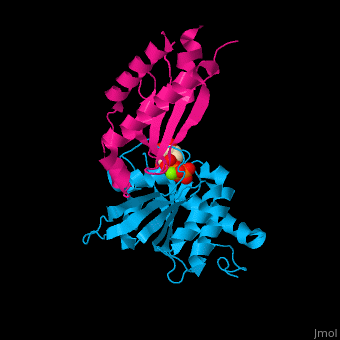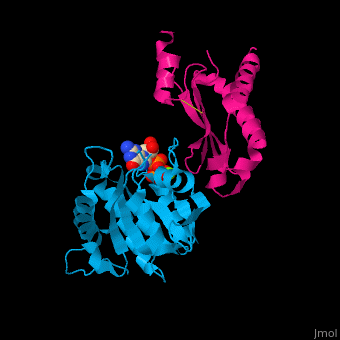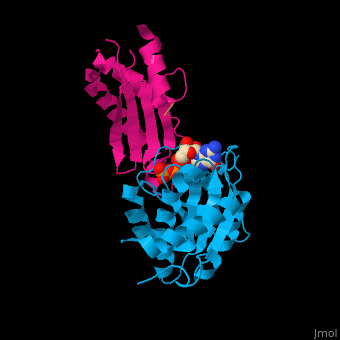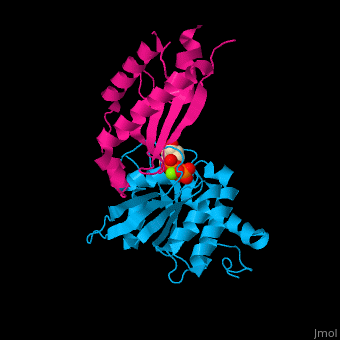Signal recognition particle receptor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
*<scene name='48/485587/Cv/4'>GTP binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | *<scene name='48/485587/Cv/4'>GTP binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
*<scene name='48/485587/Cv/5'>Mg coordination site</scene>. | *<scene name='48/485587/Cv/5'>Mg coordination site</scene>. | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
==3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor== | ==3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor== | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 10 July 2018
|
Signal recognition particle receptor (SRPR) is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. SRPR is a receptor for the signal recognition particle (SRP). SRPR is a heterodimer with α and β subunits which contain a GTP-binding domain. SRPR α subunit binds to SRP54 subunit of SRP complex. SRPR β subunit is a transmembrane GTPase. The bacterial SRPR is called FtsY.
- . Water molecules shown as red spheres.
- .
</StructureSection>
3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor3D structures of signal recognition particle receptor
Updated on 10-July-2018