2ada: Difference between revisions
m Protected "2ada" [edit=sysop:move=sysop] |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image: | ==ATOMIC STRUCTURE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE COMPLEXED WITH A TRANSITION-STATE ANALOG: UNDERSTANDING CATALYSIS AND IMMUNODEFICIENCY MUTATIONS== | ||
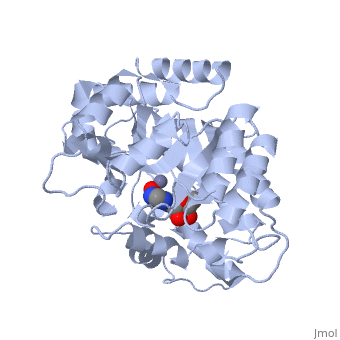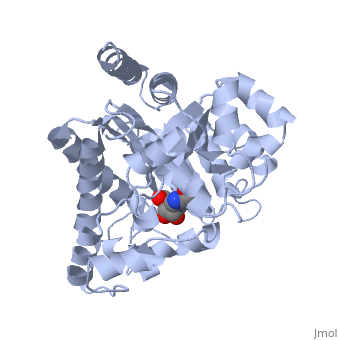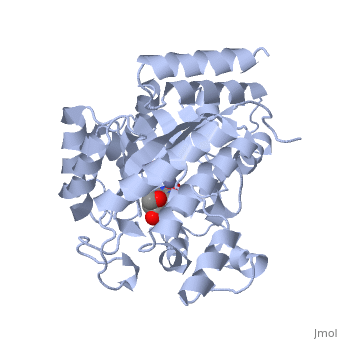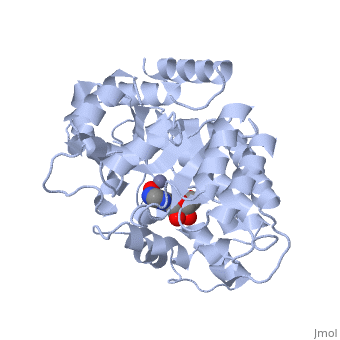
<StructureSection load='2ada' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2ada]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.40Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2ada]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entry [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=1ada 1ada]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2ADA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2ADA FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=HPR:6-HYDROXY-7,8-DIHYDRO+PURINE+NUCLEOSIDE'>HPR</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene><br> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_deaminase Adenosine deaminase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.5.4.4 3.5.4.4] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2ada FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2ada OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2ada RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2ada PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/ad/2ada_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The crystal structure of a murine adenosine deaminase complexed with 6-hydroxyl-1,6-dihydropurine ribonucleoside, a nearly ideal transition-state analog, has been determined and refined at 2.4 angstrom resolution. The structure is folded as an eight-stranded parallel alpha/beta barrel with a deep pocket at the beta-barrel COOH-terminal end wherein the inhibitor and a zinc are bound and completely sequestered. The presence of the zinc cofactor and the precise structure of the bound analog were not previously known. The 6R isomer of the analog is very tightly held in place by the coordination of the 6-hydroxyl to the zinc and the formation of nine hydrogen bonds. On the basis of the structure of the complex a stereoselective addition-elimination or SN2 mechanism of the enzyme is proposed with the zinc atom and the Glu and Asp residues playing key roles. A molecular explanation of a hereditary disease caused by several point mutations of an enzyme is also presented. | |||
Atomic structure of adenosine deaminase complexed with a transition-state analog: understanding catalysis and immunodeficiency mutations.,Wilson DK, Rudolph FB, Quiocho FA Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1278-84. PMID:1925539<ref>PMID:1925539</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Adenosine deaminase|Adenosine deaminase]] | |||
== | == References == | ||
[[ | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
== | </StructureSection> | ||
< | |||
[[Category: Adenosine deaminase]] | [[Category: Adenosine deaminase]] | ||
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | [[Category: Mus musculus]] | ||
Revision as of 03:46, 30 September 2014
ATOMIC STRUCTURE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE COMPLEXED WITH A TRANSITION-STATE ANALOG: UNDERSTANDING CATALYSIS AND IMMUNODEFICIENCY MUTATIONSATOMIC STRUCTURE OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE COMPLEXED WITH A TRANSITION-STATE ANALOG: UNDERSTANDING CATALYSIS AND IMMUNODEFICIENCY MUTATIONS
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe crystal structure of a murine adenosine deaminase complexed with 6-hydroxyl-1,6-dihydropurine ribonucleoside, a nearly ideal transition-state analog, has been determined and refined at 2.4 angstrom resolution. The structure is folded as an eight-stranded parallel alpha/beta barrel with a deep pocket at the beta-barrel COOH-terminal end wherein the inhibitor and a zinc are bound and completely sequestered. The presence of the zinc cofactor and the precise structure of the bound analog were not previously known. The 6R isomer of the analog is very tightly held in place by the coordination of the 6-hydroxyl to the zinc and the formation of nine hydrogen bonds. On the basis of the structure of the complex a stereoselective addition-elimination or SN2 mechanism of the enzyme is proposed with the zinc atom and the Glu and Asp residues playing key roles. A molecular explanation of a hereditary disease caused by several point mutations of an enzyme is also presented. Atomic structure of adenosine deaminase complexed with a transition-state analog: understanding catalysis and immunodeficiency mutations.,Wilson DK, Rudolph FB, Quiocho FA Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1278-84. PMID:1925539[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||||