1z7n: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
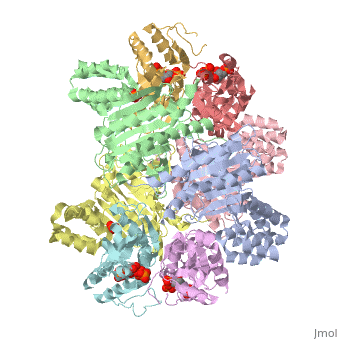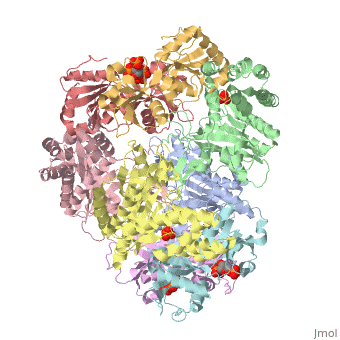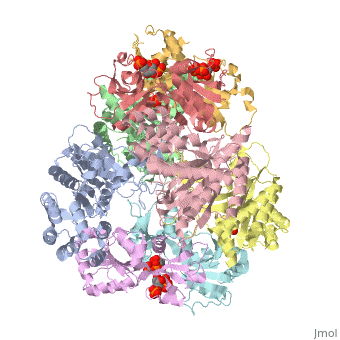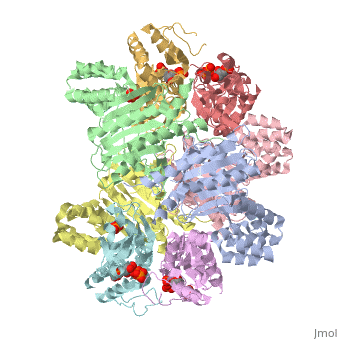
[[Image: | ==ATP Phosphoribosyl transferase (HisZG ATP-PRTase) from Lactococcus lactis with bound PRPP substrate== | ||
<StructureSection load='1z7n' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1z7n]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.25Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1z7n]] is a 8 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactococcus_lactis Lactococcus lactis]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1Z7N OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1Z7N FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=PO4:PHOSPHATE+ION'>PO4</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PRP:ALPHA-PHOSPHORIBOSYLPYROPHOSPHORIC+ACID'>PRP</scene><br> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1z7m|1z7m]]</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">hisZ ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=1358 Lactococcus lactis]), hisG ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=1358 Lactococcus lactis])</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATP_phosphoribosyltransferase ATP phosphoribosyltransferase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.4.2.17 2.4.2.17] </span></td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1z7n FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1z7n OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1z7n RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1z7n PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/z7/1z7n_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
ATP phosphoribosyl transferase (ATP-PRT) joins ATP and 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) in a highly regulated reaction that initiates histidine biosynthesis. The unusual hetero-octameric version of ATP-PRT includes four HisG(S) catalytic subunits based on the periplasmic binding protein fold and four HisZ regulatory subunits that resemble histidyl-tRNA synthetases. Here, we present the first structure of a PRPP-bound ATP-PRT at 2.9 A and provide a structural model for allosteric activation based on comparisons with other inhibited and activated ATP-PRTs from both the hetero-octameric and hexameric families. The activated state of the octameric enzyme is characterized by an interstitial phosphate ion in the HisZ-HisG interface and new contacts between the HisZ motif 2 loop and the HisG(S) dimer interface. These contacts restructure the interface to recruit conserved residues to the active site, where they activate pyrophosphate to promote catalysis. Additionally, mutational analysis identifies the histidine binding sites within a region highly conserved between HisZ and the functional HisRS. Through the oligomerization and functional re-assignment of protein domains associated with aminoacylation and phosphate binding, the HisZ-HisG octameric ATP-PRT acquired the ability to initiate the synthesis of a key metabolic intermediate in an allosterically regulated fashion. | |||
Activation of the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyl transferase through subunit interface rearrangement by a tRNA synthetase paralog.,Champagne KS, Sissler M, Larrabee Y, Doublie S, Francklyn CS J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 7;280(40):34096-104. Epub 2005 Jul 28. PMID:16051603<ref>PMID:16051603</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[ATP Phosphoribosyl Transferase|ATP Phosphoribosyl Transferase]] | *[[ATP Phosphoribosyl Transferase|ATP Phosphoribosyl Transferase]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
< | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: ATP phosphoribosyltransferase]] | [[Category: ATP phosphoribosyltransferase]] | ||
[[Category: Lactococcus lactis]] | [[Category: Lactococcus lactis]] | ||
Revision as of 23:40, 28 September 2014
ATP Phosphoribosyl transferase (HisZG ATP-PRTase) from Lactococcus lactis with bound PRPP substrateATP Phosphoribosyl transferase (HisZG ATP-PRTase) from Lactococcus lactis with bound PRPP substrate
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedATP phosphoribosyl transferase (ATP-PRT) joins ATP and 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) in a highly regulated reaction that initiates histidine biosynthesis. The unusual hetero-octameric version of ATP-PRT includes four HisG(S) catalytic subunits based on the periplasmic binding protein fold and four HisZ regulatory subunits that resemble histidyl-tRNA synthetases. Here, we present the first structure of a PRPP-bound ATP-PRT at 2.9 A and provide a structural model for allosteric activation based on comparisons with other inhibited and activated ATP-PRTs from both the hetero-octameric and hexameric families. The activated state of the octameric enzyme is characterized by an interstitial phosphate ion in the HisZ-HisG interface and new contacts between the HisZ motif 2 loop and the HisG(S) dimer interface. These contacts restructure the interface to recruit conserved residues to the active site, where they activate pyrophosphate to promote catalysis. Additionally, mutational analysis identifies the histidine binding sites within a region highly conserved between HisZ and the functional HisRS. Through the oligomerization and functional re-assignment of protein domains associated with aminoacylation and phosphate binding, the HisZ-HisG octameric ATP-PRT acquired the ability to initiate the synthesis of a key metabolic intermediate in an allosterically regulated fashion. Activation of the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyl transferase through subunit interface rearrangement by a tRNA synthetase paralog.,Champagne KS, Sissler M, Larrabee Y, Doublie S, Francklyn CS J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 7;280(40):34096-104. Epub 2005 Jul 28. PMID:16051603[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||