Beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Obtaining the structure == | == Obtaining the structure == | ||
[[Image:G protein cycle for the b2AR–Gs complex.JPG | [[Image:G protein cycle for the b2AR–Gs complex.JPG|G protein cycle for the b2AR–Gs complex. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd on behalf of Cancer Research UK: Nature 477, 549–555, copyright 2011]] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Adrenergic receptor|Adrenergic receptor]] | *[[Adrenergic receptor|Adrenergic receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 11:28, 15 May 2015
Beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complexBeta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex
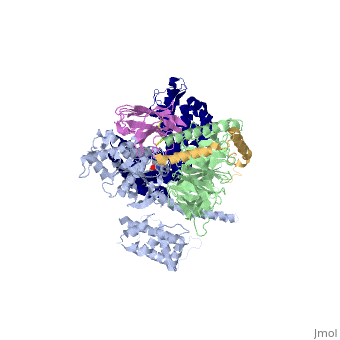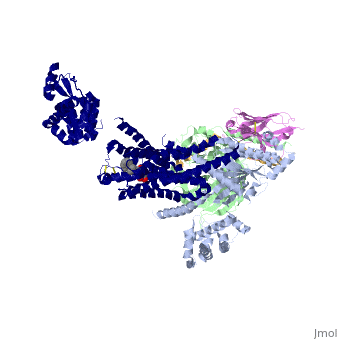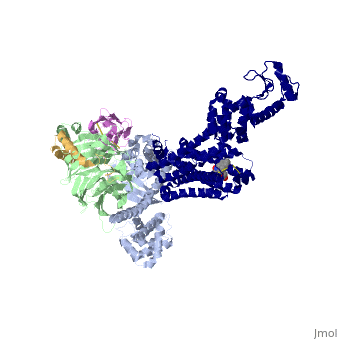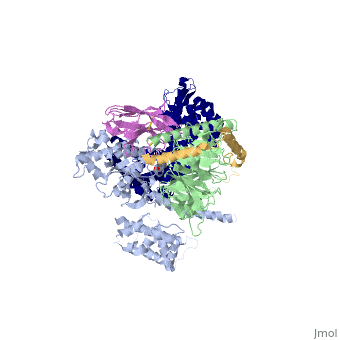
IntroductionG protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of protein receptors which have seven-transmembrane helices and are found over a large array on eukaryotic cells. These receptors take major part in a multitude of signal transduction pathways, including amongst others responses to hormones and neurotransmitters, sensing light, taste and smell, and many other responses. These receptors are also involved in many different types of diseases and are the target of almost 50% of current medical drugs. The Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptors are a type of GPCRs which are activated by catecholamine hormone ligands such as adrenaline (epinephrine). These receptors are responsible for many of the adrenaline related (“fight-or-flight”) responses and functions, and are used as a common model system for the GPCR family. GPCRs bind their ligand and overcome a conformational change which allows a Guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) to detach from the cellular end of the receptor and start the different signal transduction pathways. Since these receptors have seven transmembrane helices as well as inner and outer cell regions, they are very difficult to purify and crystalize. Some crystal structures have been determined for the inactive receptors as well as for the G protein that they bind. 3sn6 is the first structure of the full complex of the Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor bound to Gs in their active state, and it provides the first high-resolution insight into the mechanism of signal transduction across the plasma membrane by a GPCR. Obtaining the structureSee Also
|
| ||||||||||