Colicin E3: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Mechanism of uptake== | ==Mechanism of uptake== | ||
{{STRUCTURE_1ujw | PDB=1ujw | SCENE= }} | |||
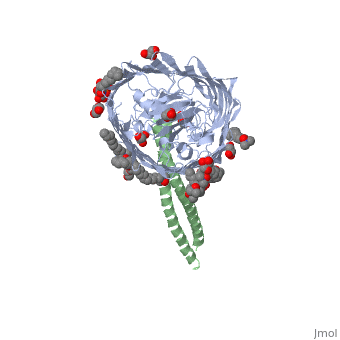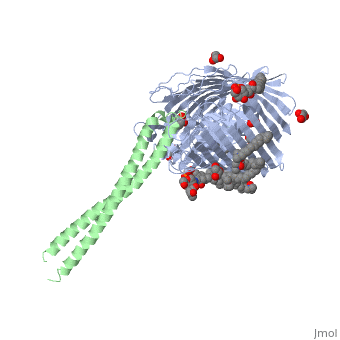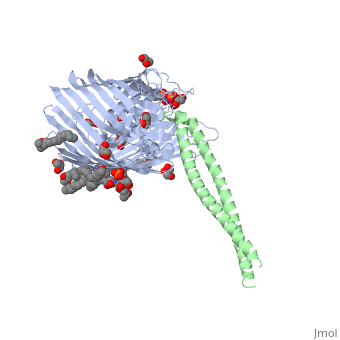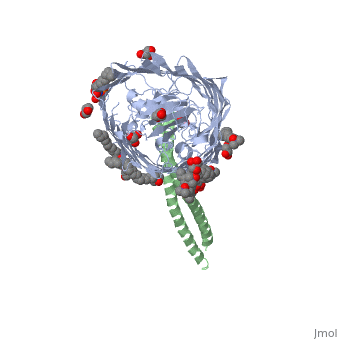
ColE3 initially binds to the BtuB vitamin B12 receptor. Formation of this complex leads to the unfolding of the N terminal receptor binding coiled-coil domain of ColE3. <ref> PMID: 17277071 </ref> | ColE3 initially binds to the BtuB vitamin B12 receptor. Formation of this complex leads to the unfolding of the N terminal receptor binding coiled-coil domain of ColE3. <ref> PMID: 17277071 </ref> | ||
The structure shows the complex formed between BtuB and the ColE3 translocation domain <ref> PMID: 14528295 </ref> | |||
==Killing Activities== | ==Killing Activities== | ||
Revision as of 19:59, 31 January 2011
Colicin E3 is a type of Colicin, a bacteriocin made by E. Coli which acts against other nearby E. Coli to kill them with its 16s rRNase activity; it digests the 16s ribosomal subunit, ultimately leading to the death of the cell.
Synthesis and releaseSynthesis and release
Mechanism of uptakeMechanism of uptake
| |||||||||
| 1ujw, resolution 2.75Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , , | ||||||||
| Related: | 1nqe, 1jch | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
ColE3 initially binds to the BtuB vitamin B12 receptor. Formation of this complex leads to the unfolding of the N terminal receptor binding coiled-coil domain of ColE3. [1]
The structure shows the complex formed between BtuB and the ColE3 translocation domain [2]
Killing ActivitiesKilling Activities
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Masi M, Vuong P, Humbard M, Malone K, Misra R. Initial steps of colicin E1 import across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(7):2667-76. Epub 2007 Feb 2. PMID:17277071 doi:10.1128/JB.01448-06
- ↑ Kurisu G, Zakharov SD, Zhalnina MV, Bano S, Eroukova VY, Rokitskaya TI, Antonenko YN, Wiener MC, Cramer WA. The structure of BtuB with bound colicin E3 R-domain implies a translocon. Nat Struct Biol. 2003 Nov;10(11):948-54. Epub 2003 Oct 5. PMID:14528295 doi:10.1038/nsb997