Antibody: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab) is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab. | Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab) is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab. | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | |||
*Fab | |||
[[7fab]], [[1mco]], [[3na9]], [[3lrs]], [[3mme]], [[3hi5]], [[1vge]], [[3nfs]], [[1ad0]], [[3w9d]], [[4nm4]], [[8fab]], [[1opg]], [[4fnl]], [[4fqh]], [[1om3]], [[1aqk]], [[2hff]], [[2agj]], [[3hc0]], [[3g6a]], [[3dgg]], [[3dif]], [[1b2w]], [[3eyo]], [[3eyq]], [[2aj3]], [[3fzu]], [[3aaz]], [[3gje]] - hFab - human<br /> | **[[7fab]], [[1mco]], [[3na9]], [[3lrs]], [[3mme]], [[3hi5]], [[1vge]], [[3nfs]], [[1ad0]], [[3w9d]], [[4nm4]], [[8fab]], [[1opg]], [[4fnl]], [[4fqh]], [[1om3]], [[1aqk]], [[2hff]], [[2agj]], [[3hc0]], [[3g6a]], [[3dgg]], [[3dif]], [[1b2w]], [[3eyo]], [[3eyq]], [[2aj3]], [[3fzu]], [[3aaz]], [[3gje]] - hFab - human<br /> | ||
[[3naa]], [[3nab]], [[3nac]], [[3ncj]], [[3o2v]], [[3hc3]], [[3hc4]] - hFab (mutant)<br /> | **[[3naa]], [[3nab]], [[3nac]], [[3ncj]], [[3o2v]], [[3hc3]], [[3hc4]] - hFab (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[3i75]], [[1nqb]], [[1f4w]], [[1aif]], [[1ghf]], [[2z91]], [[1ind]], [[3bkc]], [[3bkm]], [[1iy0]], [[3pp3]], [[3pp4]], [[3okm]], [[6fab]], 2hkh]], [[1ay1]], [[1nbv]], [[1qbm]], [[1bbd]], [[1dsf]], [[1gpo]], [[1mnu]], [[1igf]], [[1for]], [[1k6q]], [[1bz7]], [[1dqd]], [[2ipt]], [[2iq9]], [[2iqa]], [[2w60]], [[2w9d]], [[3iu4]], [[1q9k]], [[1q9l]], [[1q9o]], [[2z4q]], [[1cl7]], [[1n4x]], [[1cr9]], [[1r24]], [[1gig]], [[1uyw]], [[1cgs]], [[2cgr]], [[1q0x]], [[1ibg]], [[3eo0]], [[2op4]], [[2q76]], [[2ojz]], [[2g60]], [[2dbl]], [[1dbj]], [[1dbk]], [[1dbm]], [[1dba]], [[1mrc]], [[2gcy]], [[1flr]], [[1uz6]], [[1rfd]], [[1t2q]], [[1ggb]], [[1ggc]], [[1bm3]], [[2eh7]], [[2fat]], [[3cfc]], [[1fl3]], [[3cfe]], [[4j1u]], [[4gq9]], [[3qg7]], [[3rvt]], [[3s62]], [[4gay]] - mFab – mouse<br /> | **[[3i75]], [[1nqb]], [[1f4w]], [[1aif]], [[1ghf]], [[2z91]], [[1ind]], [[3bkc]], [[3bkm]], [[1iy0]], [[3pp3]], [[3pp4]], [[3okm]], [[6fab]], 2hkh]], [[1ay1]], [[1nbv]], [[1qbm]], [[1bbd]], [[1dsf]], [[1gpo]], [[1mnu]], [[1igf]], [[1for]], [[1k6q]], [[1bz7]], [[1dqd]], [[2ipt]], [[2iq9]], [[2iqa]], [[2w60]], [[2w9d]], [[3iu4]], [[1q9k]], [[1q9l]], [[1q9o]], [[2z4q]], [[1cl7]], [[1n4x]], [[1cr9]], [[1r24]], [[1gig]], [[1uyw]], [[1cgs]], [[2cgr]], [[1q0x]], [[1ibg]], [[3eo0]], [[2op4]], [[2q76]], [[2ojz]], [[2g60]], [[2dbl]], [[1dbj]], [[1dbk]], [[1dbm]], [[1dba]], [[1mrc]], [[2gcy]], [[1flr]], [[1uz6]], [[1rfd]], [[1t2q]], [[1ggb]], [[1ggc]], [[1bm3]], [[2eh7]], [[2fat]], [[3cfc]], [[1fl3]], [[3cfe]], [[4j1u]], [[4gq9]], [[3qg7]], [[3rvt]], [[3s62]], [[4gay]] - mFab – mouse<br /> | ||
[[3eot]], [[2d03]], [[3esv]], [[3et9]] – mFab (mutant)<br /> | **[[3eot]], [[2d03]], [[3esv]], [[3et9]] – mFab (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[3iy2]], [[3iy3]], [[3iy4]], [[3iy5]], [[3iy6]], [[3iy7]] - mFab – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[3iy2]], [[3iy3]], [[3iy4]], [[3iy5]], [[3iy6]], [[3iy7]] - mFab – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
[[1jpt]], [[3mxv]], [[2o5x]], [[1ucb]], [[1bbj]], [[1t04]], [[2fgw]], [[1fvd]], [[1fve]] - hmFab <br /> | **[[1jpt]], [[3mxv]], [[2o5x]], [[1ucb]], [[1bbj]], [[1t04]], [[2fgw]], [[1fvd]], [[1fve]] - hmFab <br /> | ||
[[1cqk]] – mFab MAK33 CH3 domain<br /> | **[[1cqk]] – mFab MAK33 CH3 domain<br /> | ||
[[3mj8]], [[3r06]] – AhFab – Armenian hamster<br /> | **[[3mj8]], [[3r06]] – AhFab – Armenian hamster<br /> | ||
[[3iy1]], [[1zan]] – rFab – rat<br /> | **[[3iy1]], [[1zan]] – rFab – rat<br /> | ||
[[4k3e]], [[4k3d]] – bFab – bovine<br /> | **[[4k3e]], [[4k3d]] – bFab – bovine<br /> | ||
[[4b41]], [[1shm]], [[2xa3]] – LgFab – ''Lama glama''<br /> | **[[4b41]], [[1shm]], [[2xa3]] – LgFab – ''Lama glama''<br /> | ||
[[1f2x]] – cFab – camel<br /> | **[[1f2x]] – cFab – camel<br /> | ||
*Anti-HIV Fab | |||
[[1rz7]], [[1rz8]], [[1rzf]], [[1rzg]], [[1rzi]], [[3mlj]], [[3mug]], [[3juy]], [[3qeh]], [[3ttn]], [[rpi]], [[3tnm]], [[4fz8]], [[4f58]], [[4f57]], [[4f5a]] - hFab <br /> | **[[1rz7]], [[1rz8]], [[1rzf]], [[1rzg]], [[1rzi]], [[3mlj]], [[3mug]], [[3juy]], [[3qeh]], [[3ttn]], [[rpi]], [[3tnm]], [[4fz8]], [[4f58]], [[4f57]], [[4f5a]] - hFab <br /> | ||
[[3nz8]], [[3o6k]], [[3ntc]], [[3qeg]] – mFab <br /> | **[[3nz8]], [[3o6k]], [[3ntc]], [[3qeg]] – mFab <br /> | ||
*Fab: small molecule complex | |||
[[3o2w]] - hFab 1e9 (mutant) + transition state analog<br /> | **[[3o2w]] - hFab 1e9 (mutant) + transition state analog<br /> | ||
[[3ra7]] – mFab + digoxigenin – mouse<br /> | **[[3ra7]] – mFab + digoxigenin – mouse<br /> | ||
[[3okd]], [[3oke]], [[3okk]], [[3okl]], [[3okn]], [[3oko]], [[3hzk]], [[3hzm]], [[3hzv]], [[3hzy]], [[3pho]], [[3phq]], [[3hns]], [[3hnt]], [[3hnv]] - mFab + liposaccharide<br /> | **[[3okd]], [[3oke]], [[3okk]], [[3okl]], [[3okn]], [[3oko]], [[3hzk]], [[3hzm]], [[3hzv]], [[3hzy]], [[3pho]], [[3phq]], [[3hns]], [[3hnt]], [[3hnv]] - mFab + liposaccharide<br /> | ||
[[3oau]] – hFab 2g12 (mutant) + mannose<br /> | **[[3oau]] – hFab 2g12 (mutant) + mannose<br /> | ||
[[1ikf]] – hFab R45 + cyclosporin<br /> | **[[1ikf]] – hFab R45 + cyclosporin<br /> | ||
[[3oay]], [[3oaz]], [[3ob0]], [[1zls]], [[1zlu]], [[1zlv]], [[1zlw]] - hFab 2g12 + glycan<br /> | **[[3oay]], [[3oaz]], [[3ob0]], [[1zls]], [[1zlu]], [[1zlv]], [[1zlw]] - hFab 2g12 + glycan<br /> | ||
