1mwp: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:1mwp.jpg|left|200px]] | [[Image:1mwp.jpg|left|200px]] | ||
<!-- | |||
The line below this paragraph, containing "STRUCTURE_1mwp", creates the "Structure Box" on the page. | |||
You may change the PDB parameter (which sets the PDB file loaded into the applet) | |||
| | or the SCENE parameter (which sets the initial scene displayed when the page is loaded), | ||
| | or leave the SCENE parameter empty for the default display. | ||
--> | |||
{{STRUCTURE_1mwp| PDB=1mwp | SCENE= }} | |||
}} | |||
'''N-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF THE AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN''' | '''N-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF THE AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN''' | ||
| Line 37: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category: Parker, M W.]] | [[Category: Parker, M W.]] | ||
[[Category: Rossjohn, J.]] | [[Category: Rossjohn, J.]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Heparin binding]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sat May 3 01:48:42 2008'' | |||
''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | |||
Revision as of 01:48, 3 May 2008
| |||||||||
| 1mwp, resolution 1.80Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
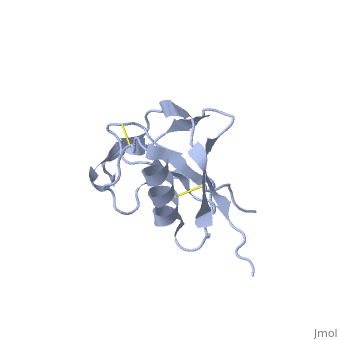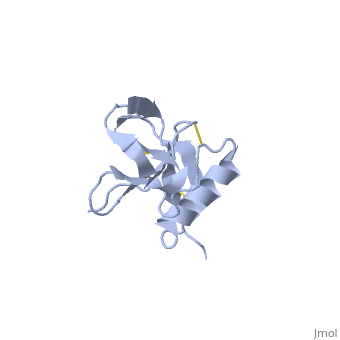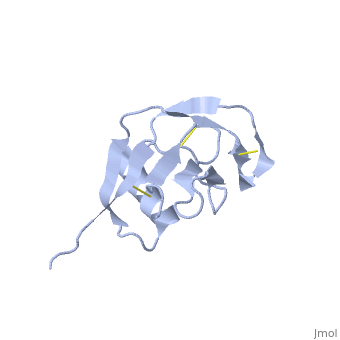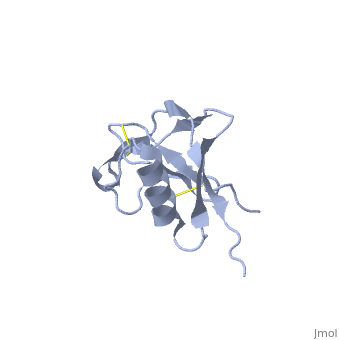
N-TERMINAL DOMAIN OF THE AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN
OverviewOverview
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) plays a central role in Alzheimer disease. A proteolytic-breakdown product of APP, called beta-amyloid, is a major component of the diffuse and fibrillar deposits found in Alzheimer diseased brains. The normal physiological role of APP remains largely unknown despite much work. A knowledge of its function will not only provide insights into the genesis of the disease but may also prove vital in the development of an effective therapy. Here we describe the 1.8 A resolution crystal structure of the N-terminal, heparin-binding domain of APP (residues 28-123), which is responsible, among other things, for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. The structure reveals a highly charged basic surface that may interact with glycosaminoglycans in the brain and an abutting hydrophobic surface that is proposed to play an important functional role such as dimerization or ligand binding. Structural similarities with cysteine-rich growth factors, taken together with its known growth-promoting properties, suggests the APP N-terminal domain could function as a growth factor in vivo.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1MWP is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. The following page contains interesting information on the relation of 1MWP with [Amyloid-beta Precursor Protein]. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Crystal structure of the N-terminal, growth factor-like domain of Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein., Rossjohn J, Cappai R, Feil SC, Henry A, McKinstry WJ, Galatis D, Hesse L, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Parker MW, Nat Struct Biol. 1999 Apr;6(4):327-31. PMID:10201399 Page seeded by OCA on Sat May 3 01:48:42 2008