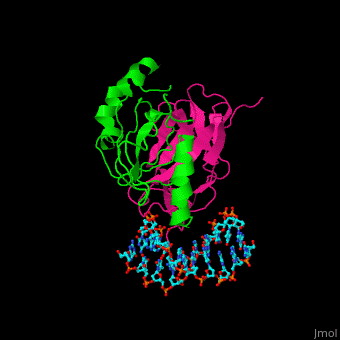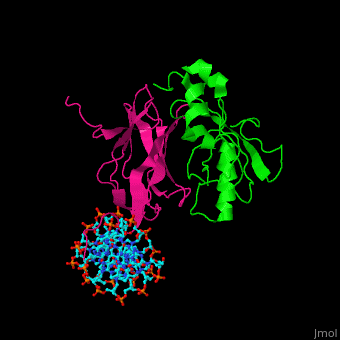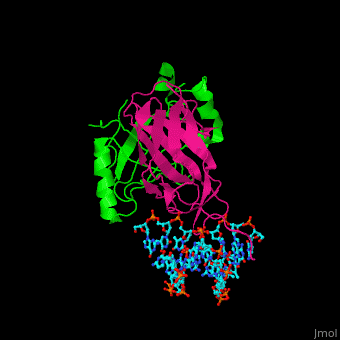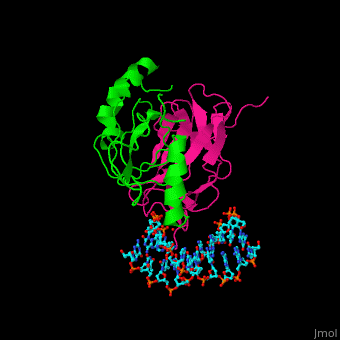
- Core-binding factor α+β subunits
- 1e50 – hCBFα runt domain + hCBFβ heterodimerization domain
- 1h9d – hCBFα runt domain + hCBFβ heterodimerization domain + DNA
- 1io4 – mCBFα runt domain + mCBFβ core domain + hEBP β + DNA
- 3wts – mCBFα runt domain (mutant) + mCBFβ heterodimerization domain + hETS1 + DNA
- 3wtt, 3wtu, 3wtx, 3wty, 3wtv, 3wtw – mCBFα residues 60-263 (mutant) + mCBFβ heterodimerization domain + hETS1 + DNA
- 1e50 – hCBFα runt domain + hCBFβ heterodimerization domain
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Bravo J, Li Z, Speck NA, Warren AJ. The leukemia-associated AML1 (Runx1)--CBF beta complex functions as a DNA-induced molecular clamp. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Apr;8(4):371-8. PMID:11276260 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/86264