[[2jb5]], [[2jb6]] - hFab/mFab + hapten<br /> | **[[2jb5]], [[2jb6]] - hFab/mFab + hapten<br /> | ||
[[1ine]], [[1ub5]], [[1ub6]] - mFab + hapten<br /> | **[[1ine]], [[1ub5]], [[1ub6]] - mFab + hapten<br /> | ||
[[3ls4]] – mFab + tetrahydrocannabinol<br /> | **[[3ls4]] – mFab + tetrahydrocannabinol<br /> | ||
[[1mfc]], [[1mfd]], [[1mfe]], [[4hgw]] – mFab + polysaccharide<br /> | **[[1mfc]], [[1mfd]], [[1mfe]], [[4hgw]] – mFab + polysaccharide<br /> | ||
[[1op3]], [[1op5]] - hFab + polysaccharide<br /> | **[[1op3]], [[1op5]] - hFab + polysaccharide<br /> | ||
[[3eyv]] - hFab/mFab 13G5 (mutant) + hapten<br /> | **[[3eyv]] - hFab/mFab 13G5 (mutant) + hapten<br /> | ||
[[2ntf]] - mFab RS2-1G9 + lactone analog<br /> | **[[2ntf]] - mFab RS2-1G9 + lactone analog<br /> | ||
[[1riu]], [[1riv]], [[1qyg]], [[1q72]] - mFab + cocaine derivative<br /> | **[[1riu]], [[1riv]], [[1qyg]], [[1q72]] - mFab + cocaine derivative<br /> | ||
[[1ynk]], [[1ynl]], [[1etz]] – mFab + sweetener<br /> | **[[1ynk]], [[1ynl]], [[1etz]] – mFab + sweetener<br /> | ||
[[1yef]] – mFab D2.3 + substrate analog<br /> | **[[1yef]] – mFab D2.3 + substrate analog<br /> | ||
[[1yeg]] - mFab D2.3 + product<br /> | **[[1yeg]] - mFab D2.3 + product<br /> | ||
[[1p7k]] – mFab + HEPES<br /> | **[[1p7k]] – mFab + HEPES<br /> | ||
[[1q0y]] – mFab 9B1 + morphine<br /> | **[[1q0y]] – mFab 9B1 + morphine<br /> | ||
[[1q9q]], [[1q9r]], [[1q9t]], [[1q9v]], [[1q9w]], [[1f4x]], [[1f4y]], [[1mfa]], [[1mfb]] - mFab + carbohydrate<br /> | **[[1q9q]], [[1q9r]], [[1q9t]], [[1q9v]], [[1q9w]], [[1f4x]], [[1f4y]], [[1mfa]], [[1mfb]] - mFab + carbohydrate<br /> | ||
[[1mex]] – mFab 29G12 + benzoic acid derivative<br /> | **[[1mex]] – mFab 29G12 + benzoic acid derivative<br /> | ||
[[1mrd]], [[1mre]], [[1mrf]] – mFab JEL103 + nucleotide<br /> | **[[1mrd]], [[1mre]], [[1mrf]] – mFab JEL103 + nucleotide<br /> | ||
[[1dbb]] – mFab DB3 + progesterone<br /> | **[[1dbb]] – mFab DB3 + progesterone<br /> | ||
[[1igj]] - mFab 26-10 + digoxin<br /> | **[[1igj]] - mFab 26-10 + digoxin<br /> | ||
[[4fab]] – mFab 4-4-20 + fluorescin<br /> | **[[4fab]] – mFab 4-4-20 + fluorescin<br /> | ||
[[1dl7]] - mFab MCPC603 + phosphocholine<br /> | **[[1dl7]] - mFab MCPC603 + phosphocholine<br /> | ||
[[3cfb]], [[3cfd]], [[2g2r]] – mFab + stilbene hapten<br /> | **[[3cfb]], [[3cfd]], [[2g2r]] – mFab + stilbene hapten<br /> | ||
[[1i3u]], [[1i3v]] - LgFab + hapten<br /> | **[[1i3u]], [[1i3v]] - LgFab + hapten<br /> | ||
*Fab: peptide complex | |||
[[3e8u]] - mFab + BNP peptide<br /> | **[[3e8u]] - mFab + BNP peptide<br /> | ||
[[2a6d]], [[2a6i]], [[2a6j]], [[2a6k]] - mFab + peptide<br /> | **[[2a6d]], [[2a6i]], [[2a6j]], [[2a6k]] - mFab + peptide<br /> | ||
[[3hr5]] – mFab + M1prime peptide<br /> | **[[3hr5]] – mFab + M1prime peptide<br /> | ||
[[3eys]], [[3eyu]] - mFab + amyloid-β-related peptide<br /> | **[[3eys]], [[3eyu]] - mFab + amyloid-β-related peptide<br /> | ||
[[3ggw]] – mFab + carbohydrate-mimetic peptide<br /> | **[[3ggw]] – mFab + carbohydrate-mimetic peptide<br /> | ||
[[3cxd]], [[3dsf]] – mFab + osteopontin peptide<br /> | **[[3cxd]], [[3dsf]] – mFab + osteopontin peptide<br /> | ||
[[2zpk]] – mFab + proteinase-activated receptor peptide<br /> | **[[2zpk]] – mFab + proteinase-activated receptor peptide<br /> | ||
[[3ifl]], [[3ifn]], [[3ifo]], [[3ifp]] - mFab + amyloid peptide<br /> | **[[3ifl]], [[3ifn]], [[3ifo]], [[3ifp]] - mFab + amyloid peptide<br /> | ||
[[3h0t]] - hFab + hepcidin peptide<br /> | **[[3h0t]] - hFab + hepcidin peptide<br /> | ||
[[1sm3]] - hFab SM3 + peptide<br /> | **[[1sm3]] - hFab SM3 + peptide<br /> | ||
[[3eyf]] – hFab + cytomegalovirus peptide<br /> | **[[3eyf]] – hFab + cytomegalovirus peptide<br /> | ||
[[2hfg]], [[2h9g]] – hFab + TNF receptor peptide<br /> | **[[2hfg]], [[2h9g]] – hFab + TNF receptor peptide<br /> | ||
[[3csy]] - hFab + Ebola envelope glycoprotein peptide<br /> | **[[3csy]] - hFab + Ebola envelope glycoprotein peptide<br /> | ||
[[2eh8]] - mFab + PRES1 peptide<br /> | **[[2eh8]] - mFab + PRES1 peptide<br /> | ||
[[2brr]] – mFab + outer membrane protein peptide<br /> | **[[2brr]] – mFab + outer membrane protein peptide<br /> | ||
[[1xgy]] – mFab + rhodopsin peptide<br /> | **[[1xgy]] – mFab + rhodopsin peptide<br /> | ||
[[1pz5]] – mFab SYA/J6 + peptide<br /> | **[[1pz5]] – mFab SYA/J6 + peptide<br /> | ||
[[1a3r]] – mFab + rhinovirus capsid peptide<br /> | **[[1a3r]] – mFab + rhinovirus capsid peptide<br /> | ||
[[1cu4]] - mFab + prion protein peptide<br /> | **[[1cu4]] - mFab + prion protein peptide<br /> | ||
[[1fpt]] – mFab + poliovirus peptide<br /> | **[[1fpt]] – mFab + poliovirus peptide<br /> | ||
[[1jp5]] – mFab + HIV-1 protease peptide<br /> | **[[1jp5]] – mFab + HIV-1 protease peptide<br /> | ||
[[1mvu]] – mFab + glycoprotein <br /> | **[[1mvu]] – mFab + glycoprotein <br /> | ||
[[2ap2]] – mFab + glycoprotein peptide + C-myc peptide<br /> | **[[2ap2]] – mFab + glycoprotein peptide + C-myc peptide<br /> | ||
[[2hh0]] – hFab/mFab + prion protein peptide<br /> | **[[2hh0]] – hFab/mFab + prion protein peptide<br /> | ||
[[1frg]], [[1him]], [[1hin]], [[1ifh]] - mFab + hemagglutinin peptide<br /> | **[[1frg]], [[1him]], [[1hin]], [[1ifh]] - mFab + hemagglutinin peptide<br /> | ||
[[1tet]] – mFab + cholera toxin peptide<br /> | **[[1tet]] – mFab + cholera toxin peptide<br /> | ||
[[1i8i]], [[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | **[[1i8i]], [[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | ||
