2pl1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
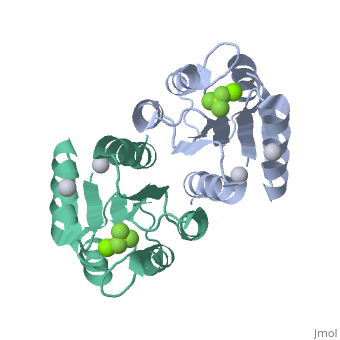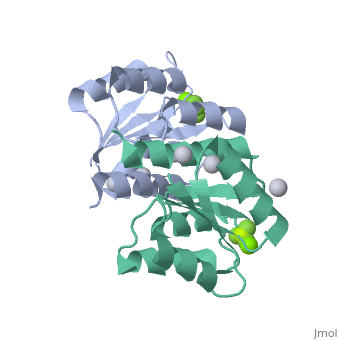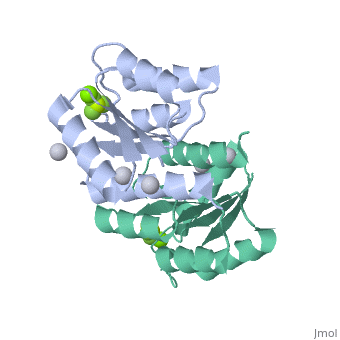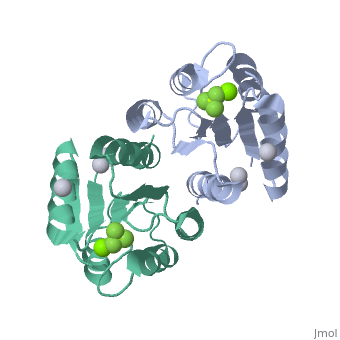
==Berrylium Fluoride activated receiver domain of E.coli PhoP== | |||
<StructureSection load='2pl1' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2pl1]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.90Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2pl1]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entry [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=2eub 2eub]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2PL1 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2PL1 FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BEF:BERYLLIUM+TRIFLUORIDE+ION'>BEF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PT:PLATINUM+(II)+ION'>PT</scene><br> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MSE:SELENOMETHIONINE'>MSE</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[2pkx|2pkx]]</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">phoP ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=562 Escherichia coli])</td></tr> | |||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2pl1 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2pl1 OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2pl1 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2pl1 PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |||
<table> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/pl/2pl1_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The response regulator PhoP is part of the PhoQ/PhoP two-component system involved in responses to depletion of extracellular Mg(2+). Here, we report the crystal structures of the receiver domain of Escherichia coli PhoP determined in the absence and presence of the phosphoryl analog beryllofluoride. In the presence of beryllofluoride, the active receiver domain forms a twofold symmetric dimer similar to that seen in structures of other regulatory domains from the OmpR/PhoB family, providing further evidence that members of this family utilize a common mode of dimerization in the active state. In the absence of activating agents, the PhoP receiver domain crystallizes with a similar structure, consistent with the previous observation that high concentrations can promote an active state of PhoP independent of phosphorylation. | |||
Crystal structures of the receiver domain of the response regulator PhoP from Escherichia coli in the absence and presence of the phosphoryl analog beryllofluoride.,Bachhawat P, Stock AM J Bacteriol. 2007 Aug;189(16):5987-95. Epub 2007 Jun 1. PMID:17545283<ref>PMID:17545283</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[PhoP Regulatory Domain|PhoP Regulatory Domain]] | *[[PhoP Regulatory Domain|PhoP Regulatory Domain]] | ||
*[[PhoP-PhoQ|PhoP-PhoQ]] | *[[PhoP-PhoQ|PhoP-PhoQ]] | ||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
< | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Escherichia coli]] | [[Category: Escherichia coli]] | ||
[[Category: Bachhawat, P.]] | [[Category: Bachhawat, P.]] | ||
Revision as of 22:57, 30 September 2014
Berrylium Fluoride activated receiver domain of E.coli PhoPBerrylium Fluoride activated receiver domain of E.coli PhoP
Structural highlights
Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe response regulator PhoP is part of the PhoQ/PhoP two-component system involved in responses to depletion of extracellular Mg(2+). Here, we report the crystal structures of the receiver domain of Escherichia coli PhoP determined in the absence and presence of the phosphoryl analog beryllofluoride. In the presence of beryllofluoride, the active receiver domain forms a twofold symmetric dimer similar to that seen in structures of other regulatory domains from the OmpR/PhoB family, providing further evidence that members of this family utilize a common mode of dimerization in the active state. In the absence of activating agents, the PhoP receiver domain crystallizes with a similar structure, consistent with the previous observation that high concentrations can promote an active state of PhoP independent of phosphorylation. Crystal structures of the receiver domain of the response regulator PhoP from Escherichia coli in the absence and presence of the phosphoryl analog beryllofluoride.,Bachhawat P, Stock AM J Bacteriol. 2007 Aug;189(16):5987-95. Epub 2007 Jun 1. PMID:17545283[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||