Prion protein: Difference between revisions
Kurt Giles (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kurt Giles (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
There are a number of technical obstacles in determining the molecular structure of PrP(sup)Sc</sup> | There are a number of technical obstacles in determining the molecular structure of PrP(sup)Sc</sup> | ||
<ref>10</ref> | |||
=Genetic prion diseases= | =Genetic prion diseases= | ||
| Line 24: | Line 26: | ||
All structures determined by NMR unless otherwise specified | All structures determined by NMR unless otherwise specified | ||
==Human PrP== | ==Human PrP== | ||
* [[ | * [[1qlx]] HuPrP residues 23-230 | ||
* [[ | * [[1qm0]] HuPrP residues 90-230 | ||
* [[ | * [[1qm2]] HuPrP residues 121-230 | ||
* [[ | * [[1i4m]] HuPrP residues 119-226 (determined by X-ray crystallography) | ||
* [[ | * [[1fkc]] HuPrP,E200K residues 90-231 (genetic prion disease) | ||
* [[ | * [[1h0l]] HuPrP residues 121-230, with an additional disulphide bond analogous to the homolog [[Doppel]] | ||
==Other species PrPs== | ==Other species PrPs== | ||
* | * [[1xyx]] Mouse PrP residues | ||
* [[ | * [[1b10]] Syrian hamster PrP residues 90-231 | ||
* [[ | * [[1dwy]] Cow PrP residues 121-230 | ||
* [[ | * [[1uw3]] Sheep PrP (determined by X-ray crystallography) | ||
* | * [[1xu0]] Frog PrP residues 98-226 | ||
* | * [[1u3m]] Chicken PrP | ||
* | * [[1u5l]] Turtle PrP residues 121-226 | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
{{Reflist}} <references/> | {{Reflist}} | ||
Zahn, R. ''et al.'' (2000) NMR solution structure of the human prion protein ''Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA'' '''97''', 145-150 | |||
Zahn R. et al. (2003) NMR structure of a variant human prion protein with two disulfide bridges'' J. Mol. Biol.'' '''326''', 225-34. | |||
<references/> | |||
Revision as of 15:18, 14 December 2008
The prion protein (PrP) is a cell surface glycoprotein. PrP can exist in two alternatively folded confirmations: the cellular isoform (PrPC) can undergo a structural conversion to a 'scrapie' or disease associated isoform termed PrPSc. Prion diseases such as Creutzfeldt Jakob disease (CJD) in people, and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) commonly known as "mad cow" disease, are characterterized by aggregates of PrPSc, which arise from autocatalytic refolding of PrPC in a template-dependent manner.
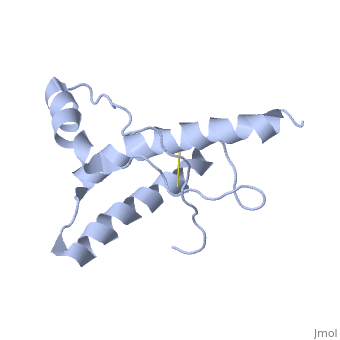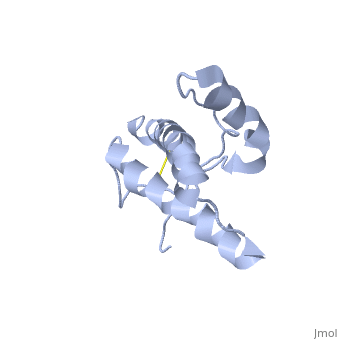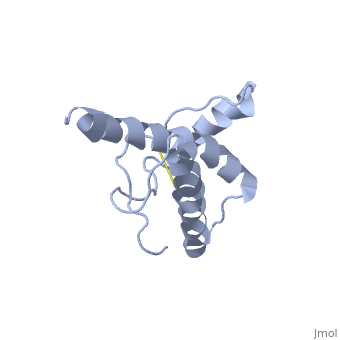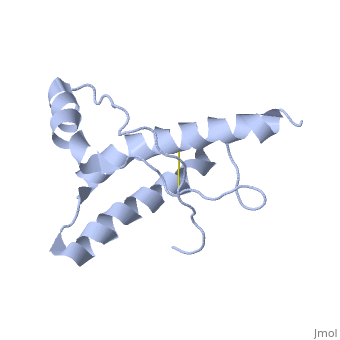
Structure of PrPCStructure of PrPC
| |||||||||
| 1hjm, 1 NMR models () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Related: | 1e1g, 1e1j, 1e1p, 1e1s, 1e1u, 1e1w, 1hjn | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
PrPC has a natively unstructured N-terminal region, and a predominantly α-helical C-terminal region from residues ~120-230, with a single disulfide bond. The presence of the N-terminus has little impact on the structure of the C-terminal domain [1].
The structure is highly conserved amongst mammals, and only differs slightly in birds, reptiles and amphibians.
ALthough having a similar overall fold, the X-ray structure of sheep PrP was dimeric
Models of PrPSc structureModels of PrPSc structure
Circular dichroism studies first demonstrated that PrPSc had very different proportions of α-helices and β-sheet to PrPC
There are a number of technical obstacles in determining the molecular structure of PrP(sup)Sc
Genetic prion diseasesGenetic prion diseases
A number of mutations in PrP have been identified which correlate with a high incidence of prion disease. The structure of HuPrP,E200K was determined nd shown to be To date, structural studies of all mutant PrPC have extremely similar structures to wild type PrPC, suggesting a kinetic basis for the difference in converting to PrPSc.
Prion strainsPrion strains
The strain phenomenon of prions ( ) was initially difficult to equate with the
Selected PrP structuresSelected PrP structures
All structures determined by NMR unless otherwise specified
Human PrPHuman PrP
- 1qlx HuPrP residues 23-230
- 1qm0 HuPrP residues 90-230
- 1qm2 HuPrP residues 121-230
- 1i4m HuPrP residues 119-226 (determined by X-ray crystallography)
- 1fkc HuPrP,E200K residues 90-231 (genetic prion disease)
- 1h0l HuPrP residues 121-230, with an additional disulphide bond analogous to the homolog Doppel
Other species PrPsOther species PrPs
- 1xyx Mouse PrP residues
- 1b10 Syrian hamster PrP residues 90-231
- 1dwy Cow PrP residues 121-230
- 1uw3 Sheep PrP (determined by X-ray crystallography)
- 1xu0 Frog PrP residues 98-226
- 1u3m Chicken PrP
- 1u5l Turtle PrP residues 121-226
ReferencesReferences
Zahn, R. et al. (2000) NMR solution structure of the human prion protein Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 145-150 Zahn R. et al. (2003) NMR structure of a variant human prion protein with two disulfide bridges J. Mol. Biol. 326, 225-34.