[[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | **[[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | ||
[[1i8i]], [[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | **[[1i8i]], [[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | ||
[[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | **[[1i8k]] – mFab + EGFR peptide<br /> | ||
[[4gag]], [[4gaj]] – mFab + genome polyprotein peptide<br /> | **[[4gag]], [[4gaj]] – mFab + genome polyprotein peptide<br /> | ||
[[3bky]] – hFab/mFab + CD20 peptide<br /> | **[[3bky]] – hFab/mFab + CD20 peptide<br /> | ||
[[4hs8]] – hFab + hepatitis virus peptide <br /> | **[[4hs8]] – hFab + hepatitis virus peptide <br /> | ||
*Anti-HIV Fab: peptide complex | |||
[[3egs]], [[3drt]], [[3drq]], [[3dro]], [[2fx7]], [[2fx8]], [[2fx9]], [[2cmr]], [[1tzg]], [[1tjg]], [[3mnw]], [[3moa]], [[3mob]], [[3mod]], [[1tjh]], [[1tji]], [[1u8h]], [[1u8i]], [[1u8j]], [[1u8k]], [[1u8l]], [[1u8m]], [[1u8n]], [[1u8o]], [[1u8p]], [[1u8q]], [[1u91]], [[1u92]], [[1u93]], [[1u95]], [[2f5b]] - hFab anti-HIV + gp41 peptide<br /> | **[[3egs]], [[3drt]], [[3drq]], [[3dro]], [[2fx7]], [[2fx8]], [[2fx9]], [[2cmr]], [[1tzg]], [[1tjg]], [[3mnw]], [[3moa]], [[3mob]], [[3mod]], [[1tjh]], [[1tji]], [[1u8h]], [[1u8i]], [[1u8j]], [[1u8k]], [[1u8l]], [[1u8m]], [[1u8n]], [[1u8o]], [[1u8p]], [[1u8q]], [[1u91]], [[1u92]], [[1u93]], [[1u95]], [[2f5b]] - hFab anti-HIV + gp41 peptide<br /> | ||
[[3ghb]], [[3ghe]], [[3c2a]] - hFab anti-HIV + envelope glycoprotein peptide<br /> | **[[3ghb]], [[3ghe]], [[3c2a]] - hFab anti-HIV + envelope glycoprotein peptide<br /> | ||
[[3go1]] - hFab anti-HIV + envelope glycoprotein gp160 peptide<br /> | **[[3go1]] - hFab anti-HIV + envelope glycoprotein gp160 peptide<br /> | ||
[[3fn0]], [[2oqj]] - hFab + peptide<br /> | **[[3fn0]], [[2oqj]] - hFab + peptide<br /> | ||
[[2b0s]], [[2b1a]], [[2b1h]], [[3se8]], [[3se9]], [[4jkp]], [[4jpv]], [[4jb9]] - hFab anti-HIV + glycoprotein gp120 peptide<br /> | **[[2b0s]], [[2b1a]], [[2b1h]], [[3se8]], [[3se9]], [[4jkp]], [[4jpv]], [[4jb9]] - hFab anti-HIV + glycoprotein gp120 peptide<br /> | ||
[[1nak]], [[2f58]], [[3f58]], [[1f58]], [[1acy]], [[1qnz]] - mFab anti-HIV + glycoprotein gp120 peptide<br /> | **[[1nak]], [[2f58]], [[3f58]], [[1f58]], [[1acy]], [[1qnz]] - mFab anti-HIV + glycoprotein gp120 peptide<br /> | ||
[[1ai1]], [[1ggi]] – mFab anti-HIV + V3 peptide<br /> | **[[1ai1]], [[1ggi]] – mFab anti-HIV + V3 peptide<br /> | ||
[[3o6l]], [[3o6m]] - mFab 11H6H1 anti-HIV + Tat peptide<br /> | **[[3o6l]], [[3o6m]] - mFab 11H6H1 anti-HIV + Tat peptide<br /> | ||
[[1svz]] - mFab anti-HIV + HIV-2 protease peptide<br /> | **[[1svz]] - mFab anti-HIV + HIV-2 protease peptide<br /> | ||
*Fab: protein complex | |||
[[3raj]] – mFab HB7 + CD38<br /> | **[[3raj]] – mFab HB7 + CD38<br /> | ||
[[3o0r]] – mFab + nitric oxide reductase<br /> | **[[3o0r]] – mFab + nitric oxide reductase<br /> | ||
[[3mac]], [[3ma9]] – hFab 8062 anti-HIV + transmembrane glycoprotein<br /> | **[[3mac]], [[3ma9]] – hFab 8062 anti-HIV + transmembrane glycoprotein<br /> | ||
[[3pnw]] – hFab + Tudor domain-containing protein 3<br /> | **[[3pnw]] – hFab + Tudor domain-containing protein 3<br /> | ||
[[3h42]] - hFab LDLR + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin<br /> | **[[3h42]] - hFab LDLR + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin<br /> | ||
[[3nh7]] – hFab ABD1556 + bone morphogenetic protein receptor<br /> | **[[3nh7]] – hFab ABD1556 + bone morphogenetic protein receptor<br /> | ||
[[3hi6]] – hFab AL-57 + integrin<br /> | **[[3hi6]] – hFab AL-57 + integrin<br /> | ||
[[2vxs]] - hFab + interleukin<br /> | **[[2vxs]] - hFab + interleukin<br /> | ||
[[3b2u]], [[3b2v]] – hFab IMC-11F8 + EGFR<br /> | **[[3b2u]], [[3b2v]] – hFab IMC-11F8 + EGFR<br /> | ||
[[2r0k]], [[2r0l]] – hFab + HGFA<br /> | **[[2r0k]], [[2r0l]] – hFab + HGFA<br /> | ||
[[3ld8]], [[3ldb]] – AhFab + bifunctional arginine demethylase <br /> | **[[3ld8]], [[3ldb]] – AhFab + bifunctional arginine demethylase <br /> | ||
[[3be1]], [[3n85]], [[1n8z]] - hFab + ERBB-2<br /> | **[[3be1]], [[3n85]], [[1n8z]] - hFab + ERBB-2<br /> | ||
[[3kr3]] – hFab + IGF-II<br /> | **[[3kr3]] – hFab + IGF-II<br /> | ||
[[3g6d]] – hFab CNTO607 + IL-13<br /> | **[[3g6d]] – hFab CNTO607 + IL-13<br /> | ||
[[3idx]], [[3idy]], [[2ny7]], [[4jpw]], [[4lsp]], [[4lsq]], [[4lsr]], [[4lss]], [[4lst]], [[4lsu]], [[4lsv]] - hFab + gp120 core<br /> | **[[3idx]], [[3idy]], [[2ny7]], [[4jpw]], [[4lsp]], [[4lsq]], [[4lsr]], [[4lss]], [[4lst]], [[4lsu]], [[4lsv]] - hFab + gp120 core<br /> | ||
[[2x7l]] – Fab anti-HIV + HIV REV<br /> | **[[2x7l]] – Fab anti-HIV + HIV REV<br /> | ||
[[3gbm]], [[3gbn]], [[3lzf]], [[3fku]], [[3sdy]], [[3ztj]], [[3ztn]], [[4fp8]], [[4fqi]], [[4fqj]], [[4fqk]], [[4fql]], [[4fqr]], [[4fqv]], [[4fqy]], [[4gxu]], [[4nm8]]- hFab + hemagglutinin<br /> | **[[3gbm]], [[3gbn]], [[3lzf]], [[3fku]], [[3sdy]], [[3ztj]], [[3ztn]], [[4fp8]], [[4fqi]], [[4fqj]], [[4fqk]], [[4fql]], [[4fqr]], [[4fqv]], [[4fqy]], [[4gxu]], [[4nm8]]- hFab + hemagglutinin<br /> | ||
[[3g6j]] – hFab + complement C3<br /> | **[[3g6j]] – hFab + complement C3<br /> | ||
[[2vxq]] – hFab + pollen allergen PHL<br /> | **[[2vxq]] – hFab + pollen allergen PHL<br /> | ||
[[1fsk]] - mFab + pollen allergen<br /> | **[[1fsk]] - mFab + pollen allergen<br /> | ||
[[2wub]], [[3k2u]] – hFab 40 + hepatocyte growth factor activator<br /> | **[[2wub]], [[3k2u]] – hFab 40 + hepatocyte growth factor activator<br /> | ||
