Tropomyosin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Revision as of 16:06, 21 December 2010
| |||||||||
| Tropomyosin from pig, 1c1g | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
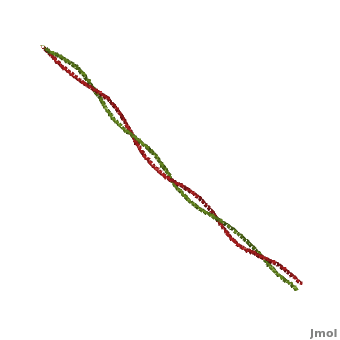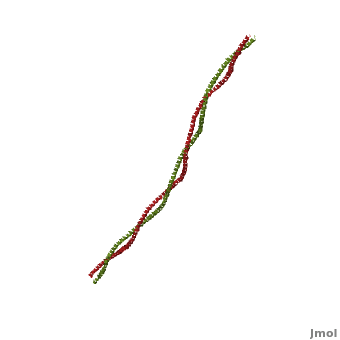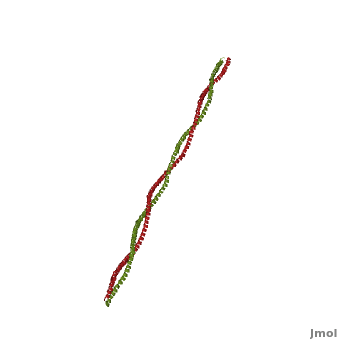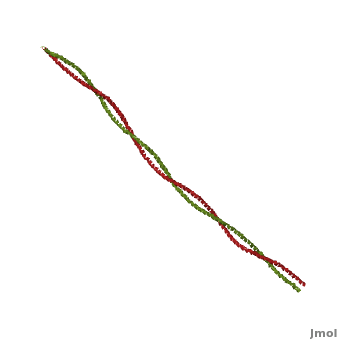
Tropomyosin (TPM) has a 4-helix coiled structure. It regulates the binding of myosin thus regulating muscle contraction [1]. In its locked conformation it binds troponin T (TnnT) and prevents the binding of myosin to actin. When Ca++ ions bind to TnnT, the TPM assumes an open conformation and myosin can bind to actin. The images on the left and the right correspond to one representative TPM structure, i.e. tropomyosin from pig (1c1g). You can at the right for clarity. The dimers of TPM in the asymmetric unit (1c1g) are , with their C-terminal ends overlapping by about 2/3 of the molecular length. This suggests head-to-tail packing of TPM, which is very important for its interaction with actin [2].
3D Structures of Tropomyosin3D Structures of Tropomyosin
3mtu, 3mud – cTPM alpha-1 – chicken
1ic2 - cTPM alpha-1 (mutant)
2w49 – cTnnC+cTnnT+cTnnI+cTPM alpha-1+cActin
2z5h – yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper+TnnT – yeast
2z5i - yTPM alpha-1 N-terminal+C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper
2efr, 2efs, 2d3e - rTPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper – rabbit
1kql - TPM alpha-1 C-terminal+GNC4 leucine zipper - rat
2b9c – TPM mid region – rat
1c1g – TPM – pig
2tma – TPM - model