1qku: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | [[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http://ispc.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Mon Nov 5 | ''Page seeded by [http://ispc.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Mon Nov 5 17:01:26 2007'' | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 5 November 2007
|
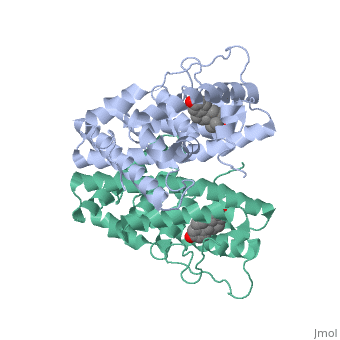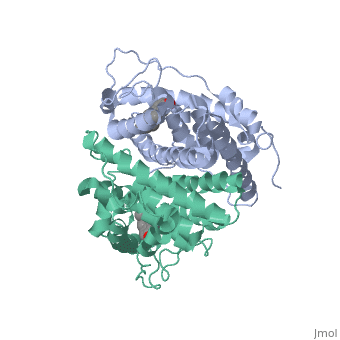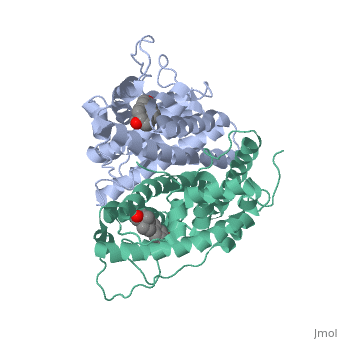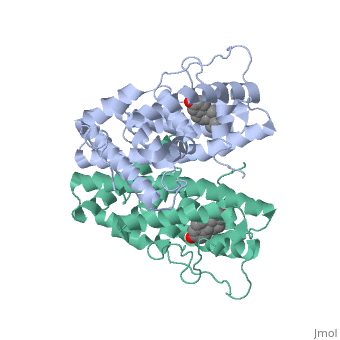
WILD TYPE ESTROGEN NUCLEAR RECEPTOR LIGAND BINDING DOMAIN COMPLEXED WITH ESTRADIOL
OverviewOverview
The crystal structure of a triple cysteine to serine mutant ERalpha, ligand-binding domain (LBD), complexed with estradiol, shows that despite, the presence of a tightly bound agonist ligand, the protein exhibits an, antagonist-like conformation, similar to that observed in raloxifen and, 4-hydroxytamoxifen-bound structures. This mutated receptor binds estradiol, with wild type affinity and displays transcriptional activity upon, estradiol stimulation, but with limited potency (about 50%). This partial, activity is efficiently repressed in antagonist competition assays. The, comparison with available LBD structures reveals key features governing, the positioning of helix H12 and highlights the importance of cysteine, residues in promoting an active conformation. Furthermore the present, study reveals a hydrogen bond network connecting ligand binding to protein, trans conformation. These observations support a dynamic view of H12, positioning, where the control of the equilibrium between two stable, locations determines the partial agonist character of a given ligand.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1QKU is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens with EST as ligand. The following page contains interesting information on the relation of 1QKU with [Estrogen Receptor]. Structure known Active Sites: AC1, AC2 and AC3. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Crystal structure of a mutant hERalpha ligand-binding domain reveals key structural features for the mechanism of partial agonism., Gangloff M, Ruff M, Eiler S, Duclaud S, Wurtz JM, Moras D, J Biol Chem. 2001 May 4;276(18):15059-65. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11278577
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Nov 5 17:01:26 2007