3sn6: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex== | |||
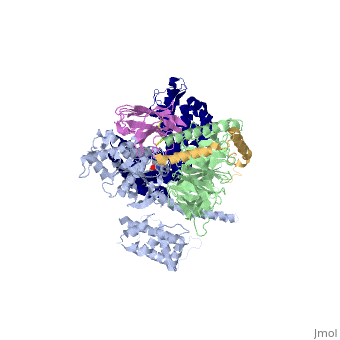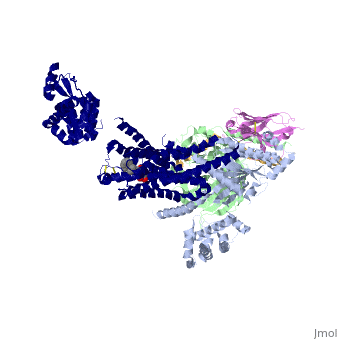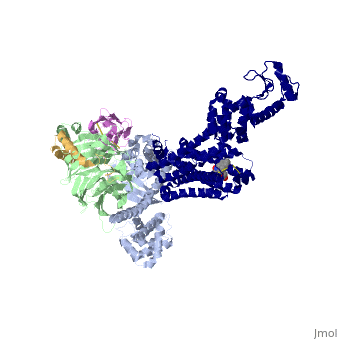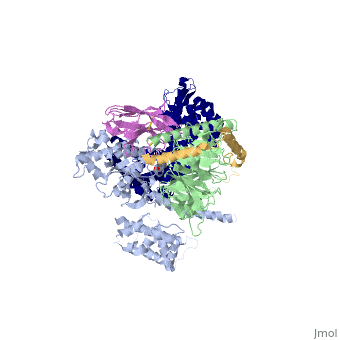
<StructureSection load='3sn6' size='340' side='right' caption='[[3sn6]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.20Å' scene=''> | |||
{ | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3sn6]] is a 5 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bos_taurus Bos taurus], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterobacteria_phage_t4 Enterobacteria phage t4], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lama_glama Lama glama] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rattus_norvegicus Rattus norvegicus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3SN6 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3SN6 FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=P0G:8-[(1R)-2-{[1,1-DIMETHYL-2-(2-METHYLPHENYL)ETHYL]AMINO}-1-HYDROXYETHYL]-5-HYDROXY-2H-1,4-BENZOXAZIN-3(4H)-ONE'>P0G</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">GNAS, GNAS1 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9913 Bos taurus]), Gnb1 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=10116 Rattus norvegicus]), GNG2 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9913 Bos taurus]), E, ADRB2, ADRB2R, B2AR ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=10665 Enterobacteria phage T4])</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lysozyme Lysozyme], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.2.1.17 3.2.1.17] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3sn6 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3sn6 OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3sn6 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3sn6 PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are responsible for the majority of cellular responses to hormones and neurotransmitters as well as the senses of sight, olfaction and taste. The paradigm of GPCR signalling is the activation of a heterotrimeric GTP binding protein (G protein) by an agonist-occupied receptor. The beta(2) adrenergic receptor (beta(2)AR) activation of Gs, the stimulatory G protein for adenylyl cyclase, has long been a model system for GPCR signalling. Here we present the crystal structure of the active state ternary complex composed of agonist-occupied monomeric beta(2)AR and nucleotide-free Gs heterotrimer. The principal interactions between the beta(2)AR and Gs involve the amino- and carboxy-terminal alpha-helices of Gs, with conformational changes propagating to the nucleotide-binding pocket. The largest conformational changes in the beta(2)AR include a 14 A outward movement at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment 6 (TM6) and an alpha-helical extension of the cytoplasmic end of TM5. The most surprising observation is a major displacement of the alpha-helical domain of Galphas relative to the Ras-like GTPase domain. This crystal structure represents the first high-resolution view of transmembrane signalling by a GPCR. | |||
Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex.,Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Chae PS, Pardon E, Calinski D, Mathiesen JM, Shah ST, Lyons JA, Caffrey M, Gellman SH, Steyaert J, Skiniotis G, Weis WI, Sunahara RK, Kobilka BK Nature. 2011 Jul 19;477(7366):549-55. doi: 10.1038/nature10361. PMID:21772288<ref>PMID:21772288</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Adrenergic receptor|Adrenergic receptor]] | *[[Adrenergic receptor|Adrenergic receptor]] | ||
*[[Antibody|Antibody]] | |||
*[[Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor|Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor]] | *[[Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor|Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor]] | ||
*[[G protein-coupled receptor|G protein-coupled receptor]] | *[[G protein-coupled receptor|G protein-coupled receptor]] | ||
*[[GTP-binding protein|GTP-binding protein]] | *[[GTP-binding protein|GTP-binding protein]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Guanine nucleotide-binding protein|Guanine nucleotide-binding protein]] | ||
*[[Hormone|Hormone]] | *[[Hormone|Hormone]] | ||
*[[Lysozyme 3D structures|Lysozyme 3D structures]] | |||
*[[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure|Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] | *[[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure|Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] | ||
*[[Suggestions for new articles|Suggestions for new articles]] | *[[Suggestions for new articles|Suggestions for new articles]] | ||
