Polygalacturonase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Krishna Amin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Krishna Amin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
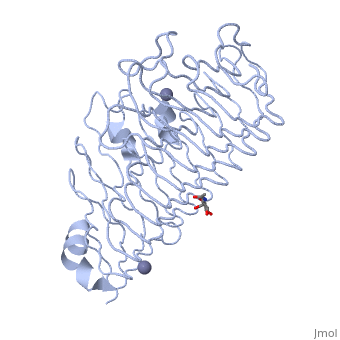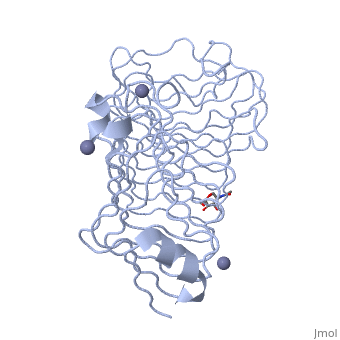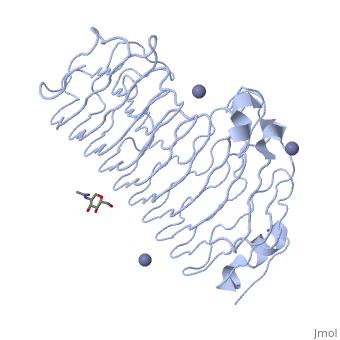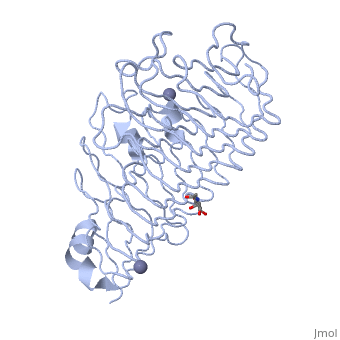
<Structure load=' | <Structure load='1czf' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />Polygalacturonases (PGs) catalyze the enzymatic depolymerization of pectins – polysaccharides that comprise the plant cell wall. Polymer disassembly of substrates by ''exo-'' and ''endo-'' PGs is carried out via a hydrolytic mechanism. Degradation of pectins in plant cell walls contributes to ripening of fruits, such as tomatoes and melons '''(Polygalacturonases: many genes in search of a function)'''. | ||
<StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 01:48, 12 July 2017
|
Polygalacturonases (PGs) catalyze the enzymatic depolymerization of pectins – polysaccharides that comprise the plant cell wall. Polymer disassembly of substrates by exo- and endo- PGs is carried out via a hydrolytic mechanism. Degradation of pectins in plant cell walls contributes to ripening of fruits, such as tomatoes and melons (Polygalacturonases: many genes in search of a function).
FunctionPGs cleave α-(1-4) – glycosidic bonds between consecutive galacturonic acid residues. DiseaseRelevanceStructural highlightsThis is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
|
| ||||||||||