4q3h: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | ==The crystal structure of NHERF1 PDZ2 CXCR2 complex revealed by the NHERF1 CXCR2 chimeric protein== | ||
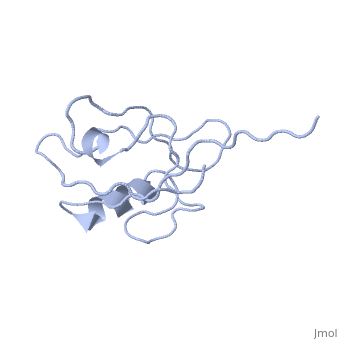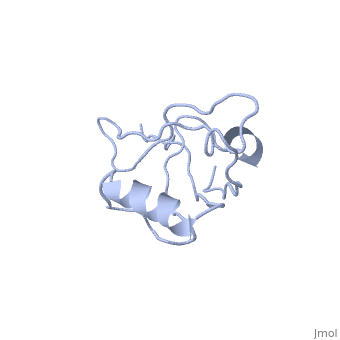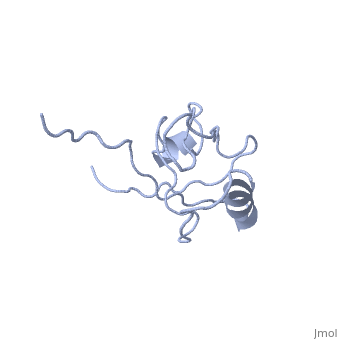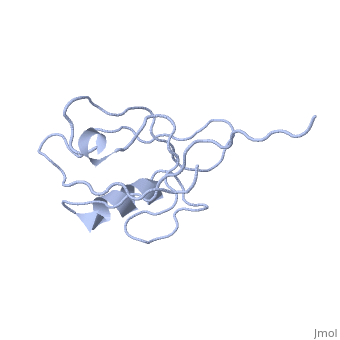
<StructureSection load='4q3h' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4q3h]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.44Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4q3h]] is a 2 chain structure. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4Q3H OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4Q3H FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4q3h FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4q3h OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4q3h RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4q3h PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Disease == | |||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NHRF1_HUMAN NHRF1_HUMAN]] Defects in SLC9A3R1 are the cause of hypophosphatemic nephrolithiasis/osteoporosis type 2 (NPHLOP2) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/612287 612287]]. Hypophosphatemia results from idiopathic renal phosphate loss. It contributes to the pathogenesis of hypophosphatemic urolithiasis (formation of urinary calculi) as well to that of hypophosphatemic osteoporosis (bone demineralization).<ref>PMID:18784102</ref> <ref>PMID:22506049</ref> | |||
== Function == | |||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NHRF1_HUMAN NHRF1_HUMAN]] Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for recycling of internalized ADRB2. Was first known to play a role in the regulation of the activity and subcellular location of SLC9A3. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3. May enhance Wnt signaling. May participate in HTR4 targeting to microvilli (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of phosphate reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules.<ref>PMID:9430655</ref> <ref>PMID:9096337</ref> <ref>PMID:10499588</ref> <ref>PMID:18784102</ref> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The formation of CXCR2-NHERF1-PLCbeta2 macromolecular complex in neutrophils regulates CXCR2 signaling and plays a key role in neutrophil chemotaxis and transepithelial neutrophilic migration. However, NHERF1 by itself, with only two PDZ domains, has a limited capacity in scaffolding the multiprotein-complex formation. Here we report the crystal structure of the NHERF1 PDZ2 domain in complex with the C-terminal CXCR2 sequence. The structure reveals that the PDZ2-CXCR2 binding specificity is achieved by numerous hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with the last four CXCR2 residues contributing to specific interactions. The structure also reveals two probable modes of PDZ2 dimerization where the two canonical ligand-binding pockets are well separated and orientated in a unique parallel fashion. This study provides not only the structural basis for the PDZ-mediated NHERF1-CXCR2 interaction, but also an additional example of how PDZ domains may dimerize, which both could prove valuable in understanding NHERF1 complex-scaffolding function in neutrophils. | |||
Crystal structure of the NHERF1 PDZ2 domain in complex with the chemokine receptor CXCR2 reveals probable modes of PDZ2 dimerization.,Holcomb J, Jiang Y, Guan X, Trescott L, Lu G, Hou Y, Wang S, Brunzelle J, Sirinupong N, Li C, Yang Z Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Apr 24. pii: S0006-291X(14)00736-0. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.085. PMID:24768637<ref>PMID:24768637</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Brunzelle, J.]] | |||
[[Category: Holcomb, J.]] | |||
[[Category: Jiang, Y.]] | |||
[[Category: Li, C.]] | |||
[[Category: Lu, G.]] | |||
[[Category: Sirinupong, N.]] | |||
[[Category: Trescott, L.]] | |||
[[Category: Yang, Z.]] | |||
[[Category: Dimerization]] | |||
[[Category: Immune system]] | |||
[[Category: Neutrophil chemotaxis]] | |||
[[Category: Scaffold protein]] | |||
Revision as of 12:04, 21 May 2014
The crystal structure of NHERF1 PDZ2 CXCR2 complex revealed by the NHERF1 CXCR2 chimeric proteinThe crystal structure of NHERF1 PDZ2 CXCR2 complex revealed by the NHERF1 CXCR2 chimeric protein
Structural highlights
Disease[NHRF1_HUMAN] Defects in SLC9A3R1 are the cause of hypophosphatemic nephrolithiasis/osteoporosis type 2 (NPHLOP2) [MIM:612287]. Hypophosphatemia results from idiopathic renal phosphate loss. It contributes to the pathogenesis of hypophosphatemic urolithiasis (formation of urinary calculi) as well to that of hypophosphatemic osteoporosis (bone demineralization).[1] [2] Function[NHRF1_HUMAN] Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for recycling of internalized ADRB2. Was first known to play a role in the regulation of the activity and subcellular location of SLC9A3. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3. May enhance Wnt signaling. May participate in HTR4 targeting to microvilli (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of phosphate reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules.[3] [4] [5] [6] Publication Abstract from PubMedThe formation of CXCR2-NHERF1-PLCbeta2 macromolecular complex in neutrophils regulates CXCR2 signaling and plays a key role in neutrophil chemotaxis and transepithelial neutrophilic migration. However, NHERF1 by itself, with only two PDZ domains, has a limited capacity in scaffolding the multiprotein-complex formation. Here we report the crystal structure of the NHERF1 PDZ2 domain in complex with the C-terminal CXCR2 sequence. The structure reveals that the PDZ2-CXCR2 binding specificity is achieved by numerous hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with the last four CXCR2 residues contributing to specific interactions. The structure also reveals two probable modes of PDZ2 dimerization where the two canonical ligand-binding pockets are well separated and orientated in a unique parallel fashion. This study provides not only the structural basis for the PDZ-mediated NHERF1-CXCR2 interaction, but also an additional example of how PDZ domains may dimerize, which both could prove valuable in understanding NHERF1 complex-scaffolding function in neutrophils. Crystal structure of the NHERF1 PDZ2 domain in complex with the chemokine receptor CXCR2 reveals probable modes of PDZ2 dimerization.,Holcomb J, Jiang Y, Guan X, Trescott L, Lu G, Hou Y, Wang S, Brunzelle J, Sirinupong N, Li C, Yang Z Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Apr 24. pii: S0006-291X(14)00736-0. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.085. PMID:24768637[7] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. References
|
| ||||||||||||||