Sandbox 215: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterylester_transfer_protein Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein] is a plasma glycoprotein which is implicated in the transport of cholesteryl esters from the atheroprotective high-density lipoproteins (HDL) to the atherogenic lower-density lipoproteins (LDL). The cristal structure of CETP at 2,2Å resolution in complex with four bound lipid molecules shows a long tunnel traversing the core of the molecule and has two distinct large openings allowing | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterylester_transfer_protein Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein] is a plasma glycoprotein which is implicated in the transport of cholesteryl esters from the atheroprotective high-density lipoproteins (HDL) to the atherogenic lower-density lipoproteins (LDL). The cristal structure of CETP at 2,2Å resolution in complex with four bound lipid molecules shows a long tunnel traversing the core of the molecule and has two distinct large openings allowing lipids access. | ||
==Role of CETP== | ==Role of CETP== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
CETP's structure can be divided into four structural units: | CETP's structure can be divided into four structural units: | ||
* At each end of the protein there is a barrel which is constitued of highly twisted | * At each end of the protein there is a barrel which is constitued of highly twisted ß-sheet and two helices called A and B at the N-terminal and A', B' at C-terminal extremity. Helices B and B' are longer than A and A' | ||
* Between the two barrels there is a central | * Between the two barrels there is a central ß-sheet which is constitued of six antiparallel strands | ||
* At the C-terminal extremity there is a distorted amphiphathic helix called helix X which is an extension of C-teminal interacting with N-terminal residues. | * At the C-terminal extremity there is a distorted amphiphathic helix called helix X which is an extension of C-teminal interacting with N-terminal residues. | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 27 December 2011
| |||||||||
| 2obd, resolution 2.10Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , , , , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | CETP (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
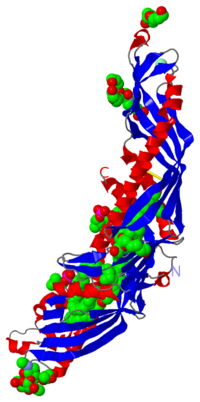
Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein is a plasma glycoprotein which is implicated in the transport of cholesteryl esters from the atheroprotective high-density lipoproteins (HDL) to the atherogenic lower-density lipoproteins (LDL). The cristal structure of CETP at 2,2Å resolution in complex with four bound lipid molecules shows a long tunnel traversing the core of the molecule and has two distinct large openings allowing lipids access.
Role of CETPRole of CETP
StructureStructure
General overview of the structureGeneral overview of the structure
CETP is a 476 amino acid residues protein which has an elongated “boomerang shape” with dimensions of 135Å X 30Å X 35Å. She has a molecular mass of 74 kDa and 28% of this mass is attributed to N-glycosylation at specific residues: 88, 240, 341 and 396. She also has a fold which is homologous to BPI (a protein which is implicated in lipid binding): two similar domains are connected by a linker.
CETP's structure can be divided into four structural units:
- At each end of the protein there is a barrel which is constitued of highly twisted ß-sheet and two helices called A and B at the N-terminal and A', B' at C-terminal extremity. Helices B and B' are longer than A and A'
- Between the two barrels there is a central ß-sheet which is constitued of six antiparallel strands
- At the C-terminal extremity there is a distorted amphiphathic helix called helix X which is an extension of C-teminal interacting with N-terminal residues.
Four lipid binding sitesFour lipid binding sites
CETP inhibitionCETP inhibition
External ressourcesExternal ressources
ReferencesReferences
- Qiu X, Mistry A, Ammirati MJ, Chrunyk BA, Clark RW, Cong Y, Culp JS, Danley DE, Freeman TB, Geoghegan KF, Griffor MC, Hawrylik SJ, Hayward CM, Hensley P, Hoth LR, Karam GA, Lira ME, Lloyd DB, McGrath KM, Stutzman-Engwall KJ, Subashi AK, Subashi TA, Thompson JF, Wang IK, Zhao H, Seddon AP. Crystal Structure of cholesteryl ester transfer protein reveals a long tunnel and four bound lipid molecules. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2007 Feb;14(2):106-13. Epub 2007 Jan 21. PMID: 17237796 doi:10.1038/nsmb1197
- James A Hamilton & Richard J Deckelbaum Crystal structure of CETP: new hopes for raising HDL to decrease risk of cardiovascular disease? Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 14, 95 - 97 (2007) PMID: 17277799 doi:10.1038/nsmb0207-95
Proteopedia Page Contributors and EditorsProteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
BLEU Mélusine, Goepfert Laetitia
