1shy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= HGF, HPTA ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]), MET ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]) | |GENE= HGF, HPTA ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]), MET ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]) | ||
|DOMAIN=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?uid=cd00190 Tryp_SPc], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?uid=pfam01437 PSI], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?uid=pfam01403 Sema]</span> | |||
|RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1shy FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1shy OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1shy PDBsum], [http://www.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1kfv JenaLib], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1shy RCSB]</span> | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 32: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category: sema domain]] | [[Category: sema domain]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Wed Mar 26 06:05:08 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 07:05, 26 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 3.22Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene: | HGF, HPTA (Homo sapiens), MET (Homo sapiens) | ||||||
| Domains: | Tryp_SPc, PSI, Sema | ||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, JenaLib, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
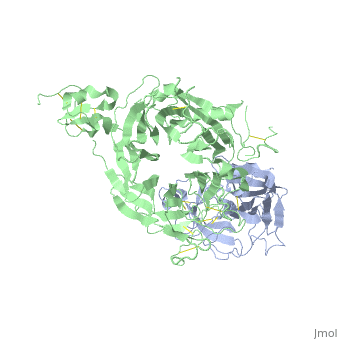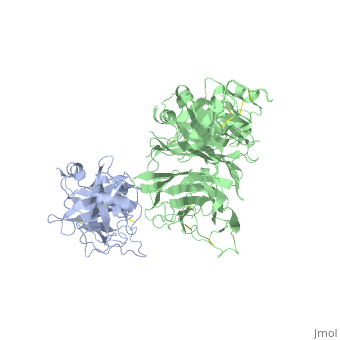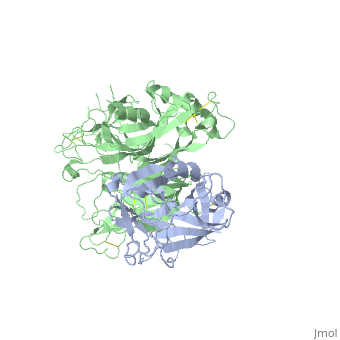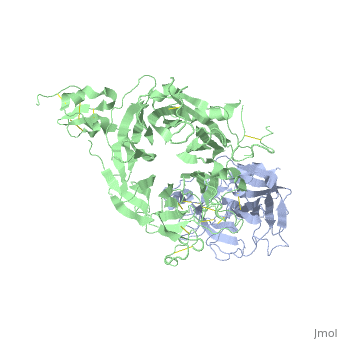
The Crystal Structure of HGF beta-chain in Complex with the Sema Domain of the Met Receptor.
OverviewOverview
The Met tyrosine kinase receptor and its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), play important roles in normal development and in tumor growth and metastasis. HGF-dependent signaling requires proteolysis from an inactive single-chain precursor into an active alpha/beta-heterodimer. We show that the serine protease-like HGF beta-chain alone binds Met, and report its crystal structure in complex with the Sema and PSI domain of the Met receptor. The Met Sema domain folds into a seven-bladed beta-propeller, where the bottom face of blades 2 and 3 binds to the HGF beta-chain 'active site region'. Mutation of HGF residues in the area that constitutes the active site region in related serine proteases significantly impairs HGF beta binding to Met. Key binding loops in this interface undergo conformational rearrangements upon maturation and explain the necessity of proteolytic cleavage for proper HGF signaling. A crystallographic dimer interface between two HGF beta-chains brings two HGF beta:Met complexes together, suggesting a possible mechanism of Met receptor dimerization and activation by HGF.
DiseaseDisease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Autism, suseptibility to, 9 OMIM:[164860], Fibromatosis, gingival OMIM:[182530], Hepatocellular carcinoma, childhood type OMIM:[164860], Noonan syndrome 4 OMIM:[182530], Renal cell carcinoma, papillary, familial and sporadic OMIM:[164860]
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1SHY is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Crystal structure of the HGF beta-chain in complex with the Sema domain of the Met receptor., Stamos J, Lazarus RA, Yao X, Kirchhofer D, Wiesmann C, EMBO J. 2004 Jun 16;23(12):2325-35. Epub 2004 May 27. PMID:15167892
Page seeded by OCA on Wed Mar 26 06:05:08 2008