3lc3: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
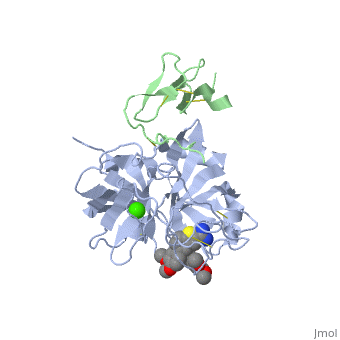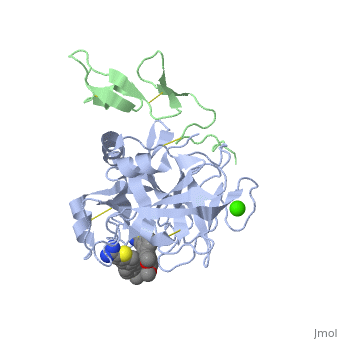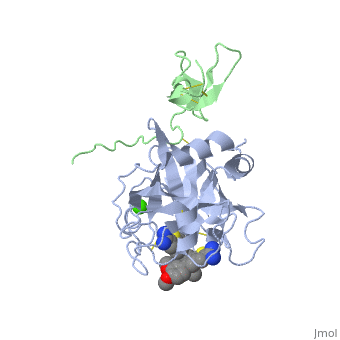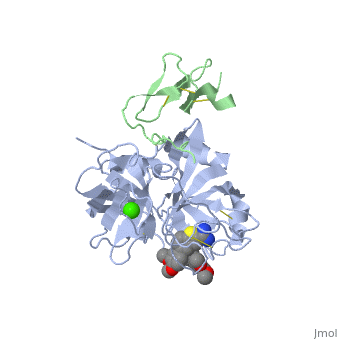
==Benzothiophene Inhibitors of Factor IXa== | |||
=== | <StructureSection load='3lc3' size='340' side='right' caption='[[3lc3]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.90Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3lc3]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3LC3 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3LC3 FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
==Disease== | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=IYX:1-[5-(3,4-DIMETHOXYPHENYL)-1-BENZOTHIOPHEN-2-YL]METHANEDIAMINE'>IYX</scene></td></tr> | ||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/FA9_HUMAN FA9_HUMAN]] Defects in F9 are the cause of recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/306900 306900]]; also known as Christmas disease.<ref>PMID:8295821</ref><ref>PMID:2592373</ref><ref>PMID:2743975</ref><ref>PMID:6603618</ref><ref>PMID:3009023</ref><ref>PMID:3790720</ref><ref>PMID:3401602</ref><ref>PMID:3243764</ref><ref>PMID:2713493</ref><ref>PMID:2714791</ref><ref>PMID:2773937</ref><ref>PMID:2775660</ref><ref>PMID:2753873</ref><ref>PMID:2738071</ref><ref>PMID:2472424</ref><ref>PMID:2339358</ref><ref>PMID:2372509</ref><ref>PMID:2162822</ref><ref>PMID:1958666</ref><ref>PMID:1902289</ref><ref>PMID:1346975</ref><ref>PMID:1615485</ref><ref>PMID:8257988</ref><ref>PMID:8076946</ref><ref>PMID:8199596</ref><ref>PMID:7981722</ref><ref>PMID:8680410</ref><ref>PMID:9222764</ref><ref>PMID:9590153</ref><ref>PMID:9452115</ref><ref>PMID:9600455</ref><ref>PMID:10698280</ref><ref>PMID:10094553</ref><ref>PMID:11122099</ref><ref>PMID:12588353</ref><ref>PMID:12604421</ref> | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[3lc5|3lc5]]</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">F9 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens])</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulation_factor_IXa Coagulation factor IXa], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.4.21.22 3.4.21.22] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3lc3 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3lc3 OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3lc3 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3lc3 PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Disease == | |||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/FA9_HUMAN FA9_HUMAN]] Defects in F9 are the cause of recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/306900 306900]]; also known as Christmas disease.<ref>PMID:8295821</ref> <ref>PMID:2592373</ref> <ref>PMID:2743975</ref> <ref>PMID:6603618</ref> <ref>PMID:3009023</ref> <ref>PMID:3790720</ref> <ref>PMID:3401602</ref> <ref>PMID:3243764</ref> <ref>PMID:2713493</ref> <ref>PMID:2714791</ref> <ref>PMID:2773937</ref> <ref>PMID:2775660</ref> <ref>PMID:2753873</ref> <ref>PMID:2738071</ref> <ref>PMID:2472424</ref> <ref>PMID:2339358</ref> <ref>PMID:2372509</ref> <ref>PMID:2162822</ref> <ref>PMID:1958666</ref> <ref>PMID:1902289</ref> <ref>PMID:1346975</ref> <ref>PMID:1615485</ref> <ref>PMID:8257988</ref> <ref>PMID:8076946</ref> <ref>PMID:8199596</ref> <ref>PMID:7981722</ref> <ref>PMID:8680410</ref> <ref>PMID:9222764</ref> <ref>PMID:9590153</ref> <ref>PMID:9452115</ref> <ref>PMID:9600455</ref> <ref>PMID:10698280</ref> <ref>PMID:10094553</ref> <ref>PMID:11122099</ref> <ref>PMID:12588353</ref> <ref>PMID:12604421</ref> Note=Mutations in position 43 (Oxford-3, San Dimas) and 46 (Cambridge) prevents cleavage of the propeptide, mutation in position 93 (Alabama) probably fails to bind to cell membranes, mutation in position 191 (Chapel-Hill) or in position 226 (Nagoya OR Hilo) prevent cleavage of the activation peptide. Defects in F9 are the cause of thrombophilia due to factor IX defect (THPH8) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/300807 300807]]. A hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis.<ref>PMID:19846852</ref> | |||
== Function == | |||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/FA9_HUMAN FA9_HUMAN]] Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca(2+) ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/lc/3lc3_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