*[[Transducin|Transducin]] | |||
*[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Analysis Workshop Session Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Analysis Workshop Session Fall 2012]] | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Analysis Workshop Session Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Analysis Workshop Session Fall 2012]] | ||
*[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012]] | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
< | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Bos taurus]] | [[Category: Bos taurus]] | ||
[[Category: Enterobacteria phage t4]] | [[Category: Enterobacteria phage t4]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category: Lysozyme]] | [[Category: Lysozyme]] | ||
[[Category: Rattus norvegicus]] | [[Category: Rattus norvegicus]] | ||
[[Category: Caffrey, M | [[Category: Caffrey, M]] | ||
[[Category: Calinski, D | [[Category: Calinski, D]] | ||
[[Category: Chae, P S | [[Category: Chae, P S]] | ||
[[Category: Chung, K Y | [[Category: Chung, K Y]] | ||
[[Category: DeVree, B T | [[Category: DeVree, B T]] | ||
[[Category: Gellman, S H | [[Category: Gellman, S H]] | ||
[[Category: Kobilka, B K | [[Category: Kobilka, B K]] | ||
[[Category: Kobilka, T S | [[Category: Kobilka, T S]] | ||
[[Category: Kruse, A C | [[Category: Kruse, A C]] | ||
[[Category: Lyons, J A | [[Category: Lyons, J A]] | ||
[[Category: Mathiesen, J M | [[Category: Mathiesen, J M]] | ||
[[Category: Pardon, E | [[Category: Pardon, E]] | ||
[[Category: Rasmussen, S G.F | [[Category: Rasmussen, S G.F]] | ||
[[Category: Shah, S T.A | [[Category: Shah, S T.A]] | ||
[[Category: Skiniotis, G | [[Category: Skiniotis, G]] | ||
[[Category: Steyaert, J | [[Category: Steyaert, J]] | ||
[[Category: Sunahara, R K | [[Category: Sunahara, R K]] | ||
[[Category: Thian, F S | [[Category: Thian, F S]] | ||
[[Category: Weis, W I | [[Category: Weis, W I]] | ||
[[Category: Zou, Y | [[Category: Zou, Y]] | ||
[[Category: G protein signaling]] | [[Category: G protein signaling]] | ||
[[Category: G protein-coupled receptor]] | [[Category: G protein-coupled receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 18 December 2014
Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complexCrystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex
Structural highlights
Publication Abstract from PubMedG protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are responsible for the majority of cellular responses to hormones and neurotransmitters as well as the senses of sight, olfaction and taste. The paradigm of GPCR signalling is the activation of a heterotrimeric GTP binding protein (G protein) by an agonist-occupied receptor. The beta(2) adrenergic receptor (beta(2)AR) activation of Gs, the stimulatory G protein for adenylyl cyclase, has long been a model system for GPCR signalling. Here we present the crystal structure of the active state ternary complex composed of agonist-occupied monomeric beta(2)AR and nucleotide-free Gs heterotrimer. The principal interactions between the beta(2)AR and Gs involve the amino- and carboxy-terminal alpha-helices of Gs, with conformational changes propagating to the nucleotide-binding pocket. The largest conformational changes in the beta(2)AR include a 14 A outward movement at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment 6 (TM6) and an alpha-helical extension of the cytoplasmic end of TM5. The most surprising observation is a major displacement of the alpha-helical domain of Galphas relative to the Ras-like GTPase domain. This crystal structure represents the first high-resolution view of transmembrane signalling by a GPCR. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex.,Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Chae PS, Pardon E, Calinski D, Mathiesen JM, Shah ST, Lyons JA, Caffrey M, Gellman SH, Steyaert J, Skiniotis G, Weis WI, Sunahara RK, Kobilka BK Nature. 2011 Jul 19;477(7366):549-55. doi: 10.1038/nature10361. PMID:21772288[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See Also
References
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
OCA- Bos taurus
- Enterobacteria phage t4
- Lama glama
- Lysozyme
- Rattus norvegicus
- Caffrey, M
- Calinski, D
- Chae, P S
- Chung, K Y
- DeVree, B T
- Gellman, S H
- Kobilka, B K
- Kobilka, T S
- Kruse, A C
- Lyons, J A
- Mathiesen, J M
- Pardon, E
- Rasmussen, S G.F
- Shah, S T.A
- Skiniotis, G
- Steyaert, J
- Sunahara, R K
- Thian, F S
- Weis, W I
- Zou, Y
- G protein signaling
- G protein-coupled receptor
- Gpcr
- Nanobody
- Seven transmembrane receptor
- Signal transduction
- Signaling protein-hydrolase complex