Molecular Playground/ADAM13: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:MP_masthead}} | {{Template:MP_masthead}} | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 10 December 2010
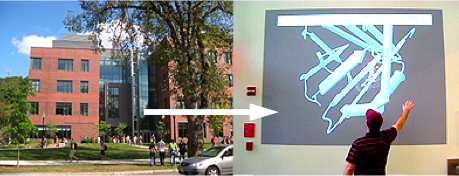 |
| Molecular Playground at the University of Massachusetts. MOVIE. |
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
|
ADAM13 is a transmembrane protein containing a metalloprotease domain (gray), and controls cell motility by shedding adhesion molecules from the cell surface. ADAM13 also exhibits adhesive activity through it's disintegrin (blue) and cysteine rich (purple) domains (EGF-like repeat, cyan).
Molecular Playground banner: ADAM13 reduces cell adhesion to promotes cell motility.
Metalloprotease domainMetalloprotease domain
Most ADAMs contain a canonical metalloprotease site (HExxHxxGxxH) with a catalytic glutamate residue (shown in red) three Histidine residues (blue) coordinating a Zinc ion (green). ADAMs are known to cleave a variety of proteins present at the cell surface in addition to cell adhesion molecules, such as signaling receptors and their ligands to either activate or inactivate the signaling pathway. The Alfandari Lab currently studies the role of the meltrin subfamily of ADAMs in early embryo development.
