1ilr: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= | |GENE= | ||
|DOMAIN= | |||
|RELATEDENTRY= | |||
|RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1ilr FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1ilr OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1ilr PDBsum], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1ilr RCSB]</span> | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
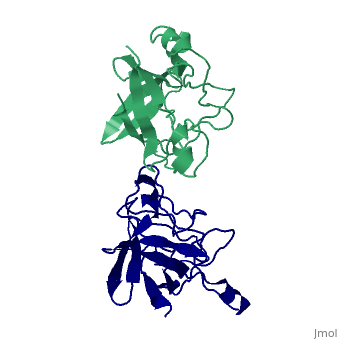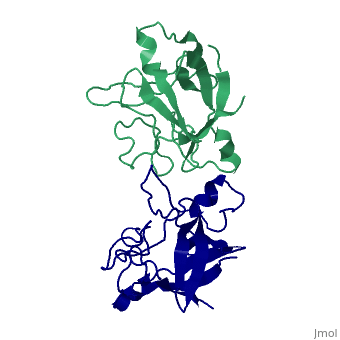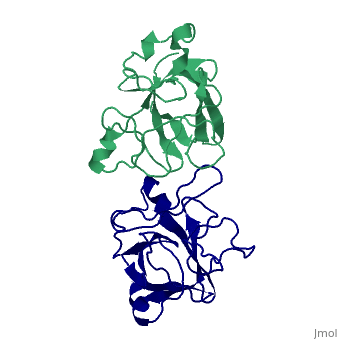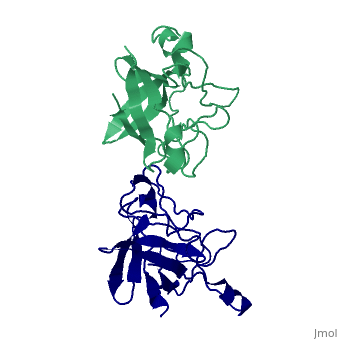
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) molecules are cytokines involved in the acute-phase response against infection and injury. Three naturally occurring IL-1 molecules are known, two agonists: IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, and one antagonist, the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Although IL-1 action protects the organism by enhancing the response to pathogens, its overproduction can lead to pathology and has been implicated in disease states that include septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, graft versus host disease and certain leukemias. The crystal structure of IL-1ra has been solved at 0.21-nm resolution by molecular replacement using the IL-1 beta structure as a search model. The crystals contain two independent IL-1ra molecules which are very similar. IL-1ra has the same fold as IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. The fold consists of twelve beta-strands which form a six-stranded beta-barrel, closed on one side by three beta-hairpin loops. Cys69 and Cys116 are linked via a disulfide bond and Pro53 has been built in the cis-conformation. Comparison of the IL-1ra structure with the IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta structures present in the Protein Data Bank shows that a putative receptor interaction region, involving the N-terminus up to the beginning of strand beta 1 and the loops D and G, is very different in the three IL-1 molecules. Other putative interaction regions, as identified with mutagenesis studies, are structurally conserved and rigid, allowing precise and specific interactions with the IL-1 receptor. | Interleukin-1 (IL-1) molecules are cytokines involved in the acute-phase response against infection and injury. Three naturally occurring IL-1 molecules are known, two agonists: IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, and one antagonist, the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Although IL-1 action protects the organism by enhancing the response to pathogens, its overproduction can lead to pathology and has been implicated in disease states that include septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, graft versus host disease and certain leukemias. The crystal structure of IL-1ra has been solved at 0.21-nm resolution by molecular replacement using the IL-1 beta structure as a search model. The crystals contain two independent IL-1ra molecules which are very similar. IL-1ra has the same fold as IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. The fold consists of twelve beta-strands which form a six-stranded beta-barrel, closed on one side by three beta-hairpin loops. Cys69 and Cys116 are linked via a disulfide bond and Pro53 has been built in the cis-conformation. Comparison of the IL-1ra structure with the IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta structures present in the Protein Data Bank shows that a putative receptor interaction region, involving the N-terminus up to the beginning of strand beta 1 and the loops D and G, is very different in the three IL-1 molecules. Other putative interaction regions, as identified with mutagenesis studies, are structurally conserved and rigid, allowing precise and specific interactions with the IL-1 receptor. | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Category: binding protein]] | [[Category: binding protein]] | ||
''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar 30 21:21:28 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 21:21, 30 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 2.1Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE INTERLEUKIN-1 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST
OverviewOverview
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) molecules are cytokines involved in the acute-phase response against infection and injury. Three naturally occurring IL-1 molecules are known, two agonists: IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, and one antagonist, the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Although IL-1 action protects the organism by enhancing the response to pathogens, its overproduction can lead to pathology and has been implicated in disease states that include septic shock, rheumatoid arthritis, graft versus host disease and certain leukemias. The crystal structure of IL-1ra has been solved at 0.21-nm resolution by molecular replacement using the IL-1 beta structure as a search model. The crystals contain two independent IL-1ra molecules which are very similar. IL-1ra has the same fold as IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. The fold consists of twelve beta-strands which form a six-stranded beta-barrel, closed on one side by three beta-hairpin loops. Cys69 and Cys116 are linked via a disulfide bond and Pro53 has been built in the cis-conformation. Comparison of the IL-1ra structure with the IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta structures present in the Protein Data Bank shows that a putative receptor interaction region, involving the N-terminus up to the beginning of strand beta 1 and the loops D and G, is very different in the three IL-1 molecules. Other putative interaction regions, as identified with mutagenesis studies, are structurally conserved and rigid, allowing precise and specific interactions with the IL-1 receptor.
About this StructureAbout this Structure
1ILR is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
ReferenceReference
Refined crystal structure of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Presence of a disulfide link and a cis-proline., Schreuder HA, Rondeau JM, Tardif C, Soffientini A, Sarubbi E, Akeson A, Bowlin TL, Yanofsky S, Barrett RW, Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 1;227(3):838-47. PMID:7867645
Page seeded by OCA on Sun Mar 30 21:21:28 2008