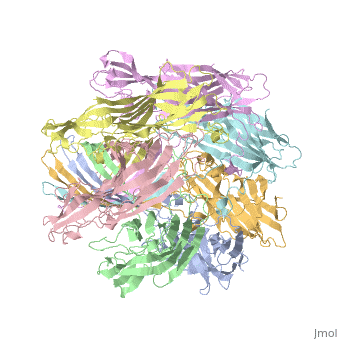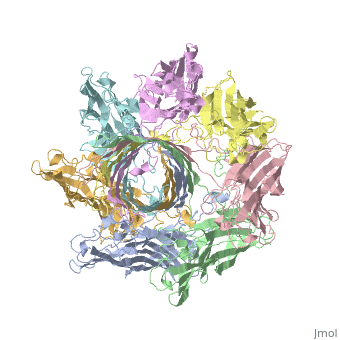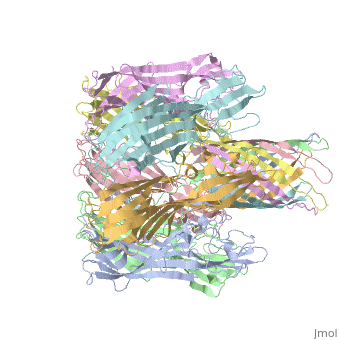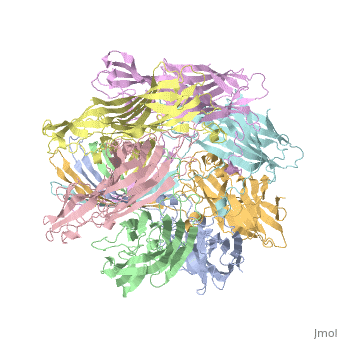7ahl: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[7ahl]] is a 7 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus Staphylococcus aureus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=7AHL OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=7AHL FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[7ahl]] is a 7 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus Staphylococcus aureus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=7AHL OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=7AHL FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=7ahl FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=7ahl OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=7ahl RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/7ahl PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=7ahl FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=7ahl OCA], [http://pdbe.org/7ahl PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=7ahl RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/7ahl PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
</jmolCheckbox> | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/ | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=7ahl ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pdbe-citations 7ahl" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Hemolysin|Hemolysin]] | *[[Hemolysin|Hemolysin]] | ||
*[[Pore forming toxin%2C ñ-hemolysin|Pore forming toxin%2C ñ-hemolysin]] | *[[Pore forming toxin%2C ñ-hemolysin|Pore forming toxin%2C ñ-hemolysin]] | ||
*[[Practical Guide to Homology Modeling|Practical Guide to Homology Modeling]] | |||
*[[User:Eric Martz/JSmol Notes|User:Eric Martz/JSmol Notes]] | *[[User:Eric Martz/JSmol Notes|User:Eric Martz/JSmol Notes]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 04:28, 7 February 2016
ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUSALPHA-HEMOLYSIN FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
Structural highlights
Function[HLA_STAAU] Alpha-toxin binds to the membrane of eukaryotic cells resulting in the release of low-molecular weight molecules and leading to an eventual osmotic lysis. Heptamer oligomerization and pore formation is required for lytic activity. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe structure of the Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin pore has been determined to 1.9 A resolution. Contained within the mushroom-shaped homo-oligomeric heptamer is a solvent-filled channel, 100 A in length, that runs along the sevenfold axis and ranges from 14 A to 46 A in diameter. The lytic, transmembrane domain comprises the lower half of a 14-strand antiparallel beta barrel, to which each protomer contributes two beta strands, each 65 A long. The interior of the beta barrel is primarily hydrophilic, and the exterior has a hydrophobic belt 28 A wide. The structure proves the heptameric subunit stoichiometry of the alpha-hemolysin oligomer, shows that a glycine-rich and solvent-exposed region of a water-soluble protein can self-assemble to form a transmembrane pore of defined structure, and provides insight into the principles of membrane interaction and transport activity of beta barrel pore-forming toxins. Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore.,Song L, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE Science. 1996 Dec 13;274(5294):1859-66. PMID:8943190[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See Also
References |
| ||||||||||||||