[[3grw]] - hFab + fibroblast growth factor receptor<br /> | **[[3grw]] - hFab + fibroblast growth factor receptor<br /> | ||
[[3bdy]], [[2qr0]], [[2fjg]], [[2fjh]], [[1cz8]] – hFab + VEGF<br /> | **[[3bdy]], [[2qr0]], [[2fjg]], [[2fjh]], [[1cz8]] – hFab + VEGF<br /> | ||
[[1tzh]], [[1tzi]] - mFab + VEGF<br /> | **[[1tzh]], [[1tzi]] - mFab + VEGF<br /> | ||
[[3bqu]] – hFab 2F5 anti-HIV + mFab 3H6<br /> | **[[3bqu]] – hFab 2F5 anti-HIV + mFab 3H6<br /> | ||
[[1adq]] – hFab IGM + igG1 Fc<br /> | **[[1adq]] – hFab IGM + igG1 Fc<br /> | ||
[[3dvg]], [[3dvn]] – hFab igG1 + ubiquitin<br /> | **[[3dvg]], [[3dvn]] – hFab igG1 + ubiquitin<br /> | ||
[[3bn9]] – hFab E2 + membrane-type serine protease<br /> | **[[3bn9]] – hFab E2 + membrane-type serine protease<br /> | ||
[[2jix]] – hFab ABT-007 + erythropoietin receptor<br /> | **[[2jix]] – hFab ABT-007 + erythropoietin receptor<br /> | ||
[[1za3]] - hFab YSD1 + TNF receptor<br /> | **[[1za3]] - hFab YSD1 + TNF receptor<br /> | ||
[[3l95]] – | **[[3l95]] – hFab + NRR1<br /> | ||
[[1uj3]], [[4dtg]] – hFab + tissue factor<br /> | **[[1uj3]], [[4dtg]] – hFab + tissue factor<br /> | ||
[[3lev]] – hFab 2F5 + RNA polymerase sigma factor<br /> | **[[3lev]] – hFab 2F5 + RNA polymerase sigma factor<br /> | ||
[[3ru8]] – hFab B12 + epitope scaffold 2BODX43<br /> | **[[3ru8]] – hFab B12 + epitope scaffold 2BODX43<br /> | ||
[[3skj]] – hFab + ephrin receptor<br /> | **[[3skj]] – hFab + ephrin receptor<br /> | ||
[[3sob]] – hFab + LPR6<br /> | **[[3sob]] – hFab + LPR6<br /> | ||
[[3vg9]] – hFab + adenosine receptor<br /> | **[[3vg9]] – hFab + adenosine receptor<br /> | ||
[[3vga]] – hFab + adenosine receptor (mutant)<br /> | **[[3vga]] – hFab + adenosine receptor (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[2qqk]], [[2qql]], [[2qqn]] – hFab + neuropilin<br /> | **[[2qqk]], [[2qql]], [[2qqn]] – hFab + neuropilin<br /> | ||
[[2vyr]] – hFab + MDM4<br /> | **[[2vyr]] – hFab + MDM4<br /> | ||
[[4c2i]] – hFab + dengue virus envelope protein<br /> | **[[4c2i]] – hFab + dengue virus envelope protein<br /> | ||
[[4dag]] – hFab + metapneumovirus glycoprotein F0<br /> | **[[4dag]] – hFab + metapneumovirus glycoprotein F0<br /> | ||
[[1jps]] - hmFab D3H44 + tissue factor<br /> | **[[1jps]] - hmFab D3H44 + tissue factor<br /> | ||
[[1ahw]] - mFab 5G9+ tissue factor<br /> | **[[1ahw]] - mFab 5G9+ tissue factor<br /> | ||
[[1eo8]], [[1ken]], [[4mhh]], [[4mhj]] - mFab + hemagglutinin<br /> | **[[1eo8]], [[1ken]], [[4mhh]], [[4mhj]] - mFab + hemagglutinin<br /> | ||
[[2w9e]], [[1tpx]], [[1tqb]], [[1tqc]] – mFAB + major prion protein<br /> | **[[2w9e]], [[1tpx]], [[1tqb]], [[1tqc]] – mFAB + major prion protein<br /> | ||
[[2oz4]] – mFab + intercellular adhesion molecule<br /> | **[[2oz4]] – mFab + intercellular adhesion molecule<br /> | ||
[[3eo1]] - mFab GC-1008 + transforming growth factor β-3<br /> | **[[3eo1]] - mFab GC-1008 + transforming growth factor β-3<br /> | ||
[[2dtg]] – mFab 83 + insulin receptor<br /> | **[[2dtg]] – mFab 83 + insulin receptor<br /> | ||
[[1egj]] – mFab + cytokine receptor<br /> | **[[1egj]] – mFab + cytokine receptor<br /> | ||
[[2bdn]] – mFab + cytokine A2<br /> | **[[2bdn]] – mFab + cytokine A2<br /> | ||
[[1jrh]] – mFab + interferon-γ receptor<br /> | **[[1jrh]] – mFab + interferon-γ receptor<br /> | ||
[[1ob1]] – mFab + major merozoite surface protein<br /> | **[[1ob1]] – mFab + major merozoite surface protein<br /> | ||
[[1qfw]] – mFab + gonadotropin<br /> | **[[1qfw]] – mFab + gonadotropin<br /> | ||
[[4cad]] – mFab + RCE1<br /> | **[[4cad]] – mFab + RCE1<br /> | ||
[[4m48]] – mFab + dopamine transporter<br /> | **[[4m48]] – mFab + dopamine transporter<br /> | ||
[[1yjd]] – mFab 5.11A1 + CD28<br /> | **[[1yjd]] – mFab 5.11A1 + CD28<br /> | ||
[[1sy6]] – mFab OKT3 + CD3<br /> | **[[1sy6]] – mFab OKT3 + CD3<br /> | ||
[[4k4m]], [[4k2u]] – mFab + erythrocyte binding antigen<br /> | **[[4k4m]], [[4k2u]] – mFab + erythrocyte binding antigen<br /> | ||
[[1afv]] – mFab anti-HIV + capsid protein C<br /> | **[[1afv]] – mFab anti-HIV + capsid protein C<br /> | ||
[[2b2x]] – rFab AQC2 + integrin<br /> | **[[2b2x]] – rFab AQC2 + integrin<br /> | ||
[[2r56]] – bFab igE + β-lactoglobulin <br /> | **[[2r56]] – bFab igE + β-lactoglobulin <br /> | ||
[[1bzq]], [[2p42]], [[2p43]], [[2p44]], [[2p45]], [[2p46]], [[2p47]], [[2p48]], [[2p49]], [[2p4a]] – bFab Cab-Rn05 + RNase<br /> | **[[1bzq]], [[2p42]], [[2p43]], [[2p44]], [[2p45]], [[2p46]], [[2p47]], [[2p48]], [[2p49]], [[2p4a]] – bFab Cab-Rn05 + RNase<br /> | ||
[[2r9h]] – mFab + exchange transporter ClCA<br /> | **[[2r9h]] – mFab + exchange transporter ClCA<br /> | ||
[[1nca]], [[1ncb]], [[1ncc]], [[1ncd]] – mFab + neuraminidase<br /> | **[[1nca]], [[1ncb]], [[1ncc]], [[1ncd]] – mFab + neuraminidase<br /> | ||
[[1rjl]] – mFab + outer surface protein<br /> | **[[1rjl]] – mFab + outer surface protein<br /> | ||
[[1mhh]] – mFab + protein L (mutant)<br /> | **[[1mhh]] – mFab + protein L (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[1pg7]] – mFab 6A6 + hmFab D3H44<br /> | **[[1pg7]] – mFab 6A6 + hmFab D3H44<br /> | ||
[[1pkq]] – hFab/mFab 8-18C5 + myelin glycoprotein<br /> | **[[1pkq]] – hFab/mFab 8-18C5 + myelin glycoprotein<br /> | ||
[[2jel]] – mFab JEL42 + histidine-containing protein<br /> | **[[2jel]] – mFab JEL42 + histidine-containing protein<br /> | ||
[[1nsn]] – mFab N10 + nuclease<br /> | **[[1nsn]] – mFab N10 + nuclease<br /> | ||
[[1rvf]] – mFab 17-IA + intact rhinovirus<br /> | **[[1rvf]] – mFab 17-IA + intact rhinovirus<br /> | ||
