1hgu: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1hgu]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. The April 2004 RCSB PDB [http://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Growth Hormone'' by Shuchismita Dutta and David S. Goodsell is [http://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_4 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_4]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1HGU OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1HGU FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1hgu]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. The April 2004 RCSB PDB [http://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Growth Hormone'' by Shuchismita Dutta and David S. Goodsell is [http://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_4 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_4]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1HGU OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1HGU FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1hgu FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1hgu OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1hgu RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1hgu PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1hgu FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1hgu OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1hgu RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1hgu PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
<table> | </table> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/SOMA_HUMAN SOMA_HUMAN]] Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/262400 262400]]; also known as pituitary dwarfism I. IGHD1A is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1A patients have an absence of GH with severe dwarfism and often develop anti-GH antibodies when given exogenous GH.<ref>PMID:8364549</ref> Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/612781 612781]]; also known as dwarfism of Sindh. IGHD1B is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1B patients have low but detectable levels of GH. Dwarfism is less severe than in IGHD1A and patients usually respond well to exogenous GH. Defects in GH1 are the cause of Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/262650 262650]]; also known as pituitary dwarfism VI.<ref>PMID:8552145</ref> <ref>PMID:9276733</ref> <ref>PMID:17519310</ref> Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/173100 173100]]. IGHD2 is an autosomal dominant deficiency of GH which causes short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/SOMA_HUMAN SOMA_HUMAN]] Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/262400 262400]]; also known as pituitary dwarfism I. IGHD1A is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1A patients have an absence of GH with severe dwarfism and often develop anti-GH antibodies when given exogenous GH.<ref>PMID:8364549</ref> Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/612781 612781]]; also known as dwarfism of Sindh. IGHD1B is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1B patients have low but detectable levels of GH. Dwarfism is less severe than in IGHD1A and patients usually respond well to exogenous GH. Defects in GH1 are the cause of Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/262650 262650]]; also known as pituitary dwarfism VI.<ref>PMID:8552145</ref> <ref>PMID:9276733</ref> <ref>PMID:17519310</ref> Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/173100 173100]]. IGHD2 is an autosomal dominant deficiency of GH which causes short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | [[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | ||
[[Category: Chantalat, L | [[Category: Chantalat, L]] | ||
[[Category: Jones, N | [[Category: Jones, N]] | ||
[[Category: Korber, F | [[Category: Korber, F]] | ||
[[Category: Navaza, J | [[Category: Navaza, J]] | ||
[[Category: Pavlovsky, A G | [[Category: Pavlovsky, A G]] | ||
[[Category: Hormone]] | [[Category: Hormone]] | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 22 December 2014
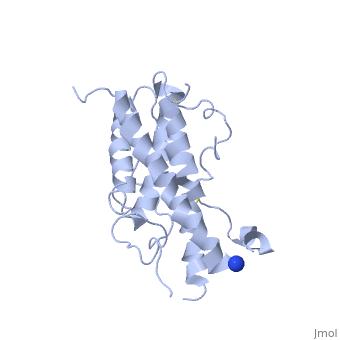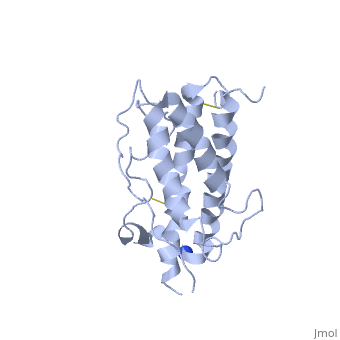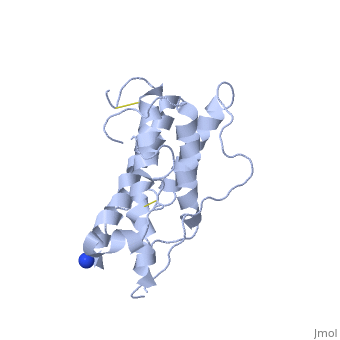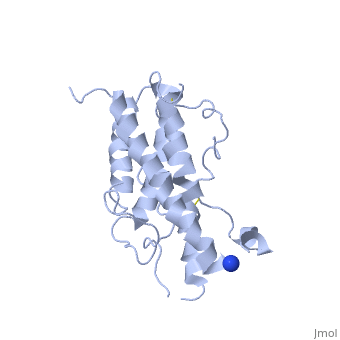
HUMAN GROWTH HORMONEHUMAN GROWTH HORMONE
Structural highlights
Disease[SOMA_HUMAN] Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1A (IGHD1A) [MIM:262400]; also known as pituitary dwarfism I. IGHD1A is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1A patients have an absence of GH with severe dwarfism and often develop anti-GH antibodies when given exogenous GH.[1] Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 1B (IGHD1B) [MIM:612781]; also known as dwarfism of Sindh. IGHD1B is an autosomal recessive deficiency of GH which causes short stature. IGHD1B patients have low but detectable levels of GH. Dwarfism is less severe than in IGHD1A and patients usually respond well to exogenous GH. Defects in GH1 are the cause of Kowarski syndrome (KWKS) [MIM:262650]; also known as pituitary dwarfism VI.[2] [3] [4] Defects in GH1 are a cause of growth hormone deficiency isolated type 2 (IGHD2) [MIM:173100]. IGHD2 is an autosomal dominant deficiency of GH which causes short stature. Clinical severity is variable. Patients have a positive response and immunologic tolerance to growth hormone therapy. Function[SOMA_HUMAN] Plays an important role in growth control. Its major role in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1. It stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts. It also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||