Single stranded binding protein: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
The structure of SSB consists of a homotetramer that has a DNA binding domain that binds to a single strand of DNA. | The structure of SSB consists of a homotetramer that has a DNA binding domain that binds to a single strand of DNA. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
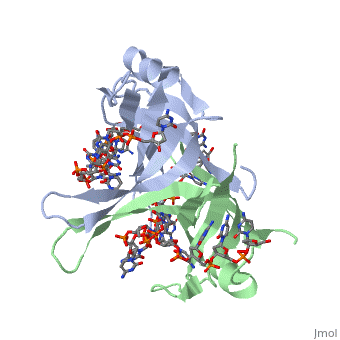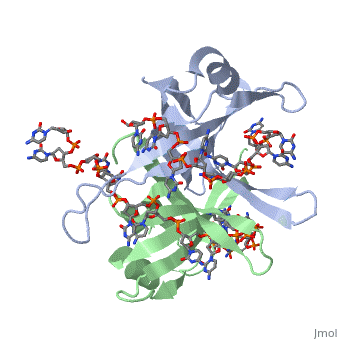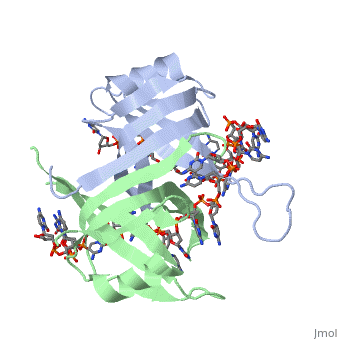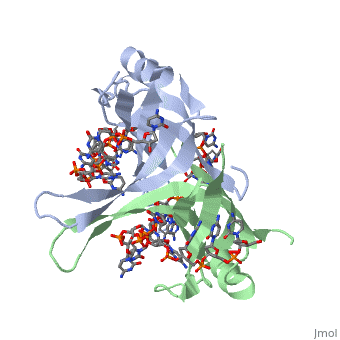
<StructureSection load='1kaw' size='500' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1kaw]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1kaw' size='500' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1kaw]])' scene=''> | ||
==Binding Interactions in the Active Site== | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 19:11, 30 October 2013
Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)
IntroductionCopies of SSB bind to the unwound DNA strands, keeping the strands separated so that both strands can serve as templates. StructureThe structure of SSB consists of a homotetramer that has a DNA binding domain that binds to a single strand of DNA.
|
| ||||||||||
Binding Interactions in the Active Site |
| ||||||||||
See AlsoSee Also
ReferencesReferences
PMID: 2087220