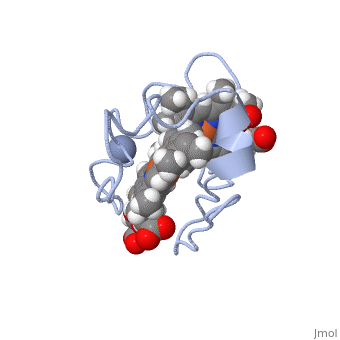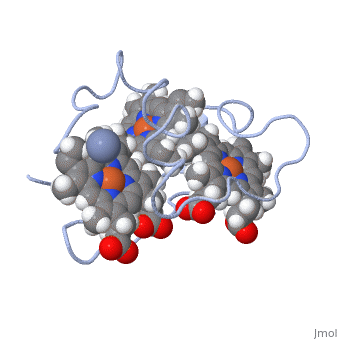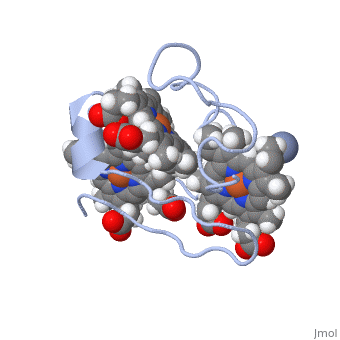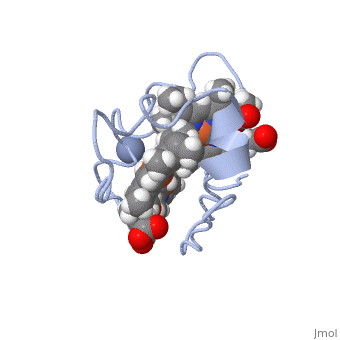Cytochrome c 7: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
<StructureSection load=' | <StructureSection load='1LM2.pdb' size='340' side='right' caption='3D Structure of Cytochrome c 7' scene=''> | ||
Cytocrhome c 7 ( | '''Cytocrhome c 7''' (Cc7) is a three heme-containing protein derived from the sulfur-reducing bacterium ''Desulfuromonas acetoxidans''. Cc7 is located in the mitochondrial intermembrane space of the bacteria where it plays a role in the electron-transfer mechanism <ref>Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 '''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC125002/''' DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999''']'''</ref>. ''Desulfuromonas acetoxidans'' bacteria have evolved to obtain their energy from anaerobic sulfure respiration, thus requiring organic disulfide compounds as electron acceptors<ref>Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12. DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962</ref>. | ||
==Structural Components== | ==Structural Components== | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 10:01, 29 November 2015
GeneralGeneral
Cytocrhome c 7 (Cc7) is a three heme-containing protein derived from the sulfur-reducing bacterium Desulfuromonas acetoxidans. Cc7 is located in the mitochondrial intermembrane space of the bacteria where it plays a role in the electron-transfer mechanism [1]. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans bacteria have evolved to obtain their energy from anaerobic sulfure respiration, thus requiring organic disulfide compounds as electron acceptors[2]. Structural ComponentsFunctionStructural highlightsThis is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12. DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962