FIXa is a serine protease enzyme involved in the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. The upstream intervention of the coagulation cascade in selectively inhibiting FIXa would leave hemostasis intact via the extrinsic pathway, leading to an optimum combination of efficacy and safety with low incidence of bleeding. We have identified 2-amindinobenzothiophene template as a lead scaffold for FIXa inhibiton based on its homology with urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). Subsequent SAR work on the template revealed a number of highly potent FIXa inhibitors, though with moderate selectivity against FXa. X-ray study with one of the analogues demonstrated active site binding interaction with the induced opening of the S1 beta pocket and a secondary binding at the S2-S4 sites, which is in direct contrast with the previous finding. | |||
Studies of Benzothiophene Template as Potent Factor IXa (FIXa) Inhibitors in Thrombosis.,Wang S, Beck R, Blench T, Burd A, Buxton S, Malic M, Ayele T, Shaikh S, Chahwala S, Chander C, Holland R, Merette S, Zhao L, Blackney M, Watts A J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1465-72. PMID:20121198<ref>PMID:20121198</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Factor IX|Factor IX]] | *[[Factor IX|Factor IX]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Coagulation factor IXa]] | [[Category: Coagulation factor IXa]] | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: Beck, R | [[Category: Beck, R]] | ||
[[Category: Wang, S | [[Category: Wang, S]] | ||
[[Category: Blood coagulation]] | [[Category: Blood coagulation]] | ||
[[Category: Cleavage on pair of basic residue]] | [[Category: Cleavage on pair of basic residue]] | ||
Revision as of 19:23, 18 December 2014
Benzothiophene Inhibitors of Factor IXaBenzothiophene Inhibitors of Factor IXa
Structural highlights
Disease[FA9_HUMAN] Defects in F9 are the cause of recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB) [MIM:306900]; also known as Christmas disease.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] Note=Mutations in position 43 (Oxford-3, San Dimas) and 46 (Cambridge) prevents cleavage of the propeptide, mutation in position 93 (Alabama) probably fails to bind to cell membranes, mutation in position 191 (Chapel-Hill) or in position 226 (Nagoya OR Hilo) prevent cleavage of the activation peptide. Defects in F9 are the cause of thrombophilia due to factor IX defect (THPH8) [MIM:300807]. A hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis.[37] Function[FA9_HUMAN] Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca(2+) ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedFIXa is a serine protease enzyme involved in the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. The upstream intervention of the coagulation cascade in selectively inhibiting FIXa would leave hemostasis intact via the extrinsic pathway, leading to an optimum combination of efficacy and safety with low incidence of bleeding. We have identified 2-amindinobenzothiophene template as a lead scaffold for FIXa inhibiton based on its homology with urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). Subsequent SAR work on the template revealed a number of highly potent FIXa inhibitors, though with moderate selectivity against FXa. X-ray study with one of the analogues demonstrated active site binding interaction with the induced opening of the S1 beta pocket and a secondary binding at the S2-S4 sites, which is in direct contrast with the previous finding. Studies of Benzothiophene Template as Potent Factor IXa (FIXa) Inhibitors in Thrombosis.,Wang S, Beck R, Blench T, Burd A, Buxton S, Malic M, Ayele T, Shaikh S, Chahwala S, Chander C, Holland R, Merette S, Zhao L, Blackney M, Watts A J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1465-72. PMID:20121198[38] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
OCA- Coagulation factor IXa
- Homo sapiens
- Beck, R
- Wang, S
- Blood coagulation
- Cleavage on pair of basic residue
- Disease mutation
- Disulfide bond
- Egf-like domain
- Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid
- Glycoprotein
- Hemophilia
- Hydrolase
- Hydrolase-hydrolase inhibitor complex
- Hydroxylation
- Peptidase s1
- Phosphoprotein
- Protease
- Protein-inhibitor complex
- Secreted
- Serine protease
- Sulfation
- Zymogen