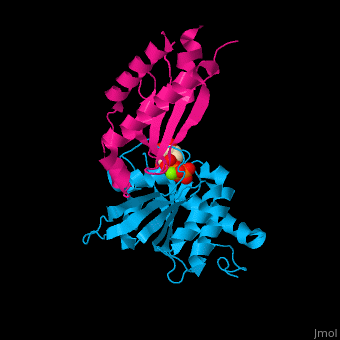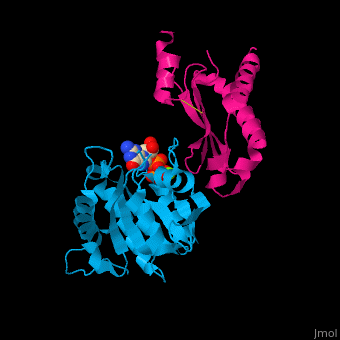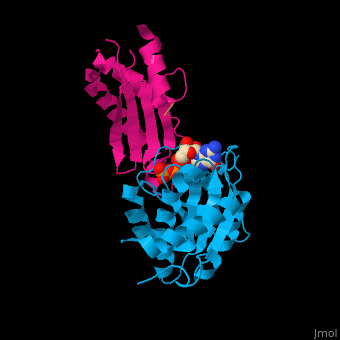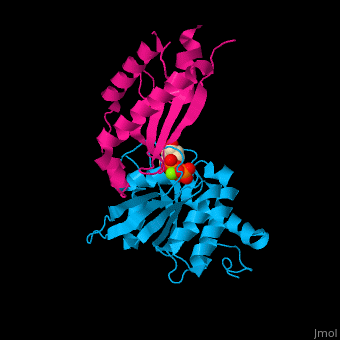|
|
| Line 24: |
Line 24: |
| **[[1zu5]], [[1zu4]] – SRPR FtsY NG domain – ''Mycoplasma mycoides''<br /> | | **[[1zu5]], [[1zu4]] – SRPR FtsY NG domain – ''Mycoplasma mycoides''<br /> |
| **[[1vma]] – SRPR FtsY – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | | **[[1vma]] – SRPR FtsY – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> |
| **[[6cy]] – EaSRPR FtsY – ''Elizabethkingia anopheles''<br /> | | **[[6cy1]] – EaSRPR FtsY – ''Elizabethkingia anopheles''<br /> |
| **[[6cy5]] – EaSRPR FtsY NG domain + GDP<br /> | | **[[6cy5]] – EaSRPR FtsY NG domain + GDP<br /> |
| **[[2q9a]] – TaSRPR FtsY – ''Thermus aquaticus''<br /> | | **[[2q9a]] – TaSRPR FtsY – ''Thermus aquaticus''<br /> |
Revision as of 21:15, 20 September 2018
Signal recognition particle receptor (SRPR) is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. SRPR is a receptor for the signal recognition particle (SRP). SRPR is a heterodimer with α and β subunits which contain a GTP-binding domain. SRPR α subunit binds to SRP54 subunit of SRP complex. SRPR β subunit is a transmembrane GTPase. The bacterial SRPR is called FtsY.
- . Water molecules shown as red spheres.
- .
| |
3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor
Updated on 20-September-2018
{"openlevels":0}
- Signal recognition particle receptor
- 1nrj – ySRPR α+β subunits + GTP – yeast
- 2fh5 - hSRPR α+β subunits + GTP – human
- 5l3q - hSRPR α subunit + SRP54 + AMP + GNP
- 2ged - ySRPR β subunit (mutant)
- 2go5 - hSRPR α subunit + mSRPR β subunit + ribosomal proteins L23, L31, L35 + dSRP19 + dSRP54 + RNA - EM
- 3dm9, 3dmd, 3e70 – SRPR + GDP – Pyrococcus furiosus
- Signal recognition particle receptor FtsY
- 1zu5, 1zu4 – SRPR FtsY NG domain – Mycoplasma mycoides
- 1vma – SRPR FtsY – Thermotoga maritima
- 6cy1 – EaSRPR FtsY – Elizabethkingia anopheles
- 6cy5 – EaSRPR FtsY NG domain + GDP
- 2q9a – TaSRPR FtsY – Thermus aquaticus
- 2q9c, 2q9b – TaSRPR FtsY NG domain + GMPPNP
- 2yhs, 2qy9, 1fts, 6cqp – EcSRPR FtsY NG domain – Escherichia coli
- 6fqd – EcSRPR FtsY NG domain + GDP
- 6c58, 6cvd, 6dlx – EcSRPR FtsY NG domain + antibiotic
- 2iyl – EcSRPR FtsY residues 20-303 + GDP
- 2xxa - EcSRPR FtsY NG domain + signal recognition particle protein residues 1-433 (mutant) + 4.5SRNA
- 3zn8 - EcSRPR FtsY NG domain + signal recognition particle protein 54 NG domain + 4.5SRNA + dipeptidyl aminopeptidase B
- 2j7p, 1rj9, 1okk – TaSRPR FtsY NG domain + signal recognition particle protein – Thermus aquaticus
- 2cnw – TaSRPR FtsY NG domain + signal recognition particle protein + GDP
- 4c7o – EcFtsY + EcSRP + SRP RNA
- 2xkv – EcFtsY + EcSRP NG+M domains + 4.5S RNA
- 5aka, 5gad, 5nco, 5gaf, 5gag, 5gah – EcFtsY in ribosome - Cryo EM
- 3jaj, 3jan – FtsY in ribosome - rabbit - Cryo EM
- 5l3r – SRPR FtsY + SRP54 - Arabidopsis thaliana
- 5l3w – SRPR FtsY NG domain - Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
- 5l3s – SRPR FtsY + SRP54 + GNP - Sulfolobus solfataricus