2djh: Difference between revisions
New page: left|200px<br /><applet load="2djh" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="2djh, resolution 1.90Å" /> '''Crystal structure of... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:2djh.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="2djh" size=" | [[Image:2djh.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="2djh" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" | ||
caption="2djh, resolution 1.90Å" /> | caption="2djh, resolution 1.90Å" /> | ||
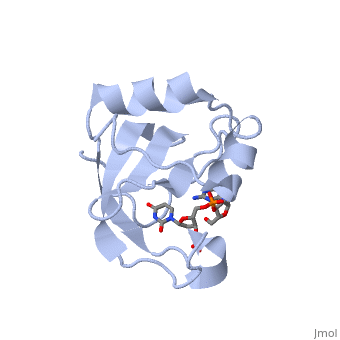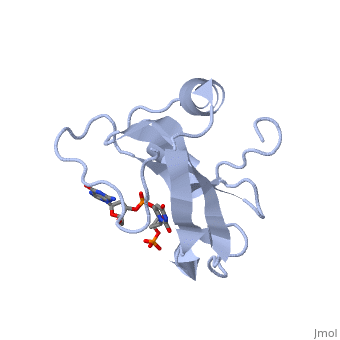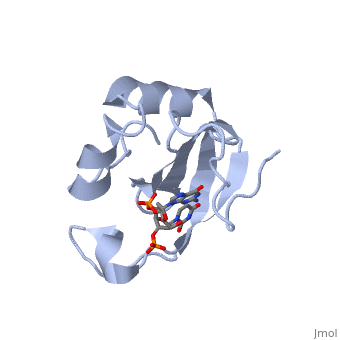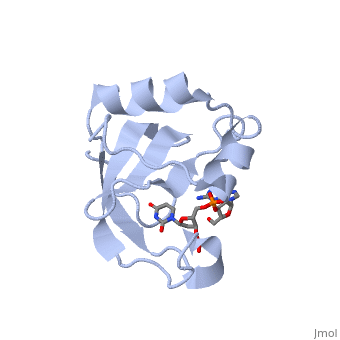
'''Crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal ribonuclease domain of Colicin E5'''<br /> | '''Crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal ribonuclease domain of Colicin E5'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Colicin E5--a tRNase toxin--specifically cleaves QUN (Q: queuosine) | Colicin E5--a tRNase toxin--specifically cleaves QUN (Q: queuosine) anticodons of the Escherichia coli tRNAs for Tyr, His, Asn and Asp. Here, we report the crystal structure of the C-terminal ribonuclease domain (CRD) of E5 complexed with a substrate analog, namely, dGpdUp, at a resolution of 1.9 A. Thisstructure is the first to reveal the substrate recognition mechanism of sequence-specific ribonucleases. E5-CRD realized the strict recognition for both the guanine and uracil bases of dGpdUp forming Watson-Crick-type hydrogen bonds and ring stacking interactions, thus mimicking the codons of mRNAs to bind to tRNA anticodons. The docking model of E5-CRD with tRNA also suggests its substrate preference for tRNA over ssRNA. In addition, the structure of E5-CRD/dGpdUp along with the mutational analysis suggests that Arg33 may play an important role in the catalytic activity, and Lys25/Lys60 may also be involved without His in E5-CRD. Finally, the comparison of the structures of E5-CRD/dGpdUp and E5-CRD/ImmE5 (an inhibitor protein) complexes suggests that the binding mode of E5-CRD and ImmE5 mimics that of mRNA and tRNA; this may represent the evolutionary pathway of these proteins from the RNA-RNA interaction through the RNA-protein interaction of tRNA/E5-CRD. | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
2DJH is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with 3PD as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | 2DJH is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with <scene name='pdbligand=3PD:'>3PD</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2DJH OCA]. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category: alpha/beta protein]] | [[Category: alpha/beta protein]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http:// | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 16:59:21 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 21 February 2008
|
Crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal ribonuclease domain of Colicin E5
OverviewOverview
Colicin E5--a tRNase toxin--specifically cleaves QUN (Q: queuosine) anticodons of the Escherichia coli tRNAs for Tyr, His, Asn and Asp. Here, we report the crystal structure of the C-terminal ribonuclease domain (CRD) of E5 complexed with a substrate analog, namely, dGpdUp, at a resolution of 1.9 A. Thisstructure is the first to reveal the substrate recognition mechanism of sequence-specific ribonucleases. E5-CRD realized the strict recognition for both the guanine and uracil bases of dGpdUp forming Watson-Crick-type hydrogen bonds and ring stacking interactions, thus mimicking the codons of mRNAs to bind to tRNA anticodons. The docking model of E5-CRD with tRNA also suggests its substrate preference for tRNA over ssRNA. In addition, the structure of E5-CRD/dGpdUp along with the mutational analysis suggests that Arg33 may play an important role in the catalytic activity, and Lys25/Lys60 may also be involved without His in E5-CRD. Finally, the comparison of the structures of E5-CRD/dGpdUp and E5-CRD/ImmE5 (an inhibitor protein) complexes suggests that the binding mode of E5-CRD and ImmE5 mimics that of mRNA and tRNA; this may represent the evolutionary pathway of these proteins from the RNA-RNA interaction through the RNA-protein interaction of tRNA/E5-CRD.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
2DJH is a Single protein structure of sequence from Escherichia coli with as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Structural basis for sequence-dependent recognition of colicin E5 tRNase by mimicking the mRNA-tRNA interaction., Yajima S, Inoue S, Ogawa T, Nonaka T, Ohsawa K, Masaki H, Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(21):6074-82. Epub 2006 Nov 11. PMID:17099236
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 16:59:21 2008