6pax: Difference between revisions
New page: left|200px<br /> <applet load="6pax" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="6pax, resolution 2.50Å" /> '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE O... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:6pax.gif|left|200px]]<br /> | [[Image:6pax.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="6pax" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" | ||
<applet load="6pax" size=" | |||
caption="6pax, resolution 2.50Å" /> | caption="6pax, resolution 2.50Å" /> | ||
'''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN PAX-6 PAIRED DOMAIN-DNA COMPLEX REVEALS A GENERAL MODEL FOR PAX PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTIONS'''<br /> | '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN PAX-6 PAIRED DOMAIN-DNA COMPLEX REVEALS A GENERAL MODEL FOR PAX PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTIONS'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
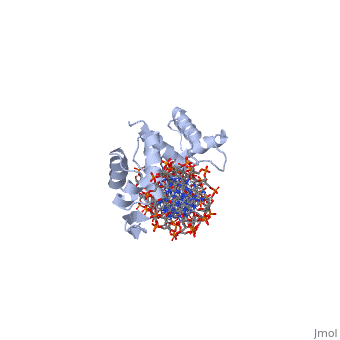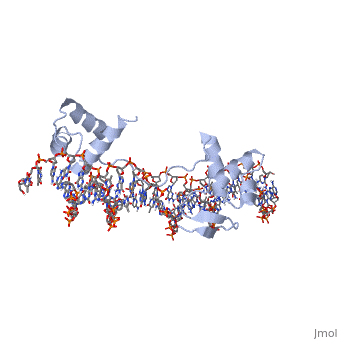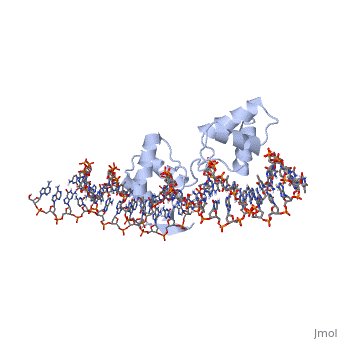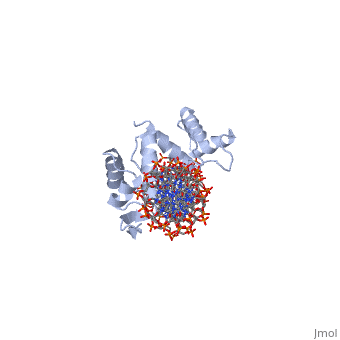
Pax6, a transcription factor containing the bipartite paired DNA-binding | Pax6, a transcription factor containing the bipartite paired DNA-binding domain, has critical roles in development of the eye, nose, pancreas, and central nervous system. The 2.5 A structure of the human Pax6 paired domain with its optimal 26-bp site reveals extensive DNA contacts from the amino-terminal subdomain, the linker region, and the carboxy-terminal subdomain. The Pax6 structure not only confirms the docking arrangement of the amino-terminal subdomain as seen in cocrystals of the Drosophila Prd Pax protein, but also reveals some interesting differences in this region and helps explain the sequence specificity of paired domain-DNA recognition. In addition, this structure gives the first detailed information about how the paired linker region and carboxy-terminal subdomain contact DNA. The extended linker makes minor groove contacts over an 8-bp region, and the carboxy-terminal helix-turn-helix unit makes base contacts in the major groove. The structure and docking arrangement of the carboxy-terminal subdomain of Pax6 is remarkably similar to that of the amino-terminal subdomain, and there is an approximate twofold symmetry axis relating the polypeptide backbones of these two helix-turn-helix units. Our structure of the Pax6 paired domain-DNA complex provides a framework for understanding paired domain-DNA interactions, for analyzing mutations that map in the linker and carboxy-terminal regions of the paired domain, and for modeling protein-protein interactions of the Pax family proteins. | ||
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
6PAX is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | 6PAX is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=6PAX OCA]. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
[[Category: Epstein, J | [[Category: Epstein, J A.]] | ||
[[Category: Maas, R | [[Category: Maas, R L.]] | ||
[[Category: Pabo, C | [[Category: Pabo, C O.]] | ||
[[Category: Rould, M | [[Category: Rould, M A.]] | ||
[[Category: Xu, H | [[Category: Xu, H E.]] | ||
[[Category: Xu, W.]] | [[Category: Xu, W.]] | ||
[[Category: paired domain]] | [[Category: paired domain]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category: transcription]] | [[Category: transcription]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http:// | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 19:16:40 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 21 February 2008
|
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN PAX-6 PAIRED DOMAIN-DNA COMPLEX REVEALS A GENERAL MODEL FOR PAX PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTIONS
OverviewOverview
Pax6, a transcription factor containing the bipartite paired DNA-binding domain, has critical roles in development of the eye, nose, pancreas, and central nervous system. The 2.5 A structure of the human Pax6 paired domain with its optimal 26-bp site reveals extensive DNA contacts from the amino-terminal subdomain, the linker region, and the carboxy-terminal subdomain. The Pax6 structure not only confirms the docking arrangement of the amino-terminal subdomain as seen in cocrystals of the Drosophila Prd Pax protein, but also reveals some interesting differences in this region and helps explain the sequence specificity of paired domain-DNA recognition. In addition, this structure gives the first detailed information about how the paired linker region and carboxy-terminal subdomain contact DNA. The extended linker makes minor groove contacts over an 8-bp region, and the carboxy-terminal helix-turn-helix unit makes base contacts in the major groove. The structure and docking arrangement of the carboxy-terminal subdomain of Pax6 is remarkably similar to that of the amino-terminal subdomain, and there is an approximate twofold symmetry axis relating the polypeptide backbones of these two helix-turn-helix units. Our structure of the Pax6 paired domain-DNA complex provides a framework for understanding paired domain-DNA interactions, for analyzing mutations that map in the linker and carboxy-terminal regions of the paired domain, and for modeling protein-protein interactions of the Pax family proteins.
DiseaseDisease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Aniridia, type II OMIM:[607108], Cataract, congenital, with late-onset corneal dystrophy OMIM:[607108], Coloboma, ocular OMIM:[607108], Ectopia pupillae OMIM:[607108], Eye anomalies, multiplex OMIM:[607108], Foveal hypoplasia, isolated OMIM:[607108], Keratitis OMIM:[607108], Morning glory disc anomaly OMIM:[607108], Optic nerve hypoplasia/aplasia OMIM:[607108], Peters anomaly OMIM:[607108]
About this StructureAbout this Structure
6PAX is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Crystal structure of the human Pax6 paired domain-DNA complex reveals specific roles for the linker region and carboxy-terminal subdomain in DNA binding., Xu HE, Rould MA, Xu W, Epstein JA, Maas RL, Pabo CO, Genes Dev. 1999 May 15;13(10):1263-75. PMID:10346815
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 19:16:40 2008