2x0s: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='2x0s' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2x0s]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2x0s' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2x0s]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2x0s]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2x0s]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypanosoma_(trypanozoon)_brucei Trypanosoma (trypanozoon) brucei]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entry [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=1h6z 1h6z]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2X0S OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2X0S FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyruvate,_phosphate_dikinase Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.7.9.1 2.7.9.1] </span></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyruvate,_phosphate_dikinase Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.7.9.1 2.7.9.1] </span></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2x0s FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2x0s OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2x0s RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2x0s PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2x0s FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2x0s OCA], [http://pdbe.org/2x0s PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2x0s RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2x0s PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
</jmolCheckbox> | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/ | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2x0s ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2x0s" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase]] | [[Category: Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase]] | ||
[[Category: Baltz, T]] | [[Category: Baltz, T]] | ||
[[Category: Bringaud, F]] | [[Category: Bringaud, F]] | ||
Revision as of 00:37, 10 February 2016
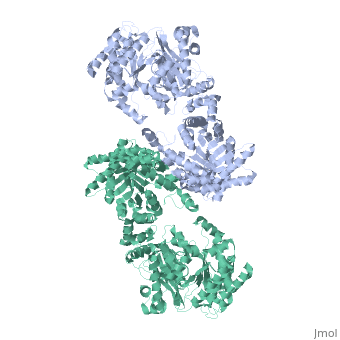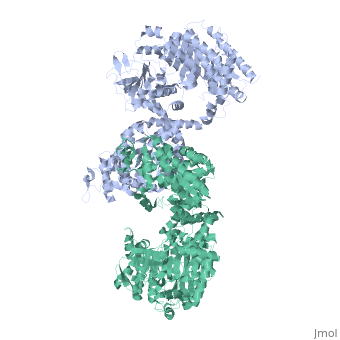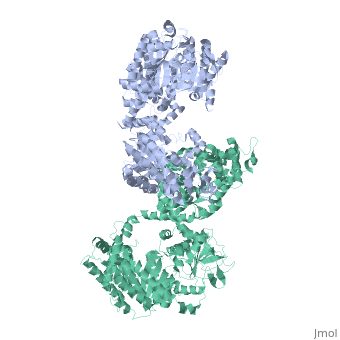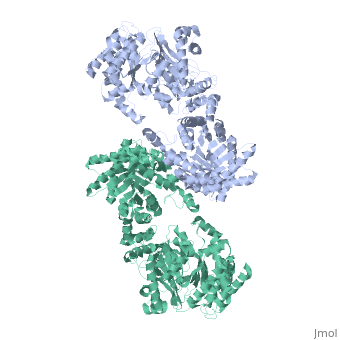
3.0 A RESOLUTION CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF GLYCOSOMAL PYRUVATE PHOSPHATE DIKINASE FROM TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI3.0 A RESOLUTION CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF GLYCOSOMAL PYRUVATE PHOSPHATE DIKINASE FROM TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe crystal structure of the glycosomal enzyme pyruvate phosphate dikinase from the African protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei has been solved to 3.0 A resolution by molecular replacement. The search model was the 2.3 A resolution structure of the Clostridium symbiosum enzyme. Due to different relative orientations of the domains and sub-domains in the two structures, molecular replacement could be achieved only by positioning these elements (four bodies altogether) sequentially in the asymmetric unit of the P2(1)2(1)2 crystal, which contains one pyruvate phosphate dikinase (PPDK) subunit. The refined model, comprising 898 residues and 188 solvent molecules per subunit, has a crystallographic residual index Rf = 0.245 (cross-validation residual index Rfree = 0.291) and displays satisfactory stereochemistry. Eight regions, comprising a total of 69 amino acid residues at the surface of the molecule, are disordered in this crystal form. The PPDK subunits are arranged around the crystallographic 2-fold axis as a dimer, analogous to that observed in the C. symbiosum enzyme. Comparison of the two structures was carried out by superposition of the models. Although the fold of each domain or sub-domain is similar, the relative orientations of these constitutive elements are different in the two structures. The trypanosome enzyme is more "bent" than the bacterial enzyme, with bending increasing from the center of the molecule (close to the molecular 2-fold axis) towards the periphery where the N-terminal domain is located. As a consequence of this increased bending and of the differences in relative positions of subdomains, the nucleotide-binding cleft in the amino-terminal domain is wider in T. brucei PPDK: the N-terminal fragment of the amino-terminal domain is distant from the catalytic, phospho-transfer competent histidine 482 (ca 10 A away). Our observations suggest that the requirements of domain motion during enzyme catalysis might include widening of the nucleotide-binding cleft to allow access and departure of the AMP or ATP ligand. The 3.0 A resolution crystal structure of glycosomal pyruvate phosphate dikinase from Trypanosoma brucei.,Cosenza LW, Bringaud F, Baltz T, Vellieux FM J Mol Biol. 2002 May 17;318(5):1417-32. PMID:12083528[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||