[[3j3o]], [[3j3p]]- mFab + poliovirus proteins – cryoEM<br /> | **[[3j3o]], [[3j3p]]- mFab + poliovirus proteins – cryoEM<br /> | ||
[[1nfd]] – mFab H57 + T-cell receptor<br /> | **[[1nfd]] – mFab H57 + T-cell receptor<br /> | ||
[[1igc]] – mFab MOPC21 + streptococcal protein G<br /> | **[[1igc]] – mFab MOPC21 + streptococcal protein G<br /> | ||
[[1iai]] – mFab idiotipic + mFab anti-idiotypic<br /> | **[[1iai]] – mFab idiotipic + mFab anti-idiotypic<br /> | ||
[[2r8s]] – mFab + RNA<br /> | **[[2r8s]] – mFab + RNA<br /> | ||
[[2fr4]], [[1xf2]], [[1xf3]], [[1xf4]], [[1i8m]], [[1cbv]] – mFab + DNA<br /> | **[[2fr4]], [[1xf2]], [[1xf3]], [[1xf4]], [[1i8m]], [[1cbv]] – mFab + DNA<br /> | ||
[[1mhp]], [[3q3g]], [[3qa3]] – mFab + integrin<br /> | **[[1mhp]], [[3q3g]], [[3qa3]] – mFab + integrin<br /> | ||
[[3ab0]] – mFab + BCLA protein<br /> | **[[3ab0]] – mFab + BCLA protein<br /> | ||
[[3etb]] – mFab M18 (mutant) + anthrax-protective antigen<br /> | **[[3etb]] – mFab M18 (mutant) + anthrax-protective antigen<br /> | ||
[[3f5w]], [[3pjs]], [[3efd]], [[3eff]], [[2hjf]], [[2w0f]], [[4msw]] – mFab + KcsA K+ channel<br /> | **[[3f5w]], [[3pjs]], [[3efd]], [[3eff]], [[2hjf]], [[2w0f]], [[4msw]] – mFab + KcsA K+ channel<br /> | ||
[[3stl]], [[3stz]], [[4i9w]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel (mutant)<br /> | **[[3stl]], [[3stz]], [[4i9w]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[1kb5]] – mFab + T-cell receptor<br /> | **[[1kb5]] – mFab + T-cell receptor<br /> | ||
[[4i18]] – mFab + pro-lactin receptor<br /> | **[[4i18]] – mFab + pro-lactin receptor<br /> | ||
[[1uwx]] – mFab + protein G prime <br /> | **[[1uwx]] – mFab + protein G prime <br /> | ||
[[4ckd]] – mFab + β-galactosidase <br /> | **[[4ckd]] – mFab + β-galactosidase <br /> | ||
[[3fmg]] – mFab + glycoprotein VP7<br /> | **[[3fmg]] – mFab + glycoprotein VP7<br /> | ||
[[3ve0]] - mFab + Ebola envelope glycoprotein<br /> | **[[3ve0]] - mFab + Ebola envelope glycoprotein<br /> | ||
[[3k7u]], [[3k80]] – LgFab + MP18 RNA editing protein – Lama glama<br /> | **[[3k7u]], [[3k80]] – LgFab + MP18 RNA editing protein – Lama glama<br /> | ||
[[3mj9]] – AhFab HL4E10 + JAML <br /> | **[[3mj9]] – AhFab HL4E10 + JAML <br /> | ||
[[3r08]] - AhFab 2C11 + CD3ε<br /> | **[[3r08]] - AhFab 2C11 + CD3ε<br /> | ||
[[4hti]] – rFab + TNF ligand<br /> | **[[4hti]] – rFab + TNF ligand<br /> | ||
[[1g6v]] – bFab + carbonic anhydrase<br /> | **[[1g6v]] – bFab + carbonic anhydrase<br /> | ||
[[4hgk]] – Fab + albumin – shark<br /> | **[[4hgk]] – Fab + albumin – shark<br /> | ||
[[4ej1]], [[4eiz]], [[4eig]] – LgFab + DHFR <br /> | **[[4ej1]], [[4eiz]], [[4eig]] – LgFab + DHFR <br /> | ||
[[3k81]], [[3stb]], [[4dk3]], [[4dk6]], [[4dka]] – LgFab + RNA editing complex protein<br /> | **[[3k81]], [[3stb]], [[4dk3]], [[4dk6]], [[4dka]] – LgFab + RNA editing complex protein<br /> | ||
[[3p0g]], [[4lde]], [[4ldl]], [[4ldo]] – LgFab + adrenergic receptor<br /> | **[[3p0g]], [[4lde]], [[4ldl]], [[4ldo]] – LgFab + adrenergic receptor<br /> | ||
[[1jto]], [[1jtp]], [[1jtt]], [[1ri8]], [[1xfp]], [[1zmy]], [[1zv5]], [[1zvh]] – cFab + lysozyme<br /> | **[[1jto]], [[1jtp]], [[1jtt]], [[1ri8]], [[1xfp]], [[1zmy]], [[1zv5]], [[1zvh]] – cFab + lysozyme<br /> | ||
[[2x89]] – cFab + β-2-microglobulin<br /> | **[[2x89]] – cFab + β-2-microglobulin<br /> | ||
[[4i0c]] – cFab + lysozyme<br /> | **[[4i0c]] – cFab + lysozyme<br /> | ||
[[4ht1]] – Fab + TNF ligand 12 – rabbit<br /> | **[[4ht1]] – Fab + TNF ligand 12 – rabbit<br /> | ||
*Fab: protein ternary complex | |||
[[3ixx]], [[3ixy]] - mFab E53 + envelope glycoprotein + West Nile virus peptide<br /> | **[[3ixx]], [[3ixy]] - mFab E53 + envelope glycoprotein + West Nile virus peptide<br /> | ||
[[1g9m]], [[1g9n]], [[1gc1]], [[2i5y]], [[2i60]], [[2nxy]], [[2nxz]], [[2ny0]], [[2ny1]], [[2ny2]], [[2ny3]], [[2ny4]], [[2ny5]], [[2ny6]], [[3jwd]], [[3jwo]] - hFab + envelope glycoprotein gp120 + CD4<br /> | **[[1g9m]], [[1g9n]], [[1gc1]], [[2i5y]], [[2i60]], [[2nxy]], [[2nxz]], [[2ny0]], [[2ny1]], [[2ny2]], [[2ny3]], [[2ny4]], [[2ny5]], [[2ny6]], [[3jwd]], [[3jwo]] - hFab + envelope glycoprotein gp120 + CD4<br /> | ||
[[2wuc]] - hFab 40 + hepatocyte growth factor activator + inhibitor<br /> | **[[2wuc]] - hFab 40 + hepatocyte growth factor activator + inhibitor<br /> | ||
[[3lqa]], [[2qad]] - hFab anti-HIV + CD4 + gp160<br /> | **[[3lqa]], [[2qad]] - hFab anti-HIV + CD4 + gp160<br /> | ||
[[3d85]] - hFab 7G10 + IL-12 + IL-23<br /> | **[[3d85]] - hFab 7G10 + IL-12 + IL-23<br /> | ||
[[3bt2]] – hFab anti-UPAR + urokinase-type plasminogen activator + vitronectin<br /> | **[[3bt2]] – hFab anti-UPAR + urokinase-type plasminogen activator + vitronectin<br /> | ||
[[3gjf]], [[3hae]] – hFab + β-2-microglobulin + MHC antigen + NYESO peptide<br /> | **[[3gjf]], [[3hae]] – hFab + β-2-microglobulin + MHC antigen + NYESO peptide<br /> | ||
[[3gb7]], [[2p7t]], [[2h8p]], [[2hfe]], [[2atk]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel + ion<br /> | **[[3gb7]], [[2p7t]], [[2h8p]], [[2hfe]], [[2atk]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel + ion<br /> | ||
[[3or6]], [[3or7]], [[3ogc]], [[3fb7]], [[3f7v]], [[3f7y]], [[3fb5]], [[3fb6]], [[3fb8]], [[3iga]], [[2itc]], [[2itd]], [[2nlj]], [[2bob]], [[2boc]], [[1s5h]], [[1r3i]], [[1r3j]], [[1r3k]], [[1r3l]], [[1k4c]], [[1k4d]], [[3hpl]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel (mutant) + ion<br /> | **[[3or6]], [[3or7]], [[3ogc]], [[3fb7]], [[3f7v]], [[3f7y]], [[3fb5]], [[3fb6]], [[3fb8]], [[3iga]], [[2itc]], [[2itd]], [[2nlj]], [[2bob]], [[2boc]], [[1s5h]], [[1r3i]], [[1r3j]], [[1r3k]], [[1r3l]], [[1k4c]], [[1k4d]], [[3hpl]] - mFab + KcsA K+ channel (mutant) + ion<br /> | ||
