Sandbox Reserved 439: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[ | *[[Chemotaxis protein]] | ||
==Credits== | ==Credits== | ||
Revision as of 21:58, 2 March 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 19, 2016, through August 31, 2016 for use for Proteopedia Team Projects by the class Chemistry 423 Biochemistry for Chemists taught by Lynmarie K Thompson at University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 425 through Sandbox Reserved 439. |
Asp Receptor Ligand-binding domain (1wat)[1]Asp Receptor Ligand-binding domain (1wat)[1]
by [list all teammate names here] Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2016
This is an example page. Edit appropriately for your project. Upon completion of each task, delete instructions in orange. See Sandbox Reserved 439 for original instructions 1. Add a citation to the primary reference at the end of the title above: you should all read this paper! Go to the pdb and search for your pdb code. Go down to the abstract and click "Search on Pubmed". In pubmed, copy the PMID code you see right below the abstract, and paste it to replace xxx after PMID in your title (first edited line above). ** I can't figure out why the title citation gets repeated (refs 1 and 2) when it is cited in the text... We'll just live with it.** 2. Each section should start with an "initial view" green scene. These can be the same for all sections or can be set by the section author.Section text should include multiple green scenes and should not exceed the length of the structure window. IntroductionThe author of the introduction section should think of a clever/ interesting caption for this structure, and edit to put this caption into the StructureSectionLoad command (4th edited line)
The ligand binding domain of the aspartate receptor is a dimer of two 4-helix bundles that is shown here with the bound.[2] Overall Structure
In this the N and C termini are at the bottom of the structure; this is where the connections to the transmembrane helices have been truncated. Binding Interactions
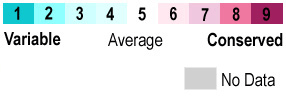
When the protein is colored according to , residues at the ligand site are the most conserved. Interactions that stabilize ligand binding[3] include hydrogen bonding from Tyr149 and Gln152 backbone carbonyls and Thr154 sidechain OH to the and hydrogen bonding from the sidechain nitrogens of Arg64, Arg69, and Arg73 to the two . Additional Features
Quiz Question 1
See AlsoCreditsIntroduction - name of team member Overall Structure - name of team member Binding Interactions - name of team member Additional Features - name of team member Quiz Question 1 - name of team member References
|
| ||||||||||