2hkq: Difference between revisions
New page: left|200px<br /> <applet load="2hkq" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="2hkq, resolution 1.86Å" /> '''Crystal structure o... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:2hkq. | [[Image:2hkq.jpg|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="2hkq" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" | ||
<applet load="2hkq" size=" | |||
caption="2hkq, resolution 1.86Å" /> | caption="2hkq, resolution 1.86Å" /> | ||
'''Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of human EB1 in complex with the CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)'''<br /> | '''Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of human EB1 in complex with the CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)'''<br /> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
2HKQ is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | 2HKQ is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2HKQ OCA]. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category: p150glued]] | [[Category: p150glued]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http:// | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Fri Feb 15 17:32:36 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 15 February 2008
|
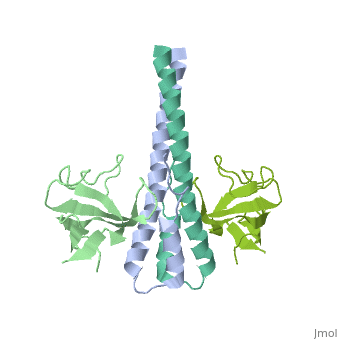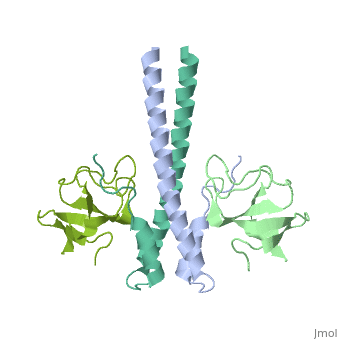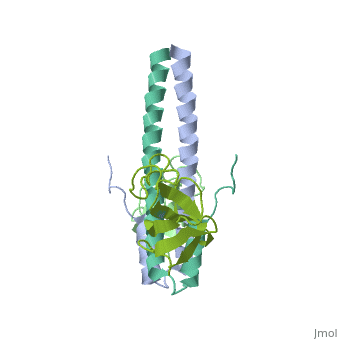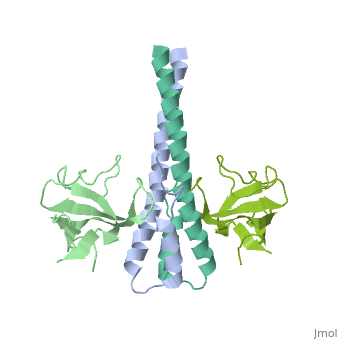
Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of human EB1 in complex with the CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)
OverviewOverview
Dynamic microtubule plus-end tracking protein (+TIP) networks are, implicated in all functions of microtubules, but the molecular, determinants of their interactions are largely unknown. Here, we have, explored key binding modes of +TIPs by analyzing the interactions between, selected CAP-Gly, EB-like, and carboxy-terminal EEY/F-COO(-) sequence, motifs. X-ray crystallography and biophysical binding studies demonstrate, that the beta2-beta3 loop of CAP-Gly domains determines EB-like motif, binding specificity. They further show how CAP-Gly domains serve as, recognition domains for EEY/F-COO(-) motifs, which represent, characteristic and functionally important sequence elements in EB, CLIP-170, and alpha-tubulin. Our findings provide a molecular basis for, understanding the modular interaction modes between alpha-tubulin, CLIPs, EB proteins, and the dynactin-dynein motor complex and suggest that, multiple low-affinity binding sites in different combinations control, dynamic +TIP networks at microtubule ends. They further offer insights, into the structural consequences of genetic CAP-Gly domain defects found, in severe human disorders.
DiseaseDisease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, susceptibility to OMIM:[601143], Neuropathy, distal hereditary motor, type VIIB OMIM:[601143]
About this StructureAbout this Structure
2HKQ is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Key interaction modes of dynamic +TIP networks., Honnappa S, Okhrimenko O, Jaussi R, Jawhari H, Jelesarov I, Winkler FK, Steinmetz MO, Mol Cell. 2006 Sep 1;23(5):663-71. PMID:16949363
Page seeded by OCA on Fri Feb 15 17:32:36 2008