[[2fd6]] – mFab ATN-615 + urokinase-type plasminogen activator + urokinase plasminogen receptor<br /> | **[[2fd6]] – mFab ATN-615 + urokinase-type plasminogen activator + urokinase plasminogen receptor<br /> | ||
[[1j5o]] – mFab + reverse transcriptase + DNA<br /> | **[[1j5o]] – mFab + reverse transcriptase + DNA<br /> | ||
[[1qkz]] – mFab + protein G prime + major outer membrane protein peptide<br /> | **[[1qkz]] – mFab + protein G prime + major outer membrane protein peptide<br /> | ||
[[2ibz]] – mFab + cytochrome bc1 complex + stigmatellin <br /> | **[[2ibz]] – mFab + cytochrome bc1 complex + stigmatellin <br /> | ||
[[3v0a]] – LgFab + BONT/A1 + NTNH<br /> | **[[3v0a]] – LgFab + BONT/A1 + NTNH<br /> | ||
[[3sn6]] – LgFab + adrenergic receptor + guanine nucleotide-binding protein<br /> | **[[3sn6]] – LgFab + adrenergic receptor + guanine nucleotide-binding protein<br /> | ||
[[4laj]] - LgFab + envelope glycoprotein gp120 + CD4<br /> | **[[4laj]] - LgFab + envelope glycoprotein gp120 + CD4<br /> | ||
*Full Immunoglobulin | |||
[[1hzh]] - hFab IgG B12<br /> | **[[1hzh]] - hFab IgG B12<br /> | ||
[[1iga]] - hIgA1 - model<br /> | **[[1iga]] - hIgA1 - model<br /> | ||
*Fc Fragments | |||
[[3dnk]] - hFc Igg1br /> | **[[3dnk]] - hFc Igg1br /> | ||
[[1qp1]] – hFc BRE<br /> | **[[1qp1]] – hFc BRE<br /> | ||
[[3muh]] – hFc PG9<br /> | **[[3muh]] – hFc PG9<br /> | ||
[[4bsv]], [[4bsw]] – hFc heterodimeric (mutant)<br /> | **[[4bsv]], [[4bsw]] – hFc heterodimeric (mutant)<br /> | ||
[[1f6a]] - hFc IgE + high-affinity receptor Fc (ε) RI (α)<br /> | **[[1f6a]] - hFc IgE + high-affinity receptor Fc (ε) RI (α)<br /> | ||
[[1fp5]] - hFc IgE C ε 3-C ε 4<br /> | **[[1fp5]] - hFc IgE C ε 3-C ε 4<br /> | ||
*Fv Fragments | |||
**[[3dur]], [[3dus]], [[3duu]], [[3dv4]], [[3dv6]] – mFv + Ig-like protein<br /> | |||
**[[3h3b]] – mFv + ERBB2<br /> | |||
**[[3hb3]] – mFv + cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1-β<br /> | |||
**[[1qle]] - mFv + cytochrome c oxidase<br /> | |||
**[[3ln9]] – cFv B10<br /> | |||
**[[3tpk]] – cFv KW1<br /> | |||
**[[3zhd]], [[3zhk]], [[3zhl]] – hFv scaffold<br /> | |||
**[[1kxq]] – cFv + α-amylase<br /> | |||
**[[1mel]], [[1rjc]], [[1zvy]] – cFv + lysozyme<br /> | |||
}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 17 November 2014
Antibodies, also known as Immunoglobulins (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These glycoproteins serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other antigens. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody and . It is this specificity that has made a critical component in laboratory and medical research. See more in IgA, Monoclonal Antibody. For Anti-HIV Fab see Human Fab PG16. 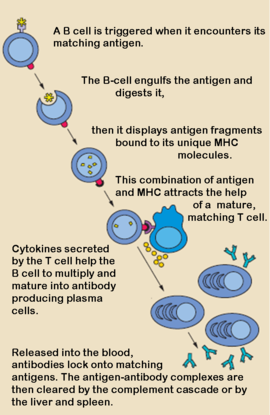 Cellular Basis of Antibody ProductionWhen a foreign antigen binds to a B-lymphocyte (B-cell), it activates the B-cell, and upon stimulation by helper T-cells, undergoes clonal proliferation and B-cell maturation into antibody forming plasma cells. Each plasma cell is programmed to make an antibody of a single specificity, which it releases into the blood. [1] Once in the blood, antibodies aid the humoral immune system in three predominant ways: They coat foreign pathogens preventing them from entering healthy cells or disrupting antigen function; they coat pathogens, stimulating their removal via opsonization by phagocytes; and they trigger destruction of pathogens by stimulating the complement pathway or by Antibody Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity, among other immune responses. [2] [3] All of these functions rely heavily on accurate antigen binding and communication with other immune effector cells. The amazing specificity antibodies operate with is made possible by the physical structure of the antibody, which appears simplistic, but contains several levels of additional complexity. Structure of the Immunoglobulin(1igt). The basic functional unit of an antibody is an immunoglobulin monomer, but antibodies secreted from plasma cells are typically dimeric with occasional higher order structures. Typical secreted antibodies have a basic four-peptide structure of two identical and two identical joined together by interchain , forming a “Y” shaped molecule. The disulfide bonds are positioned within a flexible region called the , which seperates the lobes of the antibody from one another and provides ample flexibility to bind antigens effectively. [1] Each domain (2 heavy and 2 light) contain between 70-110 amino acids and are classified into different categories according to size and function. [4] Both domains, heavy and light, contain variable and constant regions that are crucial to antibody function. [5] Heavy ChainThere are five types of immunoglobulin heavy chains, in mammals, α, δ, ε, γ, and μ, and give rise to the five unique classes or isotypes of antibodies, IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM, which differ in size and composition. Each has a and . The constant region is identical in all antibodies of the same isotype, but differ in antibodies of different isotypes; i.e. all IgA have the same sequence in their heavy chain constant region, but these constant regions differ between IgA and IgD, etc. [6] The