1ysa: Difference between revisions
New page: left|200px<br /><applet load="1ysa" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1ysa, resolution 2.900Å" /> '''THE GCN4 BASIC REGI... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:1ysa.jpg|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1ysa" size=" | [[Image:1ysa.jpg|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1ysa" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" | ||
caption="1ysa, resolution 2.900Å" /> | caption="1ysa, resolution 2.900Å" /> | ||
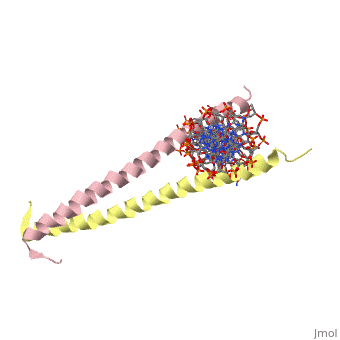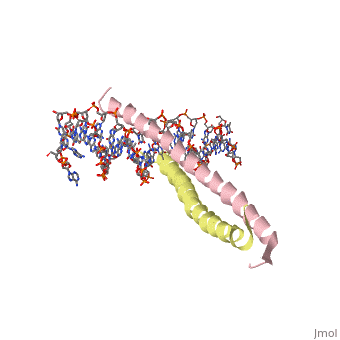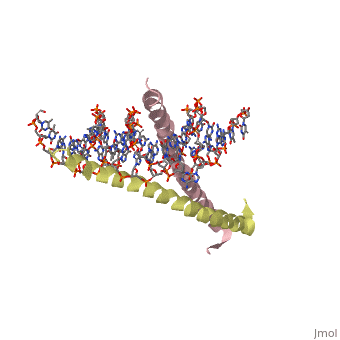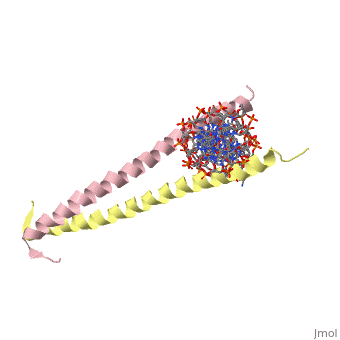
'''THE GCN4 BASIC REGION LEUCINE ZIPPER BINDS DNA AS A DIMER OF UNINTERRUPTED ALPHA HELICES: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX'''<br /> | '''THE GCN4 BASIC REGION LEUCINE ZIPPER BINDS DNA AS A DIMER OF UNINTERRUPTED ALPHA HELICES: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 is 1 of over 30 identified | The yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 is 1 of over 30 identified eukaryotic proteins containing the basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA-binding motif. We have determined the crystal structure of the GCN4 bZIP element complexed with DNA at 2.9 A resolution. The bZIP dimer is a pair of continuous alpha helices that form a parallel coiled coil over their carboxy-terminal 30 residues and gradually diverge toward their amino termini to pass through the major groove of the DNA-binding site. The coiled-coil dimerization interface is oriented almost perpendicular to the DNA axis, giving the complex the appearance of the letter T. There are no kinks or sharp bends in either bZIP monomer. Numerous contacts to DNA bases and phosphate oxygens are made by basic region residues that are conserved in the bZIP protein family. The details of the bZIP dimer interaction with DNA can explain recognition of the AP-1 site by the GCN4 protein. | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
1YSA is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae Saccharomyces cerevisiae]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | 1YSA is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae Saccharomyces cerevisiae]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1YSA OCA]. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category: Saccharomyces cerevisiae]] | [[Category: Saccharomyces cerevisiae]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
[[Category: Brandl, C | [[Category: Brandl, C J.]] | ||
[[Category: Ellenberger, T | [[Category: Ellenberger, T E.]] | ||
[[Category: Harrison, S | [[Category: Harrison, S C.]] | ||
[[Category: Struhl, K.]] | [[Category: Struhl, K.]] | ||
[[Category: double helix]] | [[Category: double helix]] | ||
[[Category: protein-dna complex]] | [[Category: protein-dna complex]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http:// | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 16:08:33 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 17:08, 21 February 2008
|
THE GCN4 BASIC REGION LEUCINE ZIPPER BINDS DNA AS A DIMER OF UNINTERRUPTED ALPHA HELICES: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX
OverviewOverview
The yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 is 1 of over 30 identified eukaryotic proteins containing the basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA-binding motif. We have determined the crystal structure of the GCN4 bZIP element complexed with DNA at 2.9 A resolution. The bZIP dimer is a pair of continuous alpha helices that form a parallel coiled coil over their carboxy-terminal 30 residues and gradually diverge toward their amino termini to pass through the major groove of the DNA-binding site. The coiled-coil dimerization interface is oriented almost perpendicular to the DNA axis, giving the complex the appearance of the letter T. There are no kinks or sharp bends in either bZIP monomer. Numerous contacts to DNA bases and phosphate oxygens are made by basic region residues that are conserved in the bZIP protein family. The details of the bZIP dimer interaction with DNA can explain recognition of the AP-1 site by the GCN4 protein.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1YSA is a Single protein structure of sequence from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex., Ellenberger TE, Brandl CJ, Struhl K, Harrison SC, Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223-37. PMID:1473154
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 16:08:33 2008