α, δ, and γ heavy chains have a constant region composed of while heavy chains ε and μ contain four. The variable region of the heavy chain in antibodies is different for all antibodies created by different B-cells. [7] 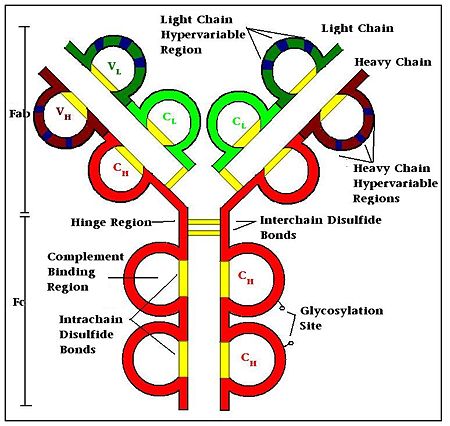 Light ChainEvery antibody contains two that are identical to each other. There are two types of immunoglobulin light chains in mammals, labeled lambda and kappa, with only one represented in each antibody. Each light chain has one followed by one , with a total length of about 215 amino acids. [1] The Regions: Fab, Fv, CDR, and Fc.The immunoglobulin can be broken down into regions, each serving a different purpose: Variable RegionsThe (Fragment, Antigen Binding region) is composed of one constant and one variable domain from each heavy and light chain of the antibody. It is the part of the antibody that gives it its famous “Y” shape.[8] Held within the Fab region is the variable domain, also known as the Fv region.[9] Within the Fv region lie positioned at one end of the variable domain where they form parts of the Beta-turn loops and are clustered close to each other in space. The clustering of the hypervariable loops at the tips of the variable regions where the antigen-binding site is located makes them perfect candidates for antigen recognition. [1]The sequence heterogeneity of the three heavy and three light chain hypervariable loops creates significant antigen specificity diversity through variations in the binding surface nature and shape. Each hypervariable region can be viewed as an independent structure contributing to the complementarity of the biding site and antigen and is often referred to as a complementarity determining region (CDR). [10] Constant RegionsThe remaining part of the antibody, namely the , does not play a role in binding the antigen, but rather is responsible for modulating the immune systems response to the formation of an antibody-antigen complex. The Fragment Crystallizable (Fc) region is composed of two heavy chain constant regions that are isotype specific. [11] Antibodies are glycoproteins because of at conserved positions in their Fc regions. This glycosylation is a critical component determing the rate of antibody clearance form the body.[12] Once an antibody binds to an antigen, the Fc region binds to Fc receptors, among other proteins, to mediate a host of different physiological responses ranging from oposonization, to degranulation of mast cells, to the release of cytokines and cytotoxic molecules, etc. resulting in the destruction of the pathogen. [13] Depending on the class of antibody, as dictated by the identity of the Fc region, the antibody half-life and distribution throughout the body varies. Further, since Fc receptors are antibody isotype specific, the type of immune response is dependent on the type of Fc region on the immunoglobulin, allowing for different immune responses to the same pathogen if necessary.[14] See table for brief characterization of Immunoglobulin isotypes:
A model of the IgG molecule is present in the figure which indicates the spatial disposition and interaction of the domains in IgG. As Dr. Ivan Roitt writes in Essential Immunolgy, “To enable the Fab arms to have the freedom to move and twist so that they can align their hypervariable regions with the antigenic sites on large immobile carriers, and to permit the Fc structures to adjust spatially in order to trigger their effector functions, it is desirable for IgG to have a high degree of flexibility. And it has just that. Structural analysis shows that the Fab can ‘elbow-bend’ at its V-C junction and twist about the hinge, which itself can more properly be described as a loose thether, allowing the Fab and the Fc to drift relative to each other with remarkable suppleness. It could be said that movements like that make it a very sexy molecule!” [1]
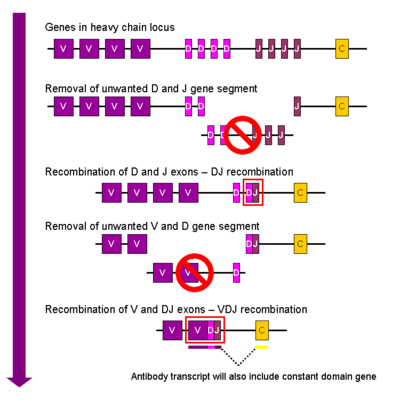 (2osl). Antibody DiversityConsidering the nearly infinite number of possible antigens that can invade the body, the immune system had to develop a method for accurately targeting each one of these compounds, ranging from small molecules, to stray proteins, to viruses capable of infecting cells. The antibody was the immune systems response to this problem. It has been estimated that humans generate about 10^10 different antigens, each capable of binding a unique epitope of an antigen. Since antibodies are proteins, and proteins are controlled by the genes from which they are transcribed, a clever system of gene shuffling and manipulations developed to enable the immune system to create a huge repertoire of antibodies from a limited number of genes. [15] The variable region of each immunoglobulin chain is encoded in several pieces known as gene segments. For heavy chains, these segments are called the variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) segments. (Only V and J exist for light chains) 50 V segments, 25 D segments, and 6 J segments exist and are randomly arranged and rearranged in the genome in a process called V(D)J recombination. Each B-cell is programmed to produce antibodies of a single V(D)J recombination order. Additional diversity is created by the proteins RAG-1 and RAG-2 which introduce the double stranded breaks between V, D, and J segments to allow recombination. At this stage, nucleotides can either be deleted or inserted between adjoining segments before being ligated together. [1] This dramatically increases antibody diversity. Further diversity is created during B-cell proliferation when the variable chains undergo a high rate of point mutations in a process called somatic hypermutation, creating daughter cells of the original B-cell that are slightly different. The antibodies which bind the antigen with the highest affinity are selected for in a process called affinity maturation. [16][17] Isotype switching is also possible after activation of the B-cell by a mechanism called “class switch recombination” allowing different immunological responses to the same antigen bound by the same variable regions.[18] Through this clever system, tens of billions of different glycoprotein antibodies can be created from less than 100 genes, allowing antibodies to bind with exquisite precision. The discovery of antobdy diversity generation won Susumu Tonegawa the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1987.  Antibody ApplicationsDetection of particular antibodies is very common in medical diagnostic testing. Numerous biochemical assays exist to detect whether antibodies for specific antigens are present in the blood or other bodily fluids such as antibodies against Lyme disease or HIV, etc. Another common medical test involving antibodies is blood type detection in which an individual’s blood is screened against anti-A and anti-B antibodies to determine the identity of that individual’s blood antigen type. [19] Antibodies are also extremely powerful tools in the laboratory setting where they are commonly used in Western Blot to detect specific proteins in a sample [20]; flow cytometry, to differentiate cell types by their protein expression profiles; immunoprecipitation, to separate proteins from other compounds in a lysate and for cellular labeling. Numerous other examples exist. [21] The last two decades have seen a dramatic increase in antibody based technologies both for the lab and medicine thanks to the invention of the monoclonal antiboy, a discovery that won Niels K. Jerne, Georges J.F. Köhler, César Milstein the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1984. See: Monoclonal Antibody for additional information. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D Structures of Immunoglobulin3D Structures of Immunoglobulin
Updated on 17-November-2014
Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab) is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab.
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Roit, I. M. Roit's Essential Immunology. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd., 1997.
- ↑ Parker DC. T cell-dependent B cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:331-60. PMID:8476565 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001555
- ↑ Rus H, Cudrici C, Niculescu F. The role of the complement system in innate immunity. Immunol Res. 2005;33(2):103-12. PMID:16234578 doi:10.1385/IR:33:2:103
- ↑ Roux KH. Immunoglobulin structure and function as revealed by electron microscopy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Oct;120(2):85-99. PMID:10545762
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Harris LJ, Larson SB, Hasel KW, McPherson A. Refined structure of an intact IgG2a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1997 Feb 18;36(7):1581-97. PMID:9048542 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi962514+
- ↑ Hochman J, Inbar D, Givol D. An active antibody fragment (Fv) composed of the variable portions of heavy and light chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1130-5. PMID:4569769
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Wright A, Morrison SL. Effect of glycosylation on antibody function: implications for genetic engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 1997 Jan;15(1):26-32. PMID:9032990 doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(96)10062-7
- ↑ Heyman B. Complement and Fc-receptors in regulation of the antibody response. Immunol Lett. 1996 Dec;54(2-3):195-9. PMID:9052877
- ↑ Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:275-90. PMID:11244038 doi:19/1/275
- ↑ Fanning LJ, Connor AM, Wu GE. Development of the immunoglobulin repertoire. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Apr;79(1):1-14. PMID:8612345
- ↑ Diaz M, Casali P. Somatic immunoglobulin hypermutation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002 Apr;14(2):235-40. PMID:11869898
- ↑ Borghesi L, Milcarek C. From B cell to plasma cell: regulation of V(D)J recombination and antibody secretion. Immunol Res. 2006;36(1-3):27-32. PMID:17337763 doi:10.1385/IR:36:1:27
- ↑ Durandy A. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: a dual role in class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation. Eur J Immunol. 2003 Aug;33(8):2069-73. PMID:12884279 doi:10.1002/eji.200324133
- ↑ CHOWN B, LEWIS M, KAITA K. A new Kell blood-group phenotype. Nature. 1957 Oct 5;180(4588):711. PMID:13477267
- ↑ Burnette WN. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195-203. PMID:6266278
- ↑ Brehm-Stecher BF, Johnson EA. Single-cell microbiology: tools, technologies, and applications. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Sep;68(3):538-59. PMID:15353569 doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.3.538-559.2004
Additional PagesAdditional Pages
See AlsoSee Also
- Variable Lymphocyte Receptors
- Antibody at High school teachers' resources, where you will find tutorials on antibody structure.
- Antibodies at